Introduction:
In electrical engineering, Joule’s law is a mathematical explanation of how quickly resistance in a circuit converts electrical energy to heat energy.
In 1840, English physicist James Prescott Joule established that the amount of heat generated per second in a wire carrying a current is proportional to the electrical resistance of the wire and the square of the current. He calculated that the heat emitted every second equals the absorbed electric power, also known as power loss.
Joule’s law of heating equation:
The heat produced by the current flow in an electric wire is measured in Joules.
The Joule’s law of heating expression is as follows:

Where, Q denotes the amount of heat,
I the amount of electric current,
R the amount of electric resistance in the conductor,
and t is the amount of time.
The amount of heat generated is proportional to the electrical resistance of the wire when the current in the circuit and the flow of current remain constant.
When the electrical resistance and current supply remain constant, the amount of heat generated in a current-carrying conductor is proportional to the square of the current flow through the circuit.
When the resistance and current flow are held constant, the amount of heat produced by the current flow is proportional to the flow time.
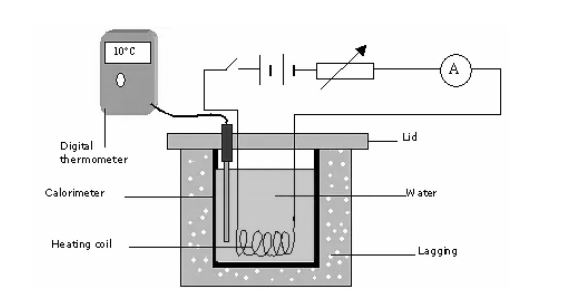
Joule’s Second law:
According to Joule’s second law, the internal energy of an ideal gas is independent of its volume and pressure and only depends on its temperature.
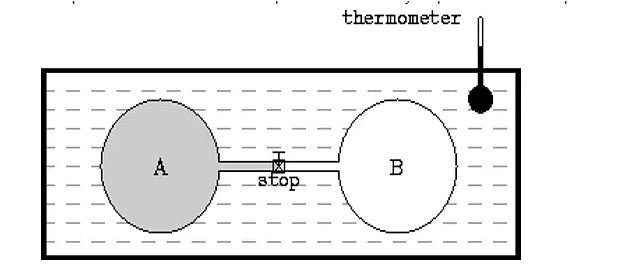
αT = 1 for an ideal gas defined by appropriate microscopic postulates, implying that the temperature change of such an ideal gas during a Joule–Thomson expansion is zero.
According to this theoretical result, for such an ideal gas:
The internal energy of a perfect gas is solely determined by its temperature (not pressure or volume).
In his experiments, Joule discovered this rule for real gases, which is known as Joule’s second law.
Application:
Electric Heating System.
Electric current’s heating effect is used in some electrical appliances such as the electric iron, electric toaster, and electric heater. Nichrome (a nickel-chromium alloy) is used as a heating element in many electrical devices. This is because of the following reasons:
- Nichrome has a high degree of specific resistance.
- Nichrome has a very high melting point.
- Nichrome is an oxidation-resistant metal.
Wire Fuse.
Fuse wire is a lead-tin alloy with a lead content of 37% and a tin content of 63%. The fuse wire is always connected in series in electric circuits. The fuse wire melts when a significant amount of electric current passes through it due to its high resistance and low melting point, opening the circuit and preventing any damage to the electrical devices.
The light bulb.
A lot of heat is generated because the filament of an electric bulb has a high resistance to the flow of electric current. This filament produces light when heated to incandescence. With a melting point of 3380°C, tungsten is the most commonly used filament. The filament of an electric bulb is encased in a glass that contains a low-pressure inert gas.
Important points:
- Joule’s law is a mathematical explanation of how quickly resistance in a circuit converts electrical energy to heat energy.
- James Prescott Joule calculated that the heat emitted every second is equal to the absorbed electric power, or power loss.
- The relationship between heat produced by passing an electric current through a conductor is demonstrated by the joule’s first law Q = I2 R t .
- The mechanical equivalent of heat is the number of units of work that must be performed on a system in order to produce a unit quantity of heat.
- The mechanical equivalent of heat is determined by the amount of work done on the system and the amount of heat produced by it.
- According to Joule’s second law, the internal energy of an ideal gas is independent of its volume and pressure and only depends on its temperature. αT = 1 for an ideal gas defined by appropriate microscopic postulates, implying that the temperature change of such an ideal gas during a Joule–Thomson expansion is zero.
Conclusion:
Excess heat is generated when an electrical current is passed through a conductor due to the resistance caused by the electrons in the conductor to the flowing current. The effort expended in overcoming this resistance to current generates heat in that conductor. The electrical heating effect of a current is the most commonly and widely applied and used effect in our daily lives. Electrical irons, kettles, toasters, and electric heaters, for example, are widely used as alternatives to traditional methods of cooking and laundry. This same effect is widely used in electrical bulbs, which are alternatives to traditional incandescent lamps. Over time, these devices have modernised and revolutionised the new sustainable world.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




