INTRODUCTION
Histones are chromosome-specific proteins. They aid in the packing and organization of DNA helix in the nucleus’ chromatin fiber. They also have a role in regulating gene expression.
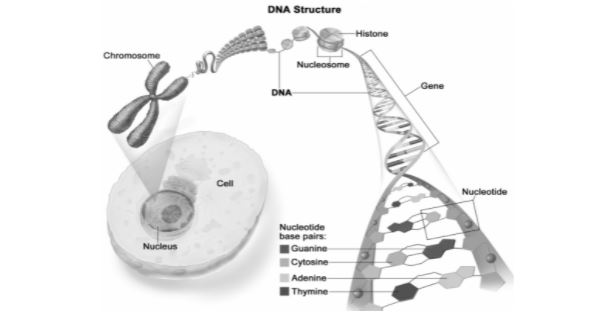
DNA is highly condensed in eukaryotes, and it is wrapped around histones to form chromatin thread, which then condenses further to form chromosomes. Histones give chromosomes a structural framework that allows them to fit more compactly inside the nucleus.
Structure
There are mainly 5 types of histones namely, H1, H2A, H2B, H3 and H4.
- A Nucleosome is formed by wrapping a DNA molecule twice around a Histone Octamer. In collaboration with H1 histones, six nucleosomes are formed into a solenoid. The solenoids are coiled onto a Scaffold, which is coiled again to form the chromosomal matrix.
- The four histones that make up the core are structurally identical and highly conserved.
- Because of the phosphate groups, DNA is negatively charged, and it is wrapped around the center of a positively charged histone octamer. The nucleosome is the structure created by this interaction.
- The H1 histone serves as a linker. It binds to the nucleosome, which is where DNA enters and exits the cell.
- The nucleosome is a chromatin repeating unit that contains roughly 200bp of DNA.
- Histones’ basic character is linked to their water solubility.
- Histones interact with DNA in a variety of ways, including hydrogen bonds, salt bridges, helix-dipoles, and non-polar interactions.
- Active genes are less related with histones, whereas inactive genes are heavily associated with histones.
- Histones that are replication-dependent are expressed during the S phase of the cell cycle, while histones that are replication-independent are expressed throughout the cell cycle.
- Histone proteins undergo post-translational changes like as methylation, acetylation, phosphorylation, and ADP-ribosylation, among other things.
- Histones have been conserved throughout evolution because any alteration in histones might be harmful.
Functions
Histone is involved in the organization and packaging of DNA within the nucleus. They also appear to influence gene expression.
- They aid in the chromosomal compacting of DNA strands. Histones are the building blocks around which DNA is bound.
- Post-translational changes are seen in histones. It controls the interaction of DNA with nuclear proteins. It controls gene expression, mitotic condensation, spermatogenesis, and DNA repair, among other things.
- Histone alterations protect against DNA damage and the sun’s UV rays.
- DNA repair is aided by it.
Charge of a Histone
Histones are simple proteins with positive charges that allow them to bind to negatively charged DNA. Some histones serve as spools around which the thread-like DNA can wrap.
Chromatin appears like beads on a string under the microscope in its expanded state. Nucleosomes are a type of bead.
Histone Modification
Histone modifications control the physical features of chromatin and their related transcriptional state either directly (e.g., acetyl groups repel negatively charged DNA to establish open chromatin conformation) or indirectly (through protein adaptors called effectors).
Effector proteins bind to certain epigenetic markers and subsequently mobilise molecular machinery to alter chromatin shape. These epigenetic readers predict the functional result of histone changes by translating the histone code into action.
Histone Methylation
Histone methylation is the transfer of methyl groups to the amino acids of histone proteins, forming nucleosomes around which the DNA double helix coils to form chromosomes. Histone methylation can boost or decrease gene transcription depending on which amino acids in histones are methylated and how many methyl groups are added.
Methylation events reduce the chemical interaction between histone tails and DNA, allowing DNA to uncoil from nucleosomes for transcription factor proteins and RNA polymerase to access the DNA.
What is Nucleoplasmin?
Nucleoplasmin was the first protein identified as a molecular chaperone. The study of nucleoplasmin has resulted in improvements in two areas of cell biology.
To begin, the nucleosome assembly mechanism in Xenopus oocytes and eggs has been elucidated, and it is the only detailed assembly pathway known. The principal chaperoning activity of nucleoplasmin is generally nucleosome assembly.
Second, nucleoplasmin was employed to investigate protein transport into the nucleus, revealing a two-step transport mechanism, as well as a selective entry mechanism for nuclear proteins.
CONCLUSION
Histone is a family of simple alkaline proteins found in cell nuclei that create nucleoproteins when ionically coupled with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). A nucleosome is a genetic material unit in which a histone molecule is linked to a segment of the DNA strand. Changes in these units are thought to be linked to changes in the physical state and function of chromatin during cell division and the transcription of the genetic code. Albrecht Kossel discovered histones in avian red blood cell nuclei about 1884. Histones are water-soluble and contain a lot of basic amino acids, including lysine and arginine. The thymus and pancreas have a lot of them.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




