Introduction:
Petroleum, often known as crude oil or oil, is a yellowish-black liquid that forms spontaneously in geological formations. It’s frequently processed into a variety of fuels and chemicals. Distillation is used to separate the components of petroleum. Petroleum is mostly made up of hydrocarbons, with traces of other organic molecules thrown in for good measure. Both naturally occurring unprocessed crude oil and petroleum products made up of refined crude oil are referred to as petroleum. Petroleum is a fossil fuel that is generated when enormous amounts of dead animals, usually zooplankton and algae, are buried beneath sedimentary rock and exposed to high heat and pressure over extended periods of time.
Elemental composition of Petroleum:
The elemental makeup of petroleum is well-defined, despite considerable variance in the ratios of organic molecules:
Carbon – 83 to 87%
Hydrogen – 10 to 14%
Nitrogen – 0.1 to 2%
Oxygen – 0.05 to 1.5%
Sulfur – 0.05 to 6.0%
Metals – < 0.1%
Iron, nickel, copper, and vanadium are the most common metals.
Hydrocarbons in Petroleum:
Crude oil has four different types of hydrocarbons:
paraffins (15-60%)
naphthenes (30-60%)
aromatics (3-30%)
asphaltics (remainder)
Alkanes, cycloalkanes, and aromatic hydrocarbons make up the majority of the hydrocarbons.
Industrial Fractions:
As stated, petroleum may be broken down into usable elements. In fact, you may not realize it, but petroleum is likely responsible for a substantial portion of the products you rely on. For example, fertilizers for your lawn, some of the substances used in dry cleaning, Vaseline in chapstick, and even the asphalt on the highway are all made from petroleum. Not to mention the gas for your car and your home! Without petroleum, life would be a lot more difficult. These are all industrial fractions, or petroleum pieces that are divided down based on their chemical makeup.
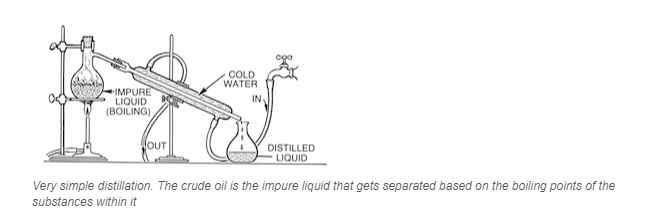
Distillation, or heating the crude oil and separating it based on the different boiling points of the fractions, is usually the first step in breaking up the petroleum into its fractions.
Before we go any further, let’s have a look at some of the petroleum fractions in the table, which is listed from lowest to highest boiling point.
Name | Uses |
Petroleum Gas | Liquified petroleum gas is used to heat homes, some is used in fertilizers |
Gasoline | Fuel for cars, dry cleaner ingredient |
Kerosene | Fuel for lanterns |
Fuel oil | Fuel for buses, trucks, generators |
Lubricating oil | Lubrication for certain types of machines |
Paraffin wax | Ingredient in Vaseline, candles, certain makeup, and match sticks |
Asphalt | Material in roads |
Petroleum ether formula and structure:
Petroleum ether is a mixture, a percentage, rather than a compound. Aliphatic hydrocarbons, with the usual chemical formula C2H2n + 2, make up this substance. Their only structural elements are C-C and C-H bonds, as well as a carbon skeleton. As a result, this compound does not have a formal chemical formula.
By definition, none of the hydrocarbons that make up petroleum ether include oxygen atoms. As a result, it’s not only not a compound, but it’s also not an ether. It is referred to as an ether because it has a boiling point that is similar to that of ethyl ether; the rest are unrelated.
Petroleum ether is composed of aliphatic hydrocarbons with short and linear chains of the form CH3(CH2)xCH3. It’s not unexpected that this liquid is volatile due to its low molecular mass. It is a suitable fat solvent because of its nonpolar nature, which is owing to the absence of oxygen or any other heteroatom or functional group.
Petroleum quartz meaning:
The faces are smooth and glossy, with no obvious striations, providing the ideal canvas for inclusions with no interference from the inside or outside.
Petroleum trapped in the voids and negative crystals is the most obvious inclusion. It’s often brilliant yellow, with a few brown spots.
Within the petroleum, some of them have methane bubbles. Some are mobile, while others are immovable. There is often a little quantity of water at the edges of the cavities, even if it is not readily visible.Black and dark asphaltite, the group name for bituminous hydrocarbons, can be found in many of these crystals.
Asphaltite can be found inside quartz without any fluid connection, and it can also be found inside petroleum holes. The asphaltite can move freely within the hollow in a few rare circumstances.The bubble goes slower on chilly days, but if you hold it for a few minutes, it heats up and begins to move quicker again.It’s already a fascinating substance because of this. But, on top of that, when exposed to long-wave UV radiation, it fluoresces vivid blue.
Quartz:
It’s a silicon dioxide mineral. SiO2 is a chemical formula. Quartz is formed when silica crystallizes. Approximately 14% of the earth’s crust. Rhombohedral crystalline quartz is a type of rhombohedral quartz. Large, colorless crystals make up the substance. As a result, it is considered one of the master stones in lithotherapy.
The most beautiful stone crystallized in the fractures due to a hydrothermal process. It’s found in silica-rich rock cracks. As a result, the name “rock crystal” was coined.
Other minerals are frequently found with it. Albite, orthose, and adular feldspars, as well as calcite The cut of a rock crystal determines its beauty. The temperature of hydrothermal solutions is the main source of information. They will be more gorgeous and translucent the higher they are.
They’re frequently grouped together in some way. As a result, a sheaf of quartz crystals resembled chrysanthemums.
Inclusions in some stones contain a variety of minerals. Rutile needles, as well as tourmaline, amphibole, and chlorite spangles, can be found. The existence of certain Elements causes the color of particular crystals. Manganese, iron oxides, and other mineral inclusions are examples.
Conclusion:
Exploitation of petroleum has serious environmental and social effects. Petroleum is one of the biggest contributors to climate change because the extraction, refining, and burning of petroleum fuels all emit huge amounts of greenhouse gasses.
Parts of the petroleum sector also intentionally suppressed science and legislation aimed at averting the climate problem. Other negative environmental repercussions include oil spills and air and water pollution at utilization sites, as well as the environmental implications of exploration and exploitation of petroleum reserves. All of these environmental factors have a direct impact on human health. Furthermore, oil has been a source of conflict, resulting in both state-led and other types of conflicts (for example, oil revenue funded the Islamic State).
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






