A sphygmomanometer, often known as a BP (Blood Pressure) Monitor, is a device that measures blood pressure in the arteries. It’s made up of an inflatable rubber cuff that wraps over your arm. A measuring gadget is used to indicate the cuff’s pressure. The cuff is inflated by a bulb, and the pressure is released by a valve. Sphygmomanometer is a combination of the Greek word “Sphygmos” (pulse) and the scientific term “Manometer” (pressure metre).
Blood Pressure:
The human heart is a muscle pump that pumps blood around the body. It pushes blood through blood vessels called arteries when it contracts (heartbeat).
Blood pressure is the pushing force imposed on artery walls by blood flow. The pressure is determined by the heart’s rhythm and power of contraction (heartbeat), as well as the diameter and elasticity of the artery walls.
The heart and blood arteries are put under a lot of strain by high blood pressure. Blood pressure must be monitored and, if required, lowered to avoid harm to the blood vessels and heart.
Sphygmomanometer Types
Sphygmomanometers are used to measure blood pressure in humans. There are three varieties of sphygmomanometers:
1.Mercury Sphygmomanometer:
Among all other types of equipment, the mercury sphygmomanometer is the “gold standard,” reflecting the conventional and time-tested way of measuring blood pressure.
An inflatable bladder and a mercury column make up the device. Different mercury levels in the column are caused by different pressures. It is not essential to recalibrate the column once it has been manufactured to their exact specifications.
Aneroid Sphygmomanometer:
The aneroid sphygmomanometer is a device consisting of a spring mechanism and a metal membrane that transforms the signals from the cuff and operates a needle in the gauge. It stands on the stans or walls. This device can be easily moved from one location to another because there is no liquid present.
The results are poor since these devices require calibration checks. The needle must be kept at zero before use. Calibrations are carried out on a regular basis to ensure that the results are accurate.
Digital Sphygmomanometer:
When you want to test your blood pressure at home without any preparations, including diastolic and systolic blood pressure, the digital sphygmomanometer comes in useful. Simply insert the rubber node into the monitor’s hole and wrap the cuff over your upper arm; when you press the button, it will use oscillometric detection to calculate your blood pressure and heart rate.
According to WHO rules, the monitor features an audio device that will alert you of the results. The best part about having such a device is that it is portable and convenient, can be charged, and allows us to monitor average results.
Sphygmomanometer Labelled Diagram
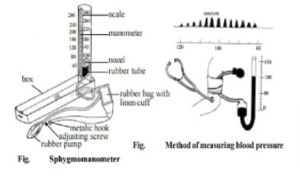
Sphygmomanometer Parts and Functions
Bladder: An inflatable bag that, when filled, squeezes the arms, obstructing the arteries.
- Cuff: The cuff is a rubber cuff that wraps over the upper arm and inflates. The pressure in the cuff is measured with a pressure metre.
- Valve: The deflation valve is necessary for accurate measurement since it allows for regulated deflation of the cuff. A check valve at the end of the line stops air from escaping.
- Bulb: The blood pressure inside the cuff is inflated using a small, handheld air pump.
- Manometer: The portion of a sphygmomanometer that measures blood pressure in millimetres of mercury is called the manometer (mmHg). This aneroid gauge, which features a watch-like movement, monitors the air pressure provided to the cuff. When air is pushed into the gauge, a series of diaphragms (copper or beryllium) expand, and gears translate the diaphragms’ linear motion into movement of the needle on a dial calibrated in millimetres of mercury.
Conclusion
The article contains all of the critical information that a student needs to know about the Sphygmomanometer at a basic level, such as its types, uses, and parts, among other things. This is a vital piece of equipment for taking blood pressure readings.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out



