Forces of ion-dipole between polar water molecules and a sodium ion, ion-dipole forces are formed. The water molecule’s oxygen atom contains a tiny negative charge, which attracts the positively charged sodium ion. Ion-dipole interactions between molecules are far weaker than covalent or ionic bonds and
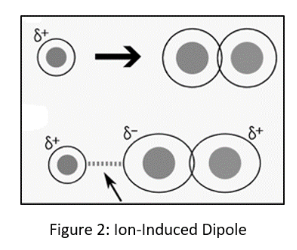
An ion-induced dipole force occurs when an ion interacts with a non-polar molecule. Similar to a dipole-induced dipole force, the charge of the ion causes a distortion of the electron cloud in the non-polar molecule, resulting in a short partial charge.
The ion and the temporary partially charged dipole attract one other and produce a brief interaction.
There are several terms used in ion-dipole and, Ion-Induced Dipole which are given below:
Non-polar: There are no positive or negative poles in a nonpolar molecule since there is no charge separation. Nonpolar molecules, in other words, have an equitable distribution of electrical charges throughout the molecule. In nonpolar solvents, such as organic solvents, nonpolar molecules dissolve readily.
Polarized: In chemistry, polarization refers to the deformation of an anion’s symmetric electron charge cloud by a cation. It has been observed that the positive electric field of a cation pulls the electronic sphere of an anion away from their equal distance in an ionic crystal.
Induced dipole: The weakest intermolecular force is the London dispersion force. When the electrons of two neighboring atoms occupy places that cause them to create transient dipoles, the London dispersion force is a temporary attractive attraction. An induced dipole attraction is a term used to describe this force.
Ion-dipole
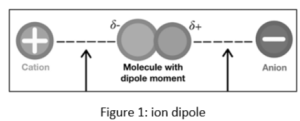
An ion-dipole force is exactly what it sounds like. It is the interaction of an ion with a dipole molecule. Remember that an ion is an atom with a negative or positive charge that has gained or lost one or more electrons. A cation is a positively charged atom that has lost a valence electron and hence has more positive protons than negative electrons. An anion is a negatively charged atom that has gained a valence electron.
For example
H2O (water molecule) with Na+ (sodium ion)
Na+ is a type of cation.
H2O’s partially positive end: from H atoms
H2O’s partially negative end: from the O atom
Sodium attracts the water molecule’s oxygen atom while repelling the hydrogen atom.
Ion-Induced Dipole
Dipole forces caused by ionizing Ion-induced dipole attraction is a weak attraction that occurs when an ion approaches and causes a dipole to form in an atom or a nonpolar molecule by disrupting the electron configuration in the nonpolar species.
When an ion interacts with a nonpolar molecule, it produces an ion-induced dipole force, which is a weak attraction. Furthermore, when a fully charged ion approaches a nonpolar molecule, the electrons respond by forming a dipole, and the molecule becomes polarized.
An anion polarizes the molecule by repelling the electron cloud, whereas a cation polarizes the molecule by attracting the electron cloud.
For example:
NO3– (nitrate ion) and I2 iodine molecule
An anion is NO3–.
I2 is a molecule that is not polar.
The polarization of the iodine molecule occurs in the presence of a nitrate ion.
Ion-Dipole vs. Ion-Induced Dipole
Ion-Dipole | Ion-Induced Dipole |
Ion-Dipole are the types of intermolecular interactions | Ion-induced Dipole are also the types of intermolecular interactions |
ion Dipole Forces are electrostatic forces | Ion-induced Dipole are electrostatic forces |
The attractive forces between ionic species and polar molecules are known as ion dipole forces. | The attractive forces between ionic species and non-polar molecules are known as ion induced dipole forces. |
Ion dipole forces are stronger than hydrogen bonds | Ion induced dipole forces are also stronger than hydrogen bonds and dipole-dipole forces. |
Between ions (cations or anions) and polar molecules, ion-dipole forces form. | Between ions and non-polar molecules, ion- induced dipole forces form. |
The ion-dipole force is proportional to the ion charge. | Between a completely charged ion and a momentarily charged dipole, the ion-induced dipole interaction occurs. |
Conclusion
We conclude in this article that Ion-dipole forces and ion-induced dipole forces are intermolecular forces that occur between different chemical species such as cations, anions, and polar molecules. Polar molecules are dipole-dipole covalent complexes electrical charge separations. A polar molecule contains both a positively and negatively charged terminal in the same molecule. As a result, opposite-charged electrostatic attraction can exist between these terminals. Ion-dipole forces exist between ionic species and polar molecules, whereas Ion-induced dipole forces exist only between polar molecules.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out