Introduction:
The bond length is the distance between covalently bound atoms that can be measured.
Atoms are not static or stationary when it comes to chemistry. When they’re joined together, they can bounce and move about.
This movement is influenced by heat and the number of bonds present (single, double, or triple bonds). At some time, though, equilibrium will be reached, and the atoms will remain in place.
The longer the distance between those two molecules, the easier it is to break them apart.
Calculation for bond length:
The length of a bond is usually between nanometre.
The covalent radius is half of the bond length when two comparable atoms are linked together. The length of a bond is determined by the number of bound electrons between two atoms or the bond order. Because of the strong pulling forces of positively charged nuclei, the bond length will be shorter as the bond order increases.
Bond length is measured in picometers. The bond length rises in the order of:
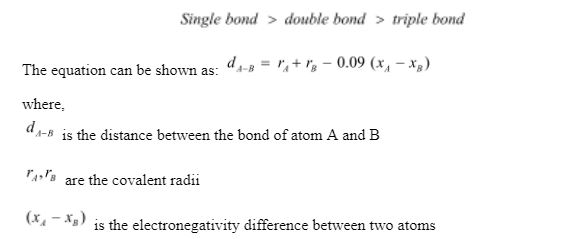
When two nuclei are brought closer and closer together to form a stronger link, the bond shortens. The coulombic attraction on the bonding electrons draws the nuclei closer together, resulting in a shorter bond.
Simultaneously, the stronger the interaction and bond, the more they pull. This is where the bond order comes in. A double bond between two atoms is stronger and lasts longer than a single bond. A triple bond is significantly more powerful and shorter.
Bond order
The number of chemical bonds between atoms in a molecule is known as bond order.
It is the indication of the stability of a bond.
The shorter the bond length and the stronger the link, the more bonds there are between two atoms. As a result, triple bonds are shorter than double bonds, which are shorter than single bonds. As a result, triple bonds outperform double bonds, while double bonds outperform single bonds.
As a result, the stronger the link between two atoms and the shorter the bond length, the higher the bond energy.
The value “zero” of the bond order indicates that there is no bond present between the atoms.
The increase in the value of bond order indicates the strengthening of the bond.
Bond enthalpy
Bond enthalpy describes the amount of energy stored in a bond between atoms in a molecule (also known as bond-dissociation enthalpy, average bond energy, or bond strength). It is the energy required for the homolytic or symmetrical cleavage of a bond in the gas phase. When a homolytic or symmetrical connection is broken, each of the original atom obtains one electron and transforms into a radical rather than an ion.
When the thermodynamics are favourable, chemical bonds form, and breaking them requires the addition of energy. As a result, bond enthalpy values are always positive, and they are commonly expressed as. The higher the bond enthalpy, the stronger the bond is and more energy is required to break the bond between atoms.. We just make the bond’s enthalpy value negative to estimate how much energy will be released when we build a new bond rather than breaking it.
Conclusion:
In chemistry, bond strength is the strength with which a chemical bond keeps two atoms together. This is commonly described in terms of how much energy is necessary to break the connection in the first place. Its unit is Kilocalories per mole.
The energy required to produce free radicals from the atoms that formed that particular bond was provided by bond dissociation energy.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out













