Let us first understand what acid is. An acid is a chemical compound that releases H+ ions in an aqueous solution. We can test the acidic or basic nature of a compound by using an acid-base indicator. Formic acid comes in the carboxylic acid group. It is written as HCOOH and formic acid is the first member of the carboxylic acid group. Formic acid is also known as methanoic acid. Formic acid was first isolated from certain ants and was named after the Latin Formica, meaning “ant”.
What does Formic acid mean?
Formic acid is the simplest form of carboxylic acid and is also known by the systematic IUPAC name as methanoic acid. It is formed naturally in the venom of bees and ants and is considered an important intermediate in chemical synthesis. The chemical formula of formic is HCOOH.
Structure of formic acid:
The structure of formic acid is simple. It is the simplest carboxylic acid that contains 2 oxygen atoms, a single carbon atom, and 2 hydrogen atoms.
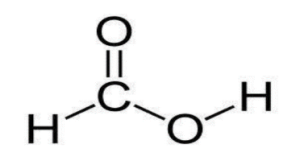
Chemical information of formic acid:
Formula: CHOOH
IUPAC name: Formic acid.
Molar mass: 46.03g/mol
Density: 1.22g/cm
Boiling point: 100.8c
Melting point: 8.4 c
Physical properties of formic acid:
- Formic acid is a colorless liquid having a highly pungent, penetrating odor at room temperature.
- It is miscible with water and most polar organic solvents and is somewhat soluble in hydrocarbons.
- In hydrocarbon and in the vapor phase, it contains hydrogen-bonded dimers rather than individual molecules.
- Solid formic acid consists of an effectively endless network of hydrogen-bonded formic acid molecules.
- Formic acid is corrosive to metals and organic tissues. Since it is a simple form of carboxylic acid, it occurs in the form of acetic acids and amino acids and is the main ingredient in vinegar.
Chemical properties of formic acid:
Special reaction for methanoic acid:
- Salt formation: Formic acid is the strongest acid among all the members of the homologous series. It forms salts with alkalis, carbonates, and bicarbonates.
HCOOH + NaOH → HCOONa + H2O
- Reaction with sulphuric acid: When formic acid is warmed with conc. Sulphuric acid decomposes to give carbon monoxide and water.
HCOOH + H2SO4 → H2O + CO
- Action of heat: When formic acid is heated above 160c under pressure, it decomposes to give carbon dioxide and hydrogen.
HCOOH → CO2 + H2
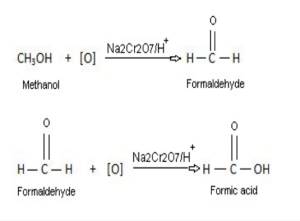
Preparation of formic acid:
Formic acid may be obtained as follows:
- From methanol: By the oxidation of methanol with acidified sodium dichromate solution.
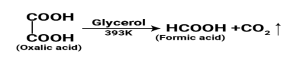
- From oxalic acid: Formic acid is prepared in the lab by heating oxalic acid with a glycerol catalyst at 110c.
Natural occurrence:
- In nature, it is found in the venom of ants.
- Formic acid is a naturally occurring component of the atmosphere due primarily to forest emissions.
Uses of formic acid:
- Formic acid is in use as a mixture with citric acid as it is unable to remove iron oxide deposits if it is in use alone.
- One of the major areas in which formic acid is useful is industrial chemicals in saturated monocarboxylic acids.
- Formic acid is very much useful as a reducing agent to reduce potassium dichromate and sodium.
- It is in use in tanning and dyeing industries, but other competing assets are cheaper and therefore formic acid is less in use or in a few cases in which it has specific advantages.
- Formic acid shows anti-bacterial properties as a result formic acid is of very high use in the agriculture industry.
- It is very well known as a pesticide and is proven beneficial to prevent crops from being prone to attacks from different kinds of pests.
Is formic acid is a strong acid?
Firstly, a strong acid is an acid that disassociates completely in an aqueous solution. Whereas a weak acid dissociates partially in an aqueous solution. Hence by this property, we can say that formic acid is a weak acid and it occurs naturally in stings of bees and ants. Formic acid can also form by the distillation of ants.
Conclusion:
Formic acid is the simplest form of organic acid comprising a hydrogen atom bonded to the carboxylic acid functional group. The structural formula of methanoic acid determines its physical and chemical properties. It is a naturally occurring acid found in the venom of ants. Due to its anti-bacterial properties, it is highly used in agriculture industries.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




