Resonance is an extension of the idea that the bonding in a chemical species can be characterized by a Lewis structure, according to valence bond theory. A single Lewis structure, consisting of atoms obeying the octet rule, possibly bearing formal charges, and connected by bonds of positive integer order, is sufficient for describing chemical bonding and rationalizing experimentally determined molecular properties such as bond lengths, angles, and dipole moment for many chemical species. In other circumstances, however, more than one Lewis structure can be drawn, and experimental properties contradict any single structure. In order to deal with situations like this, various contributing structures are averaged out, and the molecule is said to be represented by a resonance hybrid.
The resonance hybrid portrays the actual molecule as an “average” of the contributing structures, with bond lengths and partial charges intermediate to those expected for the contributors’ distinct Lewis structures if they existed as “real” chemical entities. Only the formal assignment of electrons to the atoms differs between the contributing structures, not the actual physically and chemically important electron or spin density. While the formal bond ordering and formal charge assignments of contributing structures may change, all contributing structures must have the same number of valence electrons and the same spin multiplicity.
Resonance
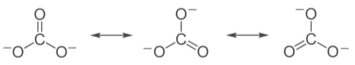
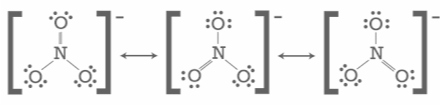
Resonance, also known as mesomerism, is a means of defining bonding in specific molecules or ions in valence bond theory by combining many contributing structures (or forms, also known as canonical structures or resonance structures) into the resonance hybrid (or hybrid structure). It’s especially useful for explaining delocalized electrons within molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding can’t be stated by a single Lewis structure.
Even while no single Lewis structure contains two N–O bonds with the same formal bond order, the two N–O bond lengths are equal in the NO2–nitrite anion. Its measured structure, on the other hand, is consistent with a description as a resonance hybrid of the two major contributing structures shown above: it has two equal N–O bonds of 125 pm, which are halfway between a typical N–O single bond (145 pm in hydroxylamine, H2N–OH) and a N–O double bond (115 pm in nitronium ion, [O=N=O]+). Each N–O bond is an average of a formal single and formal double bond, resulting in a true bond order of 1.5, according to the contributing structures. The Lewis description of bonding in NO2– is reconciled with the experimental observation that the anion possesses equivalent N–O bonds as a result of this averaging.
Delocalized Electrons
Delocalized electrons are electrons that are not associated with a single atom or a covalent link in a molecule, ion, or solid metal.
The delocalization of six electrons over the C6 ring in the simple aromatic ring of benzene is commonly visually illustrated by a circle. One sign that the electrons are delocalized is that the six C-C bonds are equidistant; if the structure had isolated double bonds alternating with discrete single bonds, the bond would have alternating greater and shorter lengths. Delocalization of atoms of benzene is represented by resonance structures in valence bond theory.
Electron delocalization reduces charge density, boosting stability. More acidic is an acid with a conjugate base that has delocalized electrons due to resonance than an acid with localized electrons.
Because it spreads energy over a greater region rather than keeping it confined to a limited area, charge delocalization is a stabilizing effect. Because electrons are charges, the presence of delocalized electrons adds stability to a system as compared to a system with localized electrons.
Polyatomic atoms-
A polyatomic ion, also known to be a molecular ion, is a covalently bound set of two or more atoms, or a metal complex, that behaves as a single unit and has a net charge greater than zero. This chemical species is an ion, as opposed to the molecule, which has a zero net charge.
To understand the nomenclature of polyatomic anions, generally there are two “rules” to follow. When prefix bi is added to a name, it adds a hydrogen to the ion’s formula and increases its charge by one, the latter being due to +1 charge of hydrogen ion. In the place of bi- prefix, the word hydrogen might be used instead.
The second rule is based on the oxidation status of the ion’s “main” atom, which is often (but not always) precisely proportional to the amount of oxygen atoms in the ion.
Conclusion
Generally, molecules with more resonance structures are more stable than those with less resonance structures, and some resonance structures contribute more to a molecule’s stability than others – formal charges can help determine this. When a single Lewis structure cannot properly describe the bonding, resonance structures are used; a resonance hybrid is defined as a combination of possible resonance structures that represents the overall delocalization of electrons inside the molecule.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




