Any liquid or frozen water that develops in the atmosphere and falls back to the Earth is called precipitation (another form of rain). The precipitate forming in the atmosphere can be formed and come to the Earth in many states or forms. The most visible precipitate forms are in liquid and solid-state; for example, rain and hail. Along with evaporation and condensation, one of the three major parts of the global water cycle is precipitation.
What is Rain?
Precipitation forms in the clouds when the water vapors start to condense and form bigger droplets of water. When the drops get heavy enough for the cloud to hold, it falls in the form of rain.
Now the form of the precipitation differs because of different altitudes where the clouds are present. If a cloud is present at a high altitude where the temperature is relatively low, the precipitate or the water droplets freeze and form ice.
Cloud Formation
The most necessary step for forming clouds is the formation of water vapors. The quantity of water vapor available in the atmosphere continuously varies due to meteorological factors and depends on the atmospheric temperature. Clouds form through evaporation and then are followed by the condensation of water vapors.
We know evaporation is the transition phase of water from the liquid to the gaseous state. The vapors we see during water boiling are relatively the same as evaporation. Likewise, in the boiling process, by the sun’s radiation, the water bodies like rivers, ponds, oceans, etc, get heated up and release water vapor. Eventually, water vapor gets suspended in the air, regains considerable free movements, or scientifically possesses kinetic energy.
The water droplets are much lighter because of their low density than the cold droplets, so the vapors tend to rise upwards than the air surrounding them. The warmer the water is, the particles possess more thermal energy and have much higher tendencies to escape into the air.
The air parcel cools down as the surrounding air cools below its dew point. Then those tiny parcels of water droplets get combined with smoke and dust, thus forming small masses of visible clouds.
Water Cycle
The hydrological cycle is the cycle that involves the continuous circulation of the water present in the Earth to the atmospheric system. Out of the many processes involved in the water cycle, the most important are evaporation, transpiration, condensation, and runoff. The amount of water needed in the process of this cycle remains essentially constant.
Well, the process consists of a total of 7 steps; Evaporation, the water cycle, begins with evaporation. The process where the surface water turns into water vapor due to the sun’s radiation.
Condensation is when the water vapors change their form due to my drop off the atmospheric pressure and temperature.
Sublimation, other than evaporation, also provides water vapors in the air. This phenomenon happens when the temperature is low, or pressure is high. Precipitation is the clouds (condensed water vapors) that pour down on Earth as rain due to the wind or temperature change.
Transpiration is similar to evaporation, where the liquid form of water is turned into vapors by the plants. The plant roots absorb the water and lead it to the leaves, where it is used in the form of photosynthesis.
When the water pours down (in any form), it leads to runoff.
Infiltration is the same as transpiration, where the water which is not washed away by runoff is absorbed by the plants and gets into the soil.
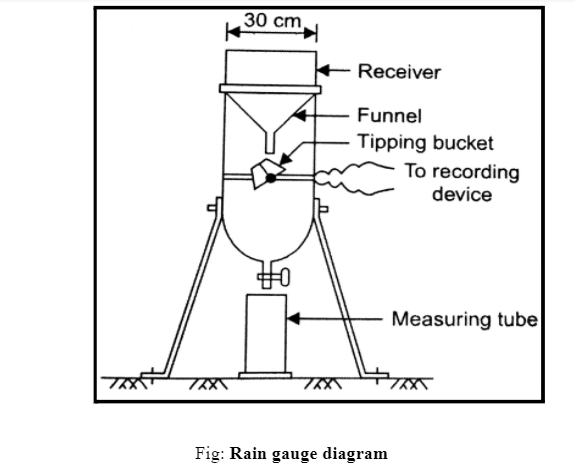
Rain Gauge
The Symon’s rain gauge has been adopted by The Indian Meteorological Department. The rain gauge diagram is made of a glass bottle, and a funnel with a brass rim is put in a metallic cylinder such that the top of the cylinder is 30.5 cm above. The rainwater is collected into the glass bottle through the funnel, the collected water is measured with the help of a standard measuring glass jar supplied with the gauge. The unit of measurement of the jar is in millimeters.
In the case of a digital gauge, it’s just as simple as reading the measurements shown on display, but for an analog rain gauge, taking the readings is quite different from the digital one. On the gauge side, we will see markings that indicate the amount of rain collected. With rainfall, the tube will fill up.
The concept of meniscus comes here; the meniscus is a slight curve on the surface of the collected rainwater, which is caused when the liquid comes in contact with the sides of the tube. To take the readings, read the measurements closest to the lowest point at the base of that curved surface ( meniscus ), then we will have our readings. The typical rain gauge diagram schematic consists of concrete block sizes of 600mm×600mm×600mm.
Conclusion
Most of the Earth’s surface is covered with water – and most of it is the water we can’t drink. Approximately 97 percent of Earth’s water is salty seawater, which is unfit to consume or use by most land-dwelling plants and animals. So this is where the necessity of rain comes; precipitation in the form of rainfall and snow is crucial for living life on Earth.
Not only for the life present on Earth, but rainfall also plays a major role in balancing the temperature on the surface of the Earth. Also a great help in farming where water supply from other water bodies is nearly impossible, rainfall provides the water needed for cultivation.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




