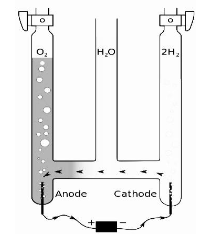
It is a reactive element that may be found in water, most rocks and minerals, as well as a variety of organic molecules. It is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless diatomic gas that makes up 21% of the atmosphere. It is utilized extensively in industry and is required for aerobic respiration and practically all combustion.
Definition:
Oxygen is a chemical element with the atomic number 8 and the symbol O. It’s a highly reactive nonmetal and oxidizer that produces oxides easily with most elements and other compounds. It belongs to the chalcogen group in the periodic table. After hydrogen and helium, oxygen is the most abundant element on Earth and the third most abundant element in the universe. Two atoms of the element join together at ordinary temperature and pressure to generate dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the formula O₂. Although the percentage of diatomic oxygen gas in the Earth’s atmosphere has fluctuated greatly over time, it today makes up 20.95 percent of the atmosphere. Oxygen, in the form of oxides, makes up over half of the Earth’s crust.
Properties and molecular structure:
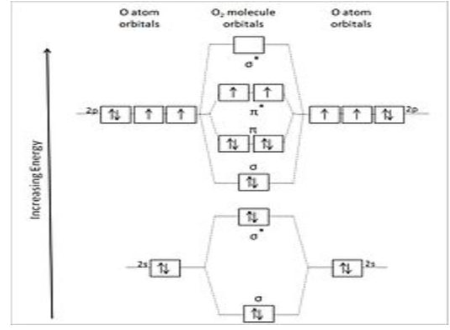
Two oxygen atoms are chemically linked together as dioxygen. The bond can be defined in a variety of ways depending on the level of theory used, but it can be simply characterized as a covalent double bond generated by the filling of molecular orbitals formed from the atomic orbitals of individual oxygen atoms, with a bond order of two. After sequential filling of the low and* orbitals, overlap of the two atomic 2p orbitals that lie along the O–O molecular axis and overlap of two pairs of atomic 2p orbitals perpendicular to the O–O molecular axis, and then cancellation of contributions from the remaining two 2p atomic orbitals, the double bond is the result of sequential, low-to-high energy, or Aufbau, which involves the filling of orbitals and the cancellation of contributions from the outside world.
Physical properties:
Water dissolved oxygen more readily than nitrogen, while freshwater dissolved oxygen more readily than seawater. In equilibrium with air, water contains around 1 molecule of dissolved O₂ for every 2 molecules of N₂ (1:2), compared to a 1:4 ratio in the atmosphere. Temperature affects the solubility of oxygen in water; at 0 °C, almost twice as much (14.6 mg/L) dissolves as it does at 20 °C (7.6 mg/L). Freshwater can dissolve around 6.04 milliliters (mL) of oxygen per liter at 25 °C and 1 standard atmosphere (101.3 kPa) of air, while the ocean contains about 4.95 mL per liter. At 5 °C, freshwater solubility increases to 9.0 mL per liter (50 percent higher than at 25 °C) while seawater solubility increases to 7.2 mL per liter (45 percent more).
Industrial production:
Two principal processes remove 100 million tons of O₂ from the air for industrial usage each year. Fractional distillation of liquefied air is the most frequent process, with N2 distilling as a vapor and O2 staying as a liquid.
Nitrogen is absorbed and a gas stream with a nitrogen concentration of 90% to 93 percent is produced by passing a stream of clean, dry air over one bed of identical zeolite molecular sieves. Combustion is the other major technique of creating O2. Simultaneously, nitrogen gas is released from the other nitrogen-saturated zeolite bed by lowering the chamber operating pressure and directing part of the oxygen gas from the production bed through it in the opposite flow direction. The operation of the two beds is switched after a predetermined cycle time, allowing for a continuous supply of gaseous oxygen to be pumped through a pipeline. Pressure swing adsorption is the term for this.
Storage:
High-pressure oxygen tanks, cryogenics, and chemical compounds are all examples of oxygen storage systems. Because one liter of liquefied oxygen is equivalent to 840 liters of gaseous oxygen at atmospheric pressure and 20 °C (68 °F), oxygen is frequently transported in bulk as a liquid in specially insulated tankers for economic reasons. These tankers are used to restock bulk liquid-oxygen storage containers that are stationed outside hospitals and other facilities that require significant amounts of pure oxygen gas. Before entering the building, liquid oxygen passes via heat exchangers, which transform the cryogenic liquid to gas. Oxygen can also be carried and shipped in smaller cylinders containing compressed gas, which is beneficial for portable medical applications as well as oxy-fuel welding and cutting.
Atomic mass of oxygen:
Oxygen has an atomic mass of 16.Oxygen has an average atomic mass of 15.9994 atomic mass units. This atomic mass, on the other hand, is the average atomic mass of all isotopes in nature. As a result, the first isotope is more prevalent. So, when most of us talk about oxygen, we’re talking about oxygen with eight neutrons.
Oxygen formula:
One of the most well-known and extensively utilized formulas in chemistry is the oxygen formula. The most common element on the earth is oxygen. The symbol for it is O, and it belongs to the chalcogen group of the periodic table. One of the most important qualities of oxygen is that it is a colorless, tasteless, and odorless gas that easily dissolves in water and forms oxides when it combines with other elements and compounds. It is also the most crucial gas for humans because it aids in their breathing.
Oxygen chemical formula:
O2 is the chemical formula for oxygen, which is also known as dioxygen. Because oxygen normally joins with another oxygen by establishing a covalent bond, this formula is given. Because it is diatomic, it requires two electrons to complete its octet, which it may easily obtain from another oxygen. Meanwhile, because oxygen is electronegative, it is extremely reactive. To obtain stability, the reaction between the two oxygen atoms proceeds quickly.
Oxygen saturation:
The fraction of oxygen-saturated hemoglobin in the blood compared to total hemoglobin (unsaturated + saturated) is called oxygen saturation. The human body necessitates and maintains an extremely precise and specialized oxygen balance in the blood. Humans have a normal arterial blood oxygen saturation level of 95–100%. Hypoxemia is defined as a low level of oxygen in the blood that is less than 90%. Arterial blood oxygen levels below 80% may jeopardize organ function, particularly in the brain and heart, and should be addressed immediately. Continued deficiency in oxygen may result in respiratory or cardiac collapse. To help raise blood oxygen levels, oxygen treatment can be employed. When oxygen molecules (O2) reach the body’s tissues, this is called oxygenation.
Conclusion:
The availability of nitrous oxide/oxygen analgesia/anxiolysis for juvenile patients creates a win-win situation for both the dentist and the patient. The patient can receive dental treatment in a relaxed, non-threatening setting, which will encourage them to return for a lifetime of dental care without the fear of discomfort. It enables the dentist to offer the best dental treatment possible by allowing him or her to focus on clinical skill rather than behavior control, resulting in less stress and higher pleasure. It is a safe way for treating patient anxiety related to dental treatment when used according to approved guidelines.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out