It is called a crystal lattice because it is made up of ions that are tightly packed together in a repeating pattern. The idea of crystal packing is based on the assumption that the ions are hard spheres. The simplest way to visualize such an array is to arrange one layer of spheres on top of another, and then arrange successive layers on top of that.
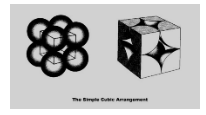
Simple cubic packing:
The simplest configuration is one in which the spheres in the base are stacked one on top of the other. The spheres from the subsequent layers of spheres are then placed directly on top of the spheres from the layer below. Simple cubic packing is the term used to describe this type of array.
The four other atoms in its own plane, as well as one atom above and one below, are all touched by each atom in this arrangement. Because each sphere is touched by six neighbouring spheres, it has a six-point coordinate system.
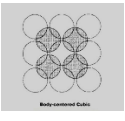
Body centered cubic:
One method of achieving a different packing arrangement is to place the second layer of spheres over the holes (or interstices) of the base layer. The third layer of spheres is placed on top of the holes created by the second layer. The addition of successive layers is done in the same manner. The term “body-centered cubic” refers to this type of array.
This is a more compact packing arrangement than the traditional cubic packing array. In this configuration, each sphere is impacted by four atoms above and four atoms below its plane, resulting in an eight-coordinate coordination number for each sphere.
Unit cell:
Known as a unit cell, this is the simplest possible arrangement of spheres that, when repeated, will reproduce the entire crystal structure in its entirety. The unit cells for the packing arrangements are depicted in the following diagram.
The ionic latice:
In most ionic compounds, the anions are significantly larger than the cations, and it is the anions that contribute to the formation of the crystal array. A small number of cations are found in the spaces between the anions.
Fundamental Concepts:
- Ions are presumed to be charged, incompressible, nonpolarizable spheres with no polarizable properties.
- Ions attempt to surround themselves with as many ions of opposite charge as possible while remaining as close as possible to one another. Ordinarily, in the packing arrangement, the cation is only large enough to allow the anions to surround it without coming into contact with one another.
- The cation to anion ratio of the compound must be proportional to its stoichiometry. For MgCl2, the lattice must consist of an array of chloride anions with only half as many magnesium ions as there are chloride anions.
It is determined by the relative sizes of the ions in an ionic compound what packing arrangement will be used by the compound. Consider the case of a lattice in which the anions are arranged in a cubic array. The diagram below depicts four spheres that represent some anions of a portion of a cubic layer layer. The anions beneath and above the plane are represented by the dashed circle. Interstitial space is represented by the shaded circle, which indicates the amount of space available for a cation to fit between the six anions. The cation has to be the same size as the shaded circle in order to be valid.
Conductivity of ionic solids:
Ionic solids do not contain any free electrons. In an ionic solid, any charged particles (including ions) can carry electric current; however, the ions are trapped in the lattice and cannot move away from their fixed positions as they do in a liquid crystal. Ionic compounds that are solid do not conduct electricity.
The charged ions are able to move around in the liquid state because of the fluid state. Ions moving in opposite directions: positive ions moving towards positive terminal, and negative ions moving towards negative terminal Consequently, the current is carried through the liquid, and the compound is capable of acting as an electrical conductor. Electricity does conduct through molten ionic compounds.
Melting point of ionic solids:
ionic crystal lattices are extremely strong due to the large number of simultaneous attractions between cations and anions that occur during the formation process. It is necessary to add large amounts of energy to the melting process of an ionic compound in order to completely break all of the ionic bonds present in the crystal structure. Example: The melting point of sodium chloride is approximately 800 degrees Celsius.
Conclusion:
ionic crystals are crystals made up of ions that are held together by electrostatic attraction A crystal lattice is a regular, geometric arrangement of ions that has a regular, symmetrical arrangement of ions. It is called a crystal lattice because it is made up of ions that are tightly packed together in a repeating pattern. The unit cell, which contains the simplest possible arrangement of spheres, will reproduce the entire crystal structure in its entirety if it is repeated many times.
Ions are presumed to be charged, incompressible, nonpolarizable spheres with no polarizable properties. Ions attempt to surround themselves with as many ions of opposite charge as possible while remaining as close as possible to one another. The cation to anion ratio of the compound must be proportional to its stoichiometry.
Ionic solids do not contain any free electrons. In an ionic solid, any charged particles (including ions) can carry electric current; however, the ions are trapped in the lattice and cannot move away from their fixed positions.
ionic crystal lattices are extremely strong due to the large number of simultaneous attractions between cations and anions that occur during the formation process.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out