Introduction:
A phospholipid is an amphiphilic molecule found in cell membranes that consists of a polar head region, a unit of glycerol, and two or more non-polar fatty acid tails. The plasma membrane is made up of a bilayer of phospholipid molecules.
The surface can operate as a cellular membrane when the phospholipid molecules are linked by other lipids and integral proteins. This semi-permeable barrier prevents polar molecules from passing through, letting the cell regulate the concentration of different chemicals via protein channels.
Phospholipid structure:
CH2OH-CHOH-CH2OH is the chemical formula of phospholipid.
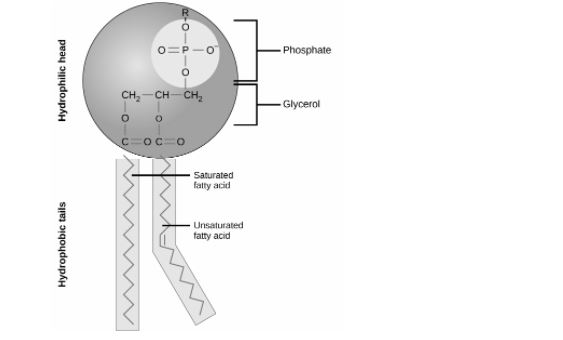
A phospholipid is an amphipathic molecule, meaning it has both hydrophobic and hydrophilic elements. A phosphate group on one end, referred to as the “head,” and two side-by-side chains of fatty acids, referred to as the “tails,” make up a single phospholipid molecule. The negatively charged phosphate group makes the head polar and hydrophilic, or “water loving.” As a result, the phosphate heads are drawn to the water molecules in their surroundings.
The lipid tails, on the other hand, are uncharged, nonpolar, and hydrophobic, which means they are afraid of water. Water repels and attracts hydrophobic molecules. Saturated fatty acids make up some lipid tails, while unsaturated fatty acids make up others. This combination contributes to the fluidity of the continually moving tails.
Phospholipid types:
It’s worth noting that not all phospholipids are created equal. Size, shape, and chemical structure would all be different. As a result, depending on the type of molecule connected to the phosphate group, they can be classified into distinct types. As a result, simple chemical compounds can change the phosphate group of the phospholipid. As a result, the following are the several types of phospholipids:
Phosphatidylcholine
This phospholipid will have an ethanolamine unit connected to the phosphate group, as the name implies. This form of phospholipid is determined to be the second most abundant in the cell membrane. Its small head would make it easier for proteins to align themselves within the membrane, allowing membrane fusion and budding to occur.Furthermore, it is discovered to be necessary for the efficient functioning of the liver as well as lipid absorption. This sort of phospholipid is revealed to be one of the bile’s components and aids fat breakdown. Additionally, this aids in the movement of cholesterol and other lipids to other organs.
Phosphatidylethanolamine
This phospholipid will have an ethanolamine unit connected to the phosphate group, as the name implies. This form of phospholipid is determined to be the second most abundant in the cell membrane. Its small head would make it easier for proteins to align themselves within the membrane, allowing membrane fusion and budding to occur.
Phosphatidylserine
The amino acid serine will be connected to the phosphate group in this phospholipid, which will be limited to the inner region of the cell membrane. This form of phospholipid has been discovered to have an important role in cell signaling. It’s worth noting that the presence of this phospholipid on the surface of the dying cells’ outer membrane would trigger macrophage digestion. These phospholipids will aid in the coagulation of blood in platelets.
Phosphatidylinositol
This is the least common kind of phospholipid, as it contains an inositol unit. This kind can be found in a variety of cells and tissues, but it is particularly prevalent in brain cells.This kind has been discovered to have an important role in the production of cell signaling molecules. These would also aid in protein and carbohydrate unit binding to the cell membrane’s outer layer.
Phospholipid uses:
This molecule serves a variety of functions as a critical component of the cell. The following are some of the most important functions and applications of phospholipids:
- Assist the flexibility of cell and organelle membranes.
- Allow for the production of vesicles.
- Endocytosis and exocytosis should be enabled.
- Serve as protein-binding sites.
- Assist in the formation of numerous tissues and organs.
- Important for the neurological, digestive, and cardiovascular systems to work properly.
- Assist with cell-to-cell communication.
- Participate in apoptosis and blood clotting mechanisms.
- Aid in cell lubrication.
- It’s a component of drug delivery systems.
- Assist in the emulsification of liquids.
Phospholipid function:
- Phospholipids aid in the protection of cell membranes, allowing them to function effectively inside the cell.
- It creates a barrier around the cell membranes to keep the cell’s interior secure and isolated from the outside world.
- Phospholipid aids in the transport of medications throughout the body in pharmaceuticals.
- It has the ability to both repair and prevent damage to the human liver.
- It also assists in the removal of cholesterol and fat absorption from the body.
- Cephalin, which is a phospholipid, aids in blood clotting.
Conclusion:
A glycerol molecule, two fatty acids, and an alcohol-modified phosphate group make up phospholipids. The phosphate group is a negatively charged, hydrophilic polar head. Hydrophobicity is found in the uncharged, nonpolar tails of fatty acid chains. The hydrophobic tails face inward, away from the water, and meet in the inner region of the membrane. The hydrophilic heads are attracted to both intracellular and extracellular fluid and face outward. Micelles are lipid molecules that form a spherical shape in aqueous solutions when phospholipids are combined with water.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




