Aristotle was the first to propose that a body must be propelled by an external force. He neglected to consider that an opposing frictional force acts on the body to counteract the external force, resulting in a net force of zero on the body.Inertia is the basic property of all bodies that prevents them from changing their state of rest or uniform motion along a straight line on their own.Although the principle of inertia is the fundamental assumption of classical mechanics, it is not intuitively obvious to the untrained eye. Objects that are not pushed tend to come to rest in Aristotelian mechanics and in everyday experience.
What is Law of inertia
The Law of Inertia, also known as Newton’s first law, states that if a body is at rest or moving in a straight line at a constant speed, it will remain at rest or moving in a straight line at a constant speed until acted on by a force. Galileo Galilei proposed the law of inertia for horizontal motion on Earth, and René Descartes later generalised it.Prior to Galileo, it was thought that all horizontal motion required a direct cause; however, Galileo reasoned from his experiments that a body in motion would stay in motion unless a force (such as friction) brought it to a halt. This established the first of Newton’s Three Laws of Motion.
The principle of inertia is the fundamental assumption and starting point of classical mechanics, but it is not immediately apparent to the untrained eye. In Aristotelian mechanics and in everyday life, objects that are not being pushed tend to come to a halt. Galileo discovered the law of inertia while studying the motion of balls rolling down inclined surfaces.. This is due to the frictional force of the ground acting on the ball, causing it to change its state of motion.
Effects of inertia:
Every day, you can feel the effects of inertia. Assume you’re driving a car. What happens if the car comes to a halt unexpectedly? Inertia exists in your body. When the car moves forward, your body tends to remain at rest due to inertia.
An oscillator is a physical system with recurrent cycles (harmonic motion). An oscillator is a child on a swing, as is a vibrating guitar string. An oscillator is not a waggon rolling down a hill.
Oscillating systems oscillate back and forth around a centre, or equilibrium, position. Consider equilibrium to be the state of a system that is at rest, undisturbed, and has zero net force. A waggon rolling down a hill is not in equilibrium because the gravitational force that causes it to accelerate is not balanced by another force. A child sitting motionless on a swing is in equilibrium because the tension in the ropes balances the force of gravity.
A restoring force is any force that always acts to bring a system back into balance. The restoring force is related to the force of gravity or weight and the lift force (or tension) of a pendulum’s string.Gravity creates a restoring force that pulls a pendulum back to equilibrium when it is pulled forward or backward. Systems with restoring forces oscillate.
Types of inertia
Inertia of rest
The inertia of rest refers to the body’s reluctance to remain at rest until some external force acts on it.
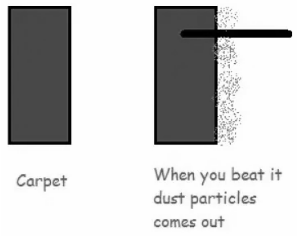
Inertia of Rest Exemplification
When we beat the carpet, dust particles that are at rest are propelled into motion. This is because dust particles tend to stay at rest and thus become separated.
Inertia of direction
Inertia of direction occurs when the body offers resistance to continuing moving in the same direction until an external force acts on it.
Inertia of direction Exemplification
- Unless we turn the bike’s handle, it moves in a straight line.
- When one end of a string connected to a stone is spun. The string snaps, and the stone flies away from the circle in a tangent. This is due to the string’s pull forcing the stone to move in a circular motion. The pull weakens as soon as the string snaps, and the stone flies off in an oblique direction.
Inertia of motion
When the body provides resistance to continuing in a regular motion unless acted on by an external force.
Inertia of motion Exemplification
- When a bus comes to a sudden halt, we are thrown forward. The top part of the body makes contact with the seat and begins to move with the bus due to inertia of motion, while the lower section tries to remain still.
- A person jumps from a moving train and lands on his or her feet. This is because his feet are in contact with the ground and remain still while the rest of his body moves due to inertia.
Law of inertia Coin drop explanation
Place a playing card atop the plastic cup.Place a coin on the card’s surface.
Hit the card out from under the coin with a sharp flick! Or quickly pull it toward you.The coin will eventually fall into the cup.
Explanation
The coin has inertia, which means it prefers to remain stationary. If you move the card slowly, you won’t be able to overcome the force. If you flick it quickly, the coin will stay in one place before falling into the cup. An object that is at rest will remain so.
Conclusion
One aspect of inertia is the tendency of objects to continue moving in a straight line at a constant speed in the absence of external forces.
On Earth’s surface, inertia is frequently obscured by gravity as well as the effects of friction and air resistance, both of which tend to slow moving objects down (commonly to the point of rest). This led Aristotle, the philosopher, to believe that objects would only move if force was applied to them.The principle of inertia is a fundamental principle in classical physics that is still used today to describe the motion of objects and how they are affected by the forces applied to them.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




