Distillation
Because of the difference in boiling points between the two liquids, the underlying principle of distillation is that a mixture of liquids can be separated. The boiling point of a liquid is defined as the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the pressure of the surrounding atmosphere. This method is used to distinguish between volatile and non-volatile liquids. The configuration is shown in the following section.
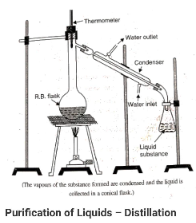
The mixture is placed in the RB flask and brought to a boil. Components that are more volatile, or those with a lower boiling point, evaporate more quickly and are collected in a separate container. A condenser is a device that is used to accelerate the process of condensation.
The separation of a mixture of chloroform and aniline, for example, can be accomplished through distillation. The boiling point of chloroform is 60 degrees Celsius, while the boiling point of aniline is 189 degrees Celsius. To separate a mixture of chloroform and aniline, distillation can be used as a separation method.
Fractional Distillation
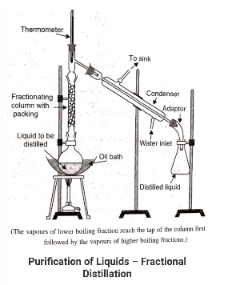
Fractional distillation is a type of distillation in which only a fraction of the liquid is distilled.
In situations where the difference between the boiling points of two different liquids is not significant, this method may be used. The presence of a fractionating column at the mouth of the RB is necessary because the vapors from such liquids may condense into one another.
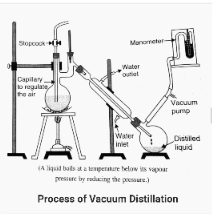
Vacuum Distillation
Due to the fact that the boiling point is dependent on the atmospheric pressure, liquids will boil at a temperature lower than their boiling points if they are distilled in an atmosphere with lower pressure than the one in which they were distilled. This is accomplished through the use of a vacuum pump. Because the atmospheric pressure is reduced, the liquids boil at a faster rate, resulting in a more rapid distillation process throughout the process.
Steam distillation
Steam Distillation is a type of distillation that uses steam to extract alcohol from water.
As in the previous variant, steam is passed into the flask containing the liquids to be separated before being separated itself. The underlying principle is that liquids will boil more quickly as a result of aqueous tension (water’s vapour pressure), which aids in the equalisation of the atmospheric pressure.
Total pressure is equal to the sum of the aqueous tension and the vapour pressure of the liquid components.
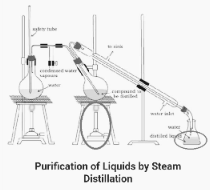
In the absence of aqueous tension, the process of boiling would have been allowed to continue until it reached the same pressure as the surrounding atmosphere. With the addition of steam, this process has been sped up considerably.
Differential Extraction
When dealing with immiscible liquids, which are liquids that do not mix together, this method is used. For example, oil and water are incompatible with one another.
The immiscible liquids are collected in a separating funnel and allowed to stand undisturbed for several hours. The liquids separate out according to their specific gravities after a period of time, with the heavier liquid at the bottom of the container. After that, they are gathered together.
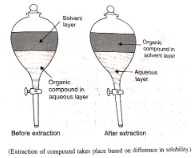
The solubilities of various substances in a liquid can also be used to separate substances from one another. Consider the case of phenol extraction: if it is necessary to extract phenol, it can be preferentially extracted by using NaOH solution as one of the liquids to be used.
Chromatography
It is an important separation technique that is used to separate constituent particles of a mixture of substances, to purify the constituents of a mixture of substances, and to check the purity of organic compounds, among other things. A mixture of substances is used in this technique, which is applied to a stationary phase (either solid or liquid). On the stationary phase, the mixture of gas or the pure solvent is allowed to move slowly in a controlled manner. In turn, the components of the mixture begin to separate from one another as a result of this separation.
Chromatography can be divided into two categories:
Adsorption Chromatography
Adsorption Chromatography is a type of chromatography that uses adsorption to separate the components of a mixture.
Partition Chromatography is a type of chromatography in which the partitions of the chromatograms are separated.
Adsorption Chromatography is a type of chromatography that uses adsorption to separate the components of a mixture.
It is based on the principle that different amounts of constituents are adsorbed on different types of adsorbents. The adsorbents that are most commonly used are silica gel or alumina. When a mobile phase is moved over a fixed phase, different constituents of the mixture are adsorbed at different distances from the fixed phase, depending on the constituent.
Adsorption Chromatography is further subdivided into the following categories:
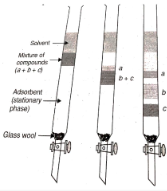
Column Chromatography
Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) is a type of chromatography in which the layers of a liquid are separated by a thin layer of air.
Chromatography on a column
An aqueous mixture is separated over a column of silica gel or alumina, which is packed in a glass column, in this procedure. The constituent with the greatest affinity for the fixed phase is adsorbed at the very top of the stack, and so on down the stack. It is then retrieved with the help of an eluent. After that, the solvent is removed in order to obtain the constituent.
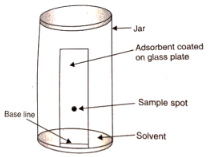
Thin-Layer Chromatography
Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) is a type of chromatography in which the layers of a liquid are separated by a thin layer of air.
Here, a sheet of alumina (0.2 mm thick) is used, over which a small spot of the mixture is placed and which is then kept in a suitable solvent until the reaction is complete. The solvent rises as a result of capillary action, and the constituents rise with the solvent as a result of their differential adsorption, resulting in the separation of the constituents from the solvent.
Conclusion
Because of the difference in boiling points between the two liquids, the underlying principle of distillation is that a mixture of liquids can be separated. The boiling point of a liquid is defined as the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the pressure of the surrounding atmosphere.Fractional distillation is a type of distillation in which only a fraction of the liquid is distilled.Due to the fact that the boiling point is dependent on the atmospheric pressure, liquids will boil at a temperature lower than their boiling points if they are distilled in an atmosphere with lower pressure than the one in which they were distilled.Steam Distillation is a type of distillation that uses steam to extract alcohol from water.Adsorption Chromatography is a type of chromatography that uses adsorption to separate the components of a mixture.Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) is a type of chromatography in which the layers of a liquid are separated by a thin layer of air.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




