Cuprous sulphate or cupric sulphate are two chemical compounds that might be referred to as copper sulphate (CuSO4). The preferred chemical described by the phrase ‘copper sulphate’ is, however, the latter. Copper(II) sulphate is the scientific term for CuSO4, although it’s also known as blue vitriol, Roman vitriol, copper vitriol, and bluestone.
Copper sulphate is most commonly found in its pentahydrate form, which has the chemical formula CuSO4.5H2O. The brilliant blue colour of this shape distinguishes it. It should be noted, however, that the anhydrous form of this salt is a white powder.The copper cation (Cu2+) and the sulphate anion form an ionic connection in the CuSO4 molecule (SO42-). The structure of a copper sulphate molecule is depicted in the diagram below.
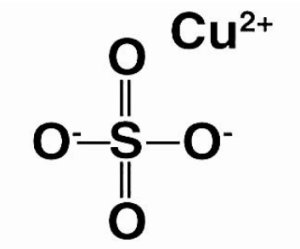
Copper sulfate can be made by heating metallic copper with hot and concentrated sulphuric acid, or by treating the oxides of copper with dilute sulphuric acid. It can be noted that the oxidation state exhibited by the copper atom in a CuSO4 molecule is +2.
Properties of CuSO4
These features of copper sulphate, both physically and chemically, are examined in greater detail in this subsection.
It should be noted that the characteristics of anhydrous CuSO4 and CuSO4.5H2O differ significantly, and these differences have been addressed in different sections.
Physical Characteristics
- The molar masses of copper sulphate in the anhydrous and pentahydrate forms are 159.609 grams per mole and 249.685 grams per mole, respectively, in the anhydrous form.
- Anhydrous CuSO4 has a powdery look and is grey-white in colour, whereas the pentahydrate is a vivid blue.
- The anhydrous and pentahydrate forms have densities of 3.6 grams per cubic centimetre and 2.286 grams per cubic centimetre, respectively.
- The boiling points of both hydrated and anhydrous copper sulphates are approximate due to the tendency for them to disintegrate when heated.
- A triclinic crystal structure is seen in anhydrous CuSO4, whereas an orthorhombic structure is found in CuSO4.5H2O crystals.
Chemical Characteristics
- The copper ions contained in copper sulphate combine with the chloride ions present in concentrated hydrochloric acid to generate tetrachlorocuprate, which is a toxic compound (II).
- It is possible to deduce the chemical equation for this reaction by using Cu2+ + 4Cl– = CuCl42-
- CuSO4 undergoes a breakdown reaction when heated to 650oC, resulting in the formation of cupric oxide (CuO) and SO3 (sulfur trioxide).
- Copper sulphate is extremely soluble in water, having solubility values of 1.055 molal and 1.502 molal at 10oC and 30oC, respectively, indicating that it is very soluble in water.
For example, the reaction between iron and copper sulphate, which is represented by the formula Fe + CuSO4 ——.>>> FeSO4 + Cu, is a classic example of a single displacement reaction in which one metal displaces another.
Uses of Copper Sulfate
Generally speaking, copper sulphate is included in the basic chemistry sets that are used as educational tools. There is a wide range of uses for the chemical compound CuSO4 in industry. Some of these applications are listed in the next section.
- This compound, CuSO4.5H2O, is utilised as a fungicide due to its ability to kill a variety of fungus when it is in its pentahydrate form.
- Benedict’s solution, as well as Fehling’s solution, which is used in the testing for reducing sugars, contain copper sulphate as a component.
- It is also used to analyse blood samples for disorders such as anaemia, among other things.
- KMnO4 (potassium permanganate) and CuSO4 (copper sulphate) are combined to generate an oxidant that can be employed in the conversion of 1o to 2o.
- Furthermore, it is employed as a dye fixative in the process of vegetable dyeing.
- Copper sulphate solutions in water can be utilised as resistive elements in liquid resistors, similar to the way that sodium chloride solutions are employed.
- Furthermore, it can be utilized as a decorative element, as it can bring colour to cement, ceramics, and other metals, among other things.
- Copper sulphate is also used to book binding glues in order to keep the printed paper from being eaten away by insects.
CONCLUSION
Copper sulphate is an inorganic salt that is highly soluble in water. Copper sulphate is a salt that is soluble in water. Copper sulphate is a compound that contains the copper ion, which has toxicological effects. In humans, copper is an important mineral, and the recommended dietary requirement for copper for adults has been established at 900 micrograms per day. Copper is also a common element found all throughout the world.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




