Isotopes are elements with the same number of protons and electrons but a different number of neutrons. Stable isotopes, primordial isotopes, and radioactive isotopes are the three categories. We’ll learn more about isotopes in this article, including examples, types, and uses, as well as the difference between isobars and isotopes.
Isotopes
Chemical species with the same atomic number but different mass numbers are referred to as isotopes. The existence of a distinct number of neutrons in the elements causes the difference in mass number. Isotopes are chemical entities that have the same number of protons and electrons in their nucleus but a different number of neutrons. The isotopes of hydrogen, for example, are hydrogen-1, hydrogen-2, and hydrogen-3. Hydrogen-1 consists of one electron, one proton, and no neutrons; Hydrogen-2 consists of one electron, one proton, and one neutron; and Hydrogen 3 consists of one electron, one proton, and two neutrons. As a result, all three hydrogen isotopes have the same amount of electrons and protons, namely 1, but different numbers of neutrons, thus 0, 1, and 2.Calculating The Neutrons in An Element
Any element’s nucleus is made up of neutrons and protons. Since neutrons and protons both have a mass of one unit, the total number of neutrons and protons makes up the element’s mass number. As a result, if we know the mass number and the atomic number (because the atomic number equals the number of protons in the nucleus), the difference between the mass number and the atomic number can be used to calculate the number of neutrons present. Tritium, for example, has a mass number of 3 and an atomic number of 1, resulting in: The number of neutrons equals the mass number minus the atomic number. I.e. No.of Neutrons=Mass No-Atomic No. In tritium, the number of neutrons is 3 – 1 = 2. As a result, tritium has two more neutrons than protium.Representation of Isotopes
There are two ways to depict isotopes:- The element’s name is put first, followed by the hyphen and the mass number of the isotope in question. Protium, for example, is represented by Hydrogen-1, Deuterium by Hydrogen-2, and tritium by Hydrogen-3
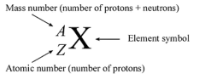
Types of Isotopes
Stable Isotopes
Stable isotopes are isotopes with extraordinarily long half-lives (a half-life is defined as the time it takes for a substance to decompose and reach a concentration or weight that is half, or 50 percent, of its initial concentration or weight). There are a few stable isotopes.- Carbon: Carbon-12, Carbon-13
- Oxygen: Oxygen-16, Oxygen-17, and Oxygen-18
Primordial Isotope
These are the isotopes that have primordial nuclei in their nucleus. The nuclides that have existed since the formation of our solar system are known as primordial nuclides. There are a total of 339 naturally occurring isotopes on the planet, with 286 of them being primordial in nature.Radioactive Isotopes
Certain isotopes have extremely short half-lives and decay fast, emitting radioactive waves. Radioactive isotopes are isotopes that are radioactive. The following are some radioactive isotopes:- Tritium is a kind of hydrogen
- Carbon: carbon-14
- Chlorine (Cl-36) is a chemical that is used in the production of chlorine
- Uranium is divided into two types: Uranium-235 and Uranium-238
Advantages of Isotopes
- Isotopes are particular elements with the same atomic number that have different properties. As a result, isotopes are utilized in elemental chemical analysis
- Since isotopes are easier to determine, they are frequently employed to measure the rate of reaction or the change in concentration of the reactants and products
- They’re also used in analytical techniques like mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




