The term “distance” refers to an object’s total movement, regardless of direction. Displacement, on the other hand, is the change in an object’s position. As a result, the primary distinction between distance and displacement is that distance is a scalar quantity, whereas displacement is a vector quantity.
Distance can be defined as the total length of the path taken when travelling from one location to another. Displacement, on the other hand, is the shortest distance between a body’s initial and final positions.
Distance definition
Distance is a scalar quantity, which means that someone’s distance will never depend on the direction of their motion. The magnitude is the only thing that distance includes. The total path travelled by any particular body or object is defined as the distance.
For example, if a bike travels north for 10 km and then turns east for another 5 km, the bike has travelled a total distance of 15 km, demonstrating that it does not matter which direction the journey occurred.
There is no such thing as a negative or zero distance. Meanwhile, it is always greater than the body’s displacement.When you consider the distance covered by any particular body, you can get a general idea of how it is being covered, i.e. which path it is taking.
Displacement definition
Displacement, on the other hand, is demonstrated as a vector quantity, implying that the displacement of any body is dependent on both its magnitude and its direction of motion. The displacement of a body is defined as the total motion of the body, or as the shortest distance between the body’s initial starting point and its end point.
Take, an example, the same example from the previous paragraph. As a result, the overall displacement of that specific body is nothing more than the length of the line that connects both positions. The displacement of the body is either less than or equal to the distance travelled by the body, but it can never be greater.
Displacement, unlike distance, does not provide a proper idea or information about the path of the object being travelled.
How are Distance and Displacement Measured?
In terms of distance:
To measure the distance, follow the steps outlined below.
- Set the pegs to mark the beginning and end of the distance to be measured.
- Hold the zero point of the tape or chain in the centre of the starting peg.
- Drag the tape or chain in the direction of the second peg. Also, before measuring, make sure to pull the tape or chain straight.
- Any knots or entangled links can cause measurement errors.
- When using a chain, the number of links between the two pegs must be counted. Most notably, the total distance would be equal to the number of links multiplied by the length of one link.
In terms of displacement:
- In physics, displacement is calculated by calculating the distance between an object’s initial position and final position.
- Consider a new golf ball that has the ability to roll around. This golf ball has a habit of rolling around on top of a large measuring stick. Place the ball at the 0 position on the measuring stick to calculate displacement.
- Displacement occurs when the golf ball rolls over to a new point. As a result, if the ball moves 3 meters to the right from its starting point of 0 meters, the displacement will be 3 meters.
Examples of Distance and Displacement:
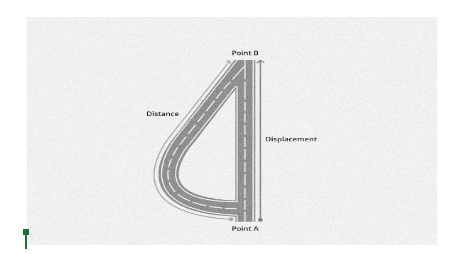
The length obtained by the straight line segment connecting points A and B in the figure is regarded as the displacement of that body moving from A to B. The length of the curve connecting both points (A and B) is simply the distance travelled by the body. We can see from this example that the distance travelled by the body is greater than the displacement of the same body. Meanwhile, displacement is defined as the body’s shortest distance travelled.
Displacement formula
Displacement is simply the change in position that an object experiences while in motion. Both magnitude and direction are considered in this case. The displacement formula is given below.
∆x=xf –x0
Where,
Xf =denotes the object’s final position.
X0 = the object’s starting position
∆x = the object’s displacement
Distance formula
As previously stated, distance is the total movement of a specific body regardless of which direction it is travelling. The formula for expressing distance is given below.
∆d=d1 + d2
Where d is the total distance travelled by the object.
d1 = an object’s movement towards the first point
d2 = the movement of an object from one point to another.
Conclusion
The primary distinction between distance and displacement is that distance is a scalar quantity, whereas displacement is a vector quantity. The displacement of a body is defined as the total motion of the body, or as the shortest distance between the body’s initial starting point and its end point. As a result, the overall displacement of that specific body is nothing more than the length of the line that connects both positions. The displacement of the body is either less than or equal to the distance travelled by the body, but it can never be greater. Distance is the length of an object’s path.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






