The Fehling’s test detects the presence of reducing sugars in a sample. The test makes use of two solutions: copper sulphate and sodium hydroxide. The copper sulphate solution is blue, while the sodium hydroxide solution is yellow. A reducing sugar in a sample will react with the copper sulphate solution to produce a red colour. The presence of a reducing sugar in the test solution is indicated by the presence of a red colour in the solution.
Fehling’s test Definition
Fehling’s test is used to detect reducing sugars and distinguish between water soluble carbohydrates and ketone functional groups. It is a deep blue alkaline solution used to detect the presence of aldehyde or any groups containing the aldehyde functional group -CHO in addition to the Tollen’s reagent in order to distinguish between reducing and non-reducing agents. Fehling solution is also used to distinguish between a ketone group and water-soluble carbohydrates. Hermann von Fehling, a German chemist, invented the test in 1849. In the test, Fehling’s solution is used to determine the outcome. In this article, we will discuss the Fehling solution preparation, the Fehling test procedure and the reactions involved, and the Fehling test result.
The substance to be tested is heated with the Fehling solution to perform the Fehling test. The presence of an aldehyde group is indicated by the formation of a brick-red precipitate.
Principle of Fehling’s test
- Carbohydrates with free or potentially free carbonyl groups (aldehyde or ketone) have the potential to act as reducing sugars.
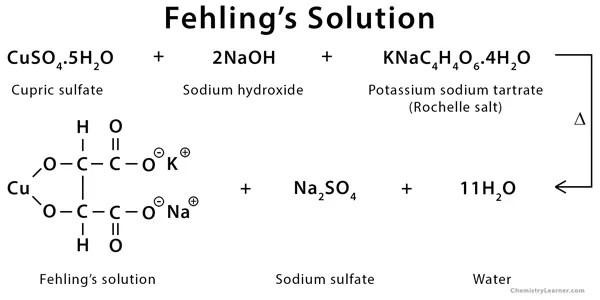
- Fehling’s solution is a deep blue solution made up of copper sulphate, potassium sodium tartrate, and a strong alkali, usually sodium hydroxide.
- The sample with the Fehling’s solution, bistartarocuprate (II) complex oxidises the aldoses to the corresponding aldonic acids when heated.
- The complex’s copper (II) ions are reduced to an insoluble yellow or red precipitate or cuprous (I) oxide (Cu2O) ions during the process.
- Ketones, on the other hand, are oxidised to produce shorter acid chains.
- By forming a bistartarocuprate (II) complex, tartrate ions prevent the formation of insoluble Cu(OH)2 from the reaction of copper sulphate and sodium hydroxide in the solution.
- This complex gradually releases cupric ions for reduction, preventing the formation of black cupric oxide.
- When Fehling’s solution is heated in the absence of reducing sugars, a black cupric oxide precipitate forms.
Procedure of Fehling’s test
The Fehling’s test is performed as follows –
- To make Fehling’s solution, combine equal parts Fehling solution A and B.
- In a clean and dry test tube, place freshly prepared Fehling’s solution.
- Fill another washed and dried test tube with a sample.
- As a control, place distilled water in another test tube.
- Observe and record the formation of red-colored precipitate.
Fehling’s solution
During the Fehling’s Test, a solution mixture known as Fehling’s Solution is used. In most cases, it is prepared fresh in laboratories. This Fehling’s Solution is a hybrid of two solutions known as Fehling’s A and Fehling’s B.
Fehling’s A is a blue liquid containing copper(II) sulphate, whereas Fehling’s B is a clear liquid containing potassium sodium tartrate (Rochelle salt) and a strong alkali, usually sodium hydroxide. During the test, these two solutions are prepared separately.
During the test, Fehling’s A and B solutions are mixed in equal parts to create the final Fehling solution, which is a deep blue colour. Cu²+ bis(tartrate) complex is the deep blue ingredient. In the solution, tartrate tetra-anions act as a chelating agent.
Requirements for Fehling’s test
- Fehling’s solution A, which is made by dissolving 7 g of CuSO47H2O in 100 ml of water.
- Fehlings solution B is made by combining 24 g of KOH and 34.6 g of potassium sodium tartrate in 100 mL of water.
- Fehling’s solution is made by combining equal parts of both solutions just before use.
- Sample for Testing (5 percent Glucose, 5 percent Sucrose, 5 percent Fructose, 5 percent Starch, 5 percent lactose)
- Pipettes, test tubes, a test tube stand, and a water bath are among the additional materials.
Results of Fehling’s test
Positive Result: The presence of reducing sugars is indicated by the appearance of reddish-brown precipitate in test tubes.
Negative Result: The lack of reddish precipitate or the appearance of a deep blue colour indicates a negative result and a lack of reducing sugars.
Conclusion
The Fehling’s test detects the presence of reducing sugars in a sample. The presence of a reducing sugar in the test solution is indicated by the presence of a red colour in the solution. In the test, Fehling’s solution is used to determine the outcome. The substance to be tested is heated with the Fehling solution to perform the Fehling test. Fehling’s solution is a deep blue solution made up of copper sulphate, potassium sodium tartrate, and a strong alkali, usually sodium hydroxide. When Fehling’s solution is heated in the absence of reducing sugars, a black cupric oxide precipitate forms.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




