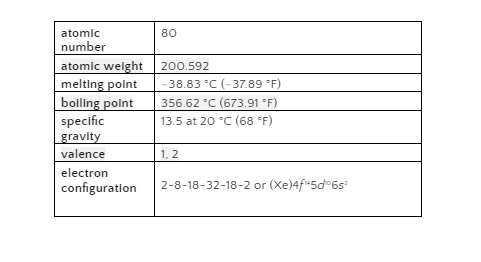
Mercury is a naturally occurring chemical element that can be found in rock throughout the earth’s crust, including coal deposits. It has the symbol “Hg” on the periodic table and an atomic number of 80.
Mercury, also known as elemental or metallic mercury, is a gleaming silver-white metal that is liquid at ambient temperature and was once known as quicksilver. Older thermometers, fluorescent light bulbs, and some electrical switches include it. When elemental mercury is spilled, it disintegrates into tiny droplets that can pass through small cracks or get strongly bound to particular materials.
Element Properties
Properties
As early as 1500 BCE, Mercury was known in Egypt and perhaps in the East. Mercury’s chemical symbol, Hg, comes from the Latin word hydrargyrum, which means “liquid silver,” and was first used in alchemy in the sixth century. It was known to be harmful, yet it was primarily used for medical purposes.
At ambient temperature, mercury is the only elemental metal that is liquid. Celanium, gallium and rubidium all melt at temperatures between 28.5 and 30.5 degrees Celsius [83 and 101 degrees Fahrenheit]. At a temperature of minus 38.83 degrees Celsius (minus 37.89 degrees Fahrenheit), mercury turns into a soft solid like tin or lead. 356.62°C (673.91°F) is the boiling point.
Uses
Amalgams or liquid alloys are formed by mixing copper, tin, and zinc with it. In dentistry, fillings made of silver amalgam are commonly utilised. Mercury does not adhere to glass, making it ideal for thermometers because of its rapid and consistent volume expansion in its liquid range. (At the dawn of the twenty-first century, mercury thermometers gave way to more precise electronic digital thermometers.) Barometers and manometers also relied on its low vapour pressure and high density. However, mercury’s toxicity has led to the replacement of this material in these devices. In the past, mercury was employed to extract gold and silver from their ores because of its ability to dissolve these metals.
Mercury is an excellent conductor of electricity, making it ideal for use in sealed switches and relays. In UV, fluorescent, and high-pressure mercury-vapour lamps, an electrical discharge through mercury vapour generates a bluish glow rich in ultraviolet light. Pharmaceuticals, agricultural, and industrial fungicides all employ mercury in some form.
To make chlorine and sodium hydroxide by electrolysis, mercury was used as a cathode because it dissolves sodium free to form a liquid amalgam when used as a negative pole or cathode. However, mercury-cell factories for the production of chlorine and sodium hydroxide have largely been phased down in the early 21st century.
Occurrence
At an average of 0.08 grams per tonne (0.003 ounces) of rock, Mercury can be found in the Earth’s crust. Cinnabar, a red sulphide, is the primary ore. Isolated droplets of native mercury can be found, as well as larger fluid masses, in volcanic areas and hot springs. Natural mercury alloys such as moschellandsbergite (a silver-mercury alloy), potarite (a palladium-mercury alloy), and gold amalgam are all extremely rare. As a byproduct of gold mining, China supplies more than 90% of the world’s mercury supply.
Shaft or open-pit mining and flotation refinement are used to extract cinnabar. In most cases, the volatile nature of mercury and the fact that cinnabar is easily destroyed by air or lime lead to the extraction of free mercury. After roasting in the air, the mercury vapour condenses out of the cinnabar, and it may be separated from the mineral. Because of mercury’s toxicity and the danger of strict pollution control, efforts are being made to find more environmentally friendly ways to extract the metal. Since sodium hypochlorite and sulfuric acid are both highly soluble in cinnabar, the mercury in these solutions can be recovered through precipitation with zinc or aluminium or electrolysis. (See mercury processing for information on commercial mercury treatment; see native element [table] for information on mineralogical qualities.)
Toxic is mercury. Ingestion of soluble compounds or skin absorption of mercury can cause poisoning when inhaled.
The stable isotopes of natural mercury are 196Hg (0.15%), 198Hg (9.97%), 199Hg (16.87%), 200Hg (23.10%), 201Hg (13.18%), 202Hg (29.86%), and 204Hg (29.86%). (6.87 percent). Using gold-197 neutrons bombarded to create mercury-198, a wavelength standard and other accurate measurements have been made with this isotopically pure mercury.
Principal compounds
+1 or +2 oxidation state compounds of mercury are the most commonly found. Primarily, we’re dealing with mercuric compounds or mercury(II). When mercury is heated to between 300 and 350 degrees Celsius (572 to 662 degrees Fahrenheit), it will not mix with oxygen to form mercury(II) oxide, HgO, at a rate that is useful. The reaction reverses when the compound reaches temperatures above around 752 °C (400 °C). For the study of oxygen, Antoine-Laurent Lavoisier and Joseph Priestley employed this reaction.
Mercury(I) and mercurous compounds are extremely rare. The Hg22+ ion, which is diatomic and stable, is mercury(I). Among the most important univalent compounds is mercury(I) chloride, Hg2Cl2 (also known as calomel). Antiseptic slaves were made with it. Perhaps the most frequent bivalent chemical is bichloride of mercury, HgCl2 (sometimes referred to as corrosive sublimate). Even though this material is exceedingly dangerous, it is used in a wide range of industries. As a fungicide in agriculture, as a topical antiseptic in concentrations of one part per 2,000 parts of water in medicine, and as a catalyst in the manufacturing of vinyl chloride and other mercury compounds in the chemical industry, it is widely used. For the synthesis of numerous organic mercury compounds and some inorganic mercury salts, HgO offers elemental mercury. As an electrode in zinc-mercuric oxide electric cells and mercury batteries, this red or yellow crystalline solid is also utilised. Black or red crystallised HgS, HgS, is an important pigment used in paints, rubber and plastics.
Mercury zodiac sign meaning
Mercenary is the planet of communication and coordination as well as creative expression and data processing.
Conclusion
Mercury and its compounds have been linked to a wide range of health problems around the world. International effort is needed to decrease mercury discharge dangers to human health and the environment.
We must have a greater grasp of the issues, but we don’t need to have a complete consensus or all the facts before we can act. At the global, regional, national, and local levels, we must address these negative repercussions.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






