The visible light spectrum, like all other types of light, is absorbed and released in the form of tiny packets of energy known as photons, which are tiny packets of energy. These photons exhibit both the characteristics of a wave and the characteristics of a particle.
As a result, this type of phenomenon is referred to as wave-particle duality, and the study of light is referred to as Optics in the field of physics.
Optics is a simple science that describes the behaviour of visible light, infrared light, and ultraviolet light in a straightforward manner. Imaging is accomplished with the assistance of a technology known as an image producing optical system.
Geometrical optics is a term that refers to ray optics. It is a branch of science that describes light transmission in terms of rays, as opposed to other branches of science.
Light And Its Optical Properties
Luminescence is a type of energy that takes the form of an electromagnetic wave and may be found practically everywhere in our environment. The visible light spectrum has wavelengths ranging from 400 to 700 nanometres in length. The Sun is the major source of light for plants, which they use to generate their own energy by photosynthesis.
While the term “light” refers to visible light, it can also refer to electromagnetic radiation of various wavelengths in physics, whether or not it is visible to the naked eye. As a result, gamma rays, microwaves, X-rays, and radio waves are all considered to be kinds of light in this context.
Light travels at the speed of light.
The speed of light refers to the velocity at which light travels across empty space at a constant distance. When compared to a vacuum, light travels 30 percent slower in water than it does in air, for example.
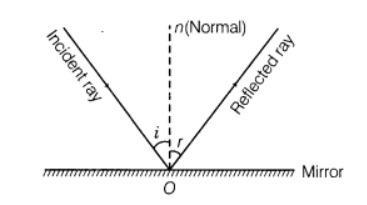
The Rules of Reflection
The following are the two laws of reflection:
(i) ∠I = ∠r, we can say that the incidence angle is equal to the reflection angle.
(ii) At the point of incidence, the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the reflecting surface are all in the same plane as the normal to the reflecting surface.
Mirror Formula
The mirror formula is a relationship between the focal length of the mirror and the distances between objects and their images in regard to the mirror’s reflection.
1 ⁄ 𝑣−1 ⁄ 𝑢= 1 ⁄ 𝑓
Where f denotes focal length, u denotes object distance from mirror, and v denotes image distance from mirror.
Refraction
Refraction is the bending of light that occurs when it passes through one medium and into another. Various technologies, such as microscopes, magnifying lenses, corrective lenses, and so on, make use of this feature of refraction to function properly. When light is transmitted through a medium, polarisation of electrons occurs, which in turn causes the speed of light to be reduced, resulting in the light’s direction being changed as a result.
Lens Makers Formula
It is the relationship between a lens’s focal length and the refractive index of its material and the curvature radius of its two surfaces that constitutes the lens maker’s formula. Glass with a specific refractive index is used by lens manufacturers to create lenses of specific powers using glass with a specific refractive index
1 ⁄ 𝑓= 𝜇−1 × 1 ⁄ 𝑅1− 1 ⁄𝑅2
Where f is the focal length, is the refractive index, and R1 and R2 are the radius of curvature of the two surfaces, respectively.
Dispersion
It is a characteristic of light in which white light divides into its constituent colours as it passes through it. The shape of a prism can be used to demonstrate dispersion.
Diffraction and interference are two further properties of light that can be observed. So, what do you notice when you step outside and take in the breathtaking scenery? When light is reflected, it can be diffused, refracted, internally reflected, or diffracted, among other things.
Applications of Optics
Optical properties are used in a variety of physics-related applications.
- A lens (convex or concave) is used to create an image of an object, and the refraction phenomenon is used to do this.
- Geometrical optics is a branch of optics that analyses the formation of pictures in optical systems.
- Medical applications include the optical diagnosis of the human body’s secrets, which is applied in the field of optometry.
- It is employed in the treatment and surgical procedures involving human tissues.
CONCLUSION
Reflection is something that can be seen if you gaze into a mirror or stare at sunlight reflecting off a lake with your eyes closed. Illustration of the law of reflection, which also demonstrates how the angles are measured relative to the perpendicular to the surface at the point where the light ray contacts the surface, may be found in For the most part, the law of reflection is straightforward: the angle of reflection must equal the angle of incidence. In a mirror, it looks like our image is actually behind the mirror since we are seeing the light coming from a direction indicated by the law of reflection when we look in the mirror. When we stand back from the mirror, our image appears to be exactly the same distance behind us as it does when we stand forward of the mirror.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




