Resonance structures are a collection of two or more Lewis structures that together represent the electronic bonding of a single polyatomic species, including fractional bonds and charges. Benzene is a highly common aromatic hydrocarbon in organic chemistry. C6H6 is the chemical formula for it. The benzene molecule’s cyclic structure is composed of alternating single and double bonds between nearby carbon atoms. Each carbon atom is connected covalently to a hydrogen atom. Below are two probable benzene resonance configurations.
Resonance is a term used in the Valence Bond Theory to describe how electrons delocalised within molecules. It compares and contrasts two or more Lewis structures that could be used to represent a given molecule. When a Lewis structure for a single molecule is insufficient to completely represent the bonding between surrounding atoms in comparison to empirical data on the actual bond lengths between those atoms, resonance structures are used. A resonance hybrid is defined as the total of legitimate resonance structures, which indicates the overall delocalization of electrons within the molecule. A molecule with multiple resonance structures is more stable than one with fewer resonance structures. Certain types of resonance structures are more advantageous than others.
Electrons do not have a fixed position in atoms, compounds, or molecules, but they do have probabilities of being found in certain regions (orbitals). Resonance forms depict places with a higher probability of occurrence (electron densities). This is analogous to holding your hat in either your right or left hand. When two or more possibilities exist, the term resonance is used.
History of resonance–
The concept was introduced in 1899 by Johannes Thiele in his “Partial Valence Hypothesis” to explain benzene’s exceptional stability, which contradicted August Kekulé’s 1865 structure with alternating single and double bonds. In contrast to alkenes, benzene undergoes substitution reactions rather than addition reactions. He hypothesised that benzene’s carbon-carbon bond is a hybrid of a single and double bond. Additionally, the resonance hypothesis helped to explain the existence of isomers of benzene derivatives. For instance, Kekulé’s structure predicts four dibromobenzene isomers, including two ortho isomers in which the brominated carbon atoms are connected through a single or double bond. In reality, there are only three dibromobenzene isomers and only one is ortho, consistent with the concept of a single type of carbon-carbon bond halfway between a single and a double bond.
Nitrobenzene’s resonance structure-
The presence of an electron-withdrawing group close to the phenyl ring of nitrobenzene results in the aromatic ring of nitrobenzene having a lower electron density than that of benzene, as demonstrated by the nitrobenzene resonance structures.
- Nitrobenzene’s phenyl ring is less nucleophilic than that of benzene.
- In resonance structures, the ortho and para locations are positive.
- As a result, in an electrophilic aromatic substitution process, the electrophile would react at the meta position rather than these locations.
- When a double bond is conjugated to a phenyl ring, the electrophilic aromatic substitution product is referred to as the meta substituted product.
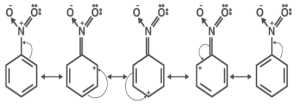
Nitrobenzene’s resonance structure reveals a double bond between the nitrogen atom and the carbon atom and a single link between the nitrogen atom and the oxygen atom. The double bond between the nitrogen and carbon atoms enables the electron density to be delocalized across both atoms. This delocalization of the electron density results in the nitrogen atom having a higher electron density and the carbon atom having a lower electron density. This enhanced electron density on the nitrogen atom is what makes it more oxidizable.
Stability Estimation Rules for Resonance Structures-
- Resonance structures with complete valence shells on all atoms are usually more stable. This signifies that the majority of atoms have a complete octet.
- Structures with fewer formal charges are more stable.
- Stable structures will always have a negative charge on the more electronegative atom. The placement of a negative charge distinguishes the two resonance structures.
- Structures having a positive charge on the least electronegative atom are more stable.
- Structures with the least amount of formal charge separation value are more stable. The two structures below are identical save for the relative placements of the positive and negative charges.
- Equivalent resonance types are identical in terms of stability.
CONCLUSION-
As resonance structures enable electrons to extend their wavelengths and thus lower their energy, they act as a stabilising force in molecules. This is why, in the absence of resonance, benzene (C6H6) has a lower heat of production than organic chemists would predict.
Nitrobenzene is used in the pharmaceutical sector to manufacture the painkiller acetaminophen, or paracetamol. Nitrobenzene is also used to hide disagreeable scents in shoe and floor polishes, leather dressings, and paint solvents.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




