Introduction
The rivers have a huge impact on the lives of people in India. They provide water, electricity, and transport for a large number of people. We can trace the history and culture of our country through these magnificent rivers. Freshwater is an essential resource that we regularly utilize for a variety of functions.
- The river water is routed into well-defined channels referred to as ‘drainage,’ and
- The network of these channels is referred to as a ‘drainage system
- A drainage basin is an area drained by a single river system
- The direction in which the river flows is called the ‘Course of A river‘
Three courses of a river:
A river has three main courses, namely:
- The upper course of a river
- The middle course of a river
- The lower course of a river
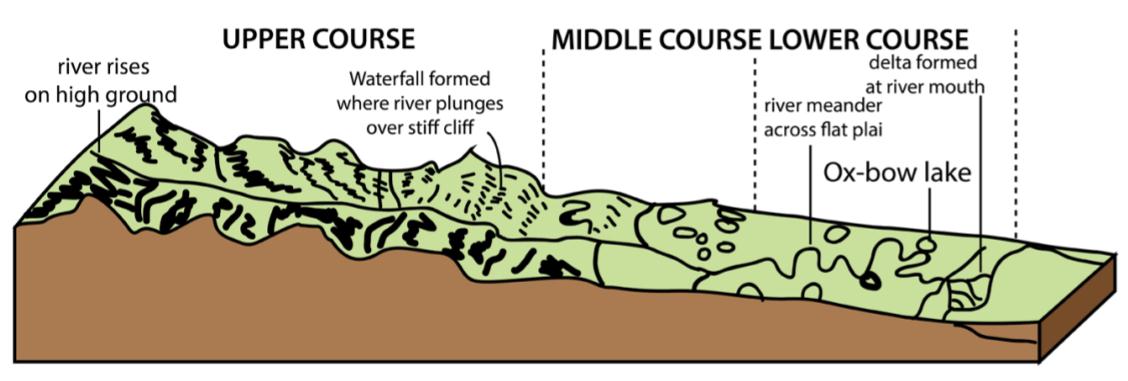
The Upper Course of a River
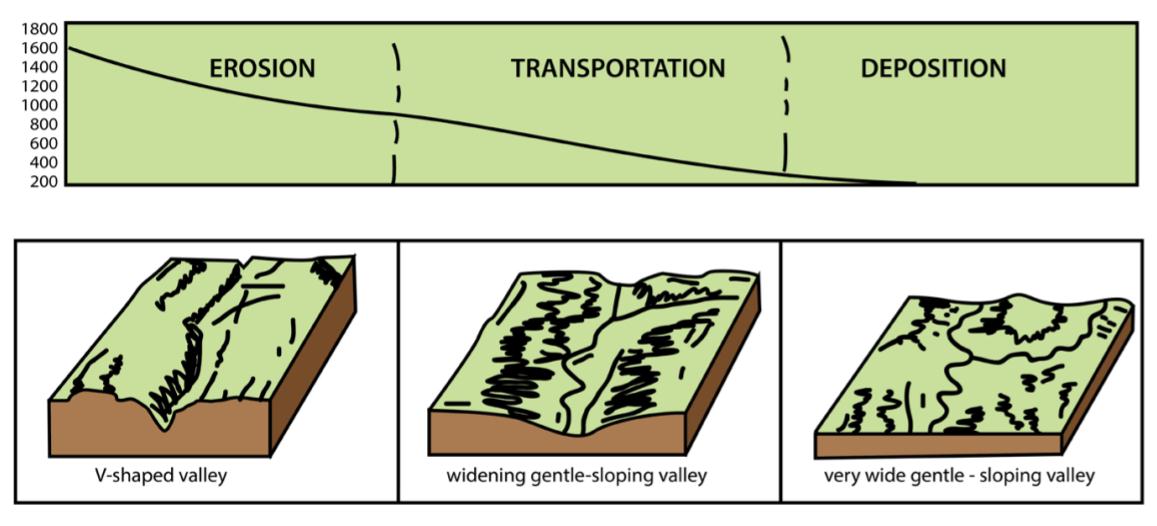
This stretch of the river originates from mountains where the river’s momentum is high. They are highly erosive in their upper courses and carry massive amounts of silt and sand. In the upper stretch, the water is crystal clear, cool, and rapidly flowing. The river passes through steep terrain. When the water travels down along the upper course, the river channel becomes increasingly narrow.
The river moves over rocks as it flows. The speed of the water produces energy, and the force of the water allows it to transport stones and boulders. Under these circumstances, the river bed gets dredged deeply. Different layers of hard and soft rock lead to the formation of waterfalls. In its upper course, rivers primarily perform two functions: erosion and transportation.
Check out the complete UPSC Syllabus
Features:
- Rugged and have steep slopes
- River beds are rocky and narrow
- Steep and V-shaped
- Water current increases as Several tributaries connect into the main river
Middle course of a river
The terrain becomes flat in the middle course of the river. The water flow gradually slows down, and soil erosion is reduced substantially. Rivers erode as they move, so the shape of the river constantly changes during the middle course. In the middle course of the river, water flow is at moderate speed. Because of the slow water flow, rivers deposit eroded particles that are brought along. The river widens and deepens in the middle course, and it begins to curve to form meanders and oxbow lakes. The middle course of the river bottom consists of silt and gravel.
Meanders
Meanders are produced as a result of both erosion and sedimentation. Meanders are U-shaped with curves and bends. They resemble horseshoes. A meander scar is formed when the water dries up, and the area fills up with sediment.
Visit to know more about UPSC Preparation Books
Oxbow lakes
Oxbow lakes are formed when the meander gradually narrows. Eventually, the neck of the meander contacts the opposite side, where the river cuts through the channel, cutting off the meander and forming the oxbow lake.
Features of the middle course :
- Plain like flat terrain
- Wider river channel
- Moderate water flow
- May consist of Meanders and oxbow lake
- River bottom consists of gravel
The lower course of a river
This is the last stretch of the river’s course. Due to the smooth slope of the Lower Course, the river flows gently and has an appearance of a lake habitat. The terrain in the lower course is very flat. On the river’s lower course, you’ll find muddy, slightly warmer water that flows more slowly. Rivers are usually at the widest point in their lower course. A deposition is the main activity in the lower course. The water deposits carry silt at the mouth of the river. The deposited debris forms a triangle island at the river’s mouth, which is called the Delta. An estuary is the meeting place of the river and the sea. The lower course of the river consists of well-developed deltas. Riverbanks and river beds are home to a variety of plants.
Features of the lower course :
- Extremely flat terrain
- Muddy and warm water
- The deposition is the major activity
- Well developed Delta is formed
Read about UPSC Notes
Conclusion:
Rivers and streams originate at the peaks of mountains or hills, where other watercourses eventually join them. India is home to hundreds of rivers. A river’s journey begins at its origin and ends at its mouth or Delta, where it meets the sea or the ocean. As rivers move over and through the terrain, they alter it through various processes, including erosion, deposition, and sedimentation. The rapid melting of glaciers as a result of climate change is altering river water flow patterns.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out











