Prokaryotes are unicellular creatures with no membrane-bound structures, the nucleus being the most notable. Prokaryotic cells are small, basic cells that range in size from 0.1 to 5 micrometres in diameter. Eukaryotes have a nucleus and other organelles enclosed by a plasma membrane in their cells. Organelles are internal structures that perform a wide range of tasks, including energy production and protein synthesis. Prokaryotes are creatures that are mostly single-celled and belong to the Bacteria and Archaea domains (pro– = before; –karyon– = nucleus). Eukaryotes (EU– = true) include animal cells, plant cells, fungus, and protists components.
Characteristics of prokaryotic cells
- The nucleoid is the cell’s nucleus, which contains the cell’s DNA.
- Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis.
- The cell wall provides structure and provides a barrier to the environment.
- Most bacteria contain a type of cell wall consisting of peptidoglycans. Peptidoglycans are made up of carbohydrates and proteins.
- The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, separates the cell from the outside environment in every prokaryote.
- The capsule is a coating of carbohydrates that surrounds the cell wall in some bacteria. The bacterium may stick to surfaces, thanks to the capsule.
- Fimbriae are little, hair-like structures that aid in cellular adhesion.
- Pili: Pili are rod-shaped structures that play a role in the game.
Eukaryotic cell characteristics
- Chromatin is a type of genetic information that is stored in the nucleus.
- The nucleolus is an inside-the-nucleus structure of eukaryotic cells that manufactures ribosomal RNA.
- The cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer that surrounds and protects the cell’s organelles.
- The cytoskeleton, commonly known as a cell wall, gives cells shape, permits them to move around, and helps them divide.
- Ribosomes: Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis.
- Mitochondria, also referred to as the cell’s powerhouses are responsible for energy production.
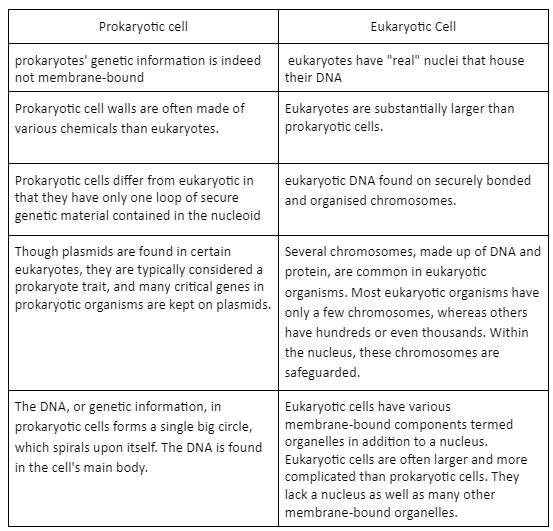
Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell
Conclusion
Scientists created the idea that all creatures can be classed as prokaryotic organisms or eukaryotic in the 1950s. A plasma membrane, often known as a cellular membrane, and cytoplasm are two basic components of all prokaryotic organisms and eukaryotic cells.
Prokaryotes, on the other hand, have simpler cells than eukaryotes. Prokaryotic cells, for example, lack a nucleus, whereas eukaryotic cells do. Inner cellular bodies (organelles) are absent in prokaryotic cells, but they are present in eukaryotic cells. Bacteria and archaea are examples of prokaryotes. Protists, fungi, plants, and vertebrates are examples of eukaryotes.
Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus. Cells with a nucleus are referred to as eukaryotic cells. Aside from the nucleus, eukaryotes have many other organelles. Ribosomes seem to be the only organelles in a bacterial cell.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






