Polarity in chemical bonding refers to the distribution of electrical charge across the atoms connected by the bond. While bonds between identical atoms, such as H2, are electrically uniform because both hydrogen atoms are electrically neutral, bonds between atoms of different elements are electrically inequivalent. For example, the hydrogen atom in hydrogen chloride is slightly positively charged, while the chlorine atom is slightly negatively charged. Partial charges are the little electrical charges that exist on different atoms, and the presence of partial charges indicates the presence of a polar bond.
Define Polarity
The polarity of bonds is caused by the interaction of molecules and atoms with varying electronegativities. Moving on, the term polarity is commonly employed in fields such as magnetism, electricity, and electronic device signaling. The points, or poles as they are generally called, have more electrons than the other.
When it comes to chemistry, polarity refers to the separation of an electric charge, which results in a molecule having a positive and negative end.
For e.g.-
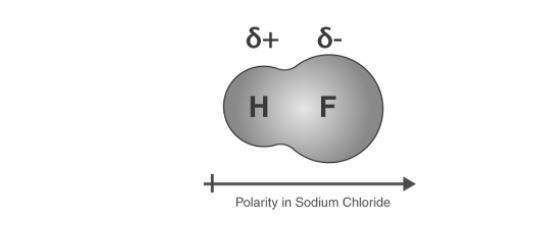
The fluorine atom in an H-F bond is said to be more electronegative than the hydrogen atom. Eventually, the electrons spend more time at the Fluorine atom. As a result, the F atom becomes slightly negative, whilst the Hydrogen atom becomes slightly positive.
Polarity of Molecules
Depending on whether a molecule is polar, non-polar, or ionic, it is classed as polar, non-polar, or ionic.
- Polar Molecules: A polar molecule is generated when one end of the molecule has a higher amount of positive charges than the opposite end, resulting in an electrical pole. When a molecule is stated to have a polar bond, the negative charge center will be on one side, while the positive charge center will be on the other. It will be a polar molecule from beginning to end.
- Non- Polar Molecules: A non-polar molecule is one that does not contain charges at the end due to finely dispersed electrons that symmetrically cancel each other. Take, for example, water and oil. Water is a polar molecule in this solution, but oil is a non-polar molecule. Because these two molecules cannot be combined, they do not produce a solution.
Polar and Non-polar Molecules examples
- The atoms in a non-polar molecule are organised so that the orbital electrons in the outer region balance out the electronegativity.
- The molecules that have a pyramidal or V-shaped shape are known as polar molecules. Non-polar molecules, on the other hand, are linear molecules.
- Water is categorised as a polar molecule because the electronegativity of the oxygen and hydrogen atoms differs.
- Non-polar molecules include fats, petrol, oil, and gasoline, which do not dissolve in water and are insoluble in water.
Polarity Reversal
A seismic attribute anomaly known as polarity reversal or phase change occurs when a brine saturated formation with a high acoustic impedance is overlain by a low acoustic impedance shale.
A seismic amplitude anomaly known as a polarity reversal can indicate the presence of hydrocarbons in a seismic segment. When water-saturated sand has a higher acoustic impedance than the overlying shale (shale has a lower acoustic impedance), polarity reversals occur; however, hydrocarbon sand is softer.
The character of the earth is described by two quantities to a seismic interpreter concerned with structure. The first parameter is velocity, which determines ray trajectories and seismic reflection periods. The size of the reflected amplitudes is defined by the second quantity, acoustic impedance. The difference in velocities in the layer above and below an interface determines the strength of the reflected amplitude, with a stronger reflector happening when the difference is greater. The greater the strength, the greater the swing of the trace; in other words, the greater the amplitude.
Factors that Determine Whether a Molecule Is Polar?
- Even if polar links are present, if the molecule or atom is fully symmetric, the molecule will not be polar.
- When one atom in a bond has a substantially stronger attraction to electrons than the other, polar bonds occur. When comparing electronegativity values, a difference in strength can be expected. If one atom’s electronegativity is higher, it will pull the electron in closer and develop a partial negative charge, while the other atom will develop a partial positive charge.
CONCLUSION
Every molecule has a fixed number of electrons that are organized in a shell at specific energy levels. The valence shell’s electrons are involved in chemical bonding with other atoms. Atoms tend to adopt the noble gas structure in order to achieve stability. As a result, chemical bonding is thought to be responsible for atom and molecule stability Chemical bonds based on the participation of atoms and the flow of electrons include metallic bonds, covalent bonds, and ionic bonds. Ions are generated when electrons are displaced. An anion is formed when an atom accepts an electron and gains a negative charge. When an atom loses one of its electrons, it gains a positive charge and is transformed into a cation. The opposite charges of a cation and anion attract one another, and this electrostatic attraction force is known as an ionic bond. Ions have both negative and positive charges because electrons travel completely to atoms during the formation of an ionic bond. Metals and non-metals can develop these kinds of relationships. Metals have a proclivity for releasing electrons and forming cations. Non-metals, on the other hand, are more likely to accept electrons and create anion.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




