Introduction
Birds and mammals possess a closed circulatory system with a network of blood vessels to take the blood to and fro from the heart. It is also responsible for the excretion of harmful components like CO2 out of our bodies. The body fluids and circulation deal with how the cardiac system supports double circulation, while the fishes and most reptiles have single circulation.
How is double circulation evolutionary beneficial? Where does our natural pacemaker reside in our heart? What is the significance of the lub-dub sounds, and what are some common human blood circulatory system disorders? We’ll look at all these answers and many more in the following sections.
Body Fluids and Circulation: Classification
Vascular Connective Tissues: Blood and Lymph
|
Blood |
Lymph/Tissue Fluid/Interstitial Fluid |
|
It forms the blood circulatory system |
It forms the Lymphatic system |
|
It comprises plasma and formed elements |
It comprises plasma with formed elements (erythrocytes absent) |
|
Red |
Colourless |
|
Soluble proteins in a large amount |
The lower amount of soluble protein |
Blood Circulatory System
Blood: Components
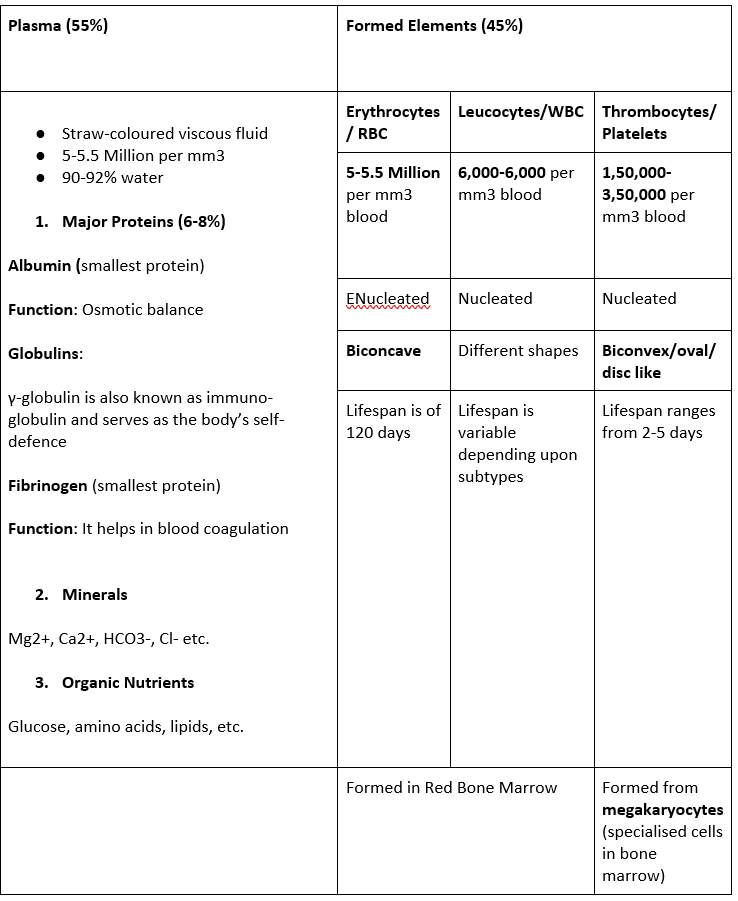
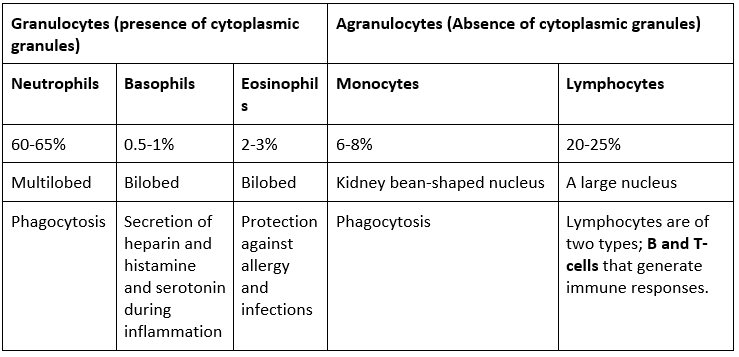
Leucocytes
Blood Grouping
In humans, two types of blood grouping are common: ABO and Rh Grouping.
- ABO Blood Grouping
The RBC with A antigen determines A blood group, with B antigen is the B blood group while with both antigens, AB blood group.
- Rh Grouping
Those with Rh antigen on the RBC surface are Rh-positive, while those without it are Rh-negative.
Blood Transfusion
Blood transfusion should be performed after checking the ABO and Rh compatibility of the donor’s blood group with the receipt. Blood group incompatibility can prove fatal and will result in blood clotting.
| Blood Group | Antibodies |
| A | anti-B |
| B | anti-A |
| AB | nil |
| O | anti-A, B |
Rh-Incompatibility
- When the mother is Rh-ve, and the foetus is Rh+ve, the foetal blood may mix during delivery with the mother’s blood. It will result in the generation of antibodies against the foetal RBCs
- In subsequent pregnancies, it will be fatal for the Rh+ve baby (erythroblastosis foetalis)
- You can prevent it by administering anti-Rh antibodies immediately after the first delivery
Blood Coagulation
- Platelets and localised cells from the injury site release some clotting factors and activate the clotting process
- Prothrombin from plasma gets activated by thrombokinase to form thrombin
- Thrombin acts on the Pro fibrinogen in plasma to form fibrinogen
Double Circulation
- Impure blood from the body reaches the right ventricles and is sent to the lungs for oxygenation via the pulmonary artery
- Lungs send oxygenated blood to the left ventricles to the body via the aorta
- Since blood passes twice through the heart before its supply to organs, it doubles circulation
Cardiac Cycle
Duration: 0.8 sec
Joint Diastole
- Tricuspid and Bicuspid valves open
- The heart receives blood from pulmonary veins and the Vena cava
Atrial Systole
- SA- node generates action potential and atria contract
- Blood flow to ventricles increases by 30%
Ventricular Systole
- Close tricuspid and bicuspid valves with lub sound
- Semilunar valves open
Ventricular Diastole
- Ventricles relax
- Close semilunar valves with dub sound.
- Stroke volume: each ventricle pumps 70 mL
- Cardiac output: Stroke Volume X Heart Rate
Electrocardiograph
Graphical representation of cardiac activity during:
Blood Circulatory System Disorders
-
Hypertension
Blood pressure higher than 120/80 mm Hg
-
Coronary Artery Disease/ Atherosclerosis
Deposition of Calcium, fat, fibrous tissue and cholesterol in the walls of blood vessels, making its lumen narrower
-
Angina Pectoris
Acute chest pain caused by low supply of oxygen to the heart is common in middle-aged and elderly
-
Congestive Heart Failure
The heart fails to pump out blood effectively, and lung congestion is the primary symptom
Conclusion
The human body is composed mainly of fluids that are circulated throughout the body and its organs. The human circulatory system comprises a muscular heart, blood and blood vessels. The most responsible bodily fluid is human blood, containing plasma and formed elements (RBC, WBC and platelets). Though responsible for bodily functions, these fluids may result in disorders if there is a lack of circulation.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




