When any material shows a linear relationship between stress and strain and exhibits elasticity in some form or the other, it is called linearly elastic material. For elastic materials, stress is directly proportional to strain, this means for small deformation, stress is directly proportional to strain.
Therefore, in simple terms, As per Hooke’s law, the strain in a solid is directly proportional to the applied stress within the elastic limit of that solid.
Mathematical expression for Hooke’s Law
Mathematically, Hooke’s Law is expressed as:
Stress Strain
Stress = Young’s modulus of elasticity Strain
σ = E ε
Where,
σ denotes the stress applied on the body
E denotes the modulus of elasticity (Young’s modulus of elasticity)
ε denotes strain produced in the body
All materials exhibit some kind of elasticity. This elastic property of material gives rise to the concept of restoring force. This restoring force opposes the force trying to produce the deformation in the object. This restoring force from within the body is unidimensional in nature.
Now consider the elasticity in just one dimension. To verify Hooke’s Law on this spring-mass system now we discover the relation between the restoring force and stretch (elongation) for a material called ‘a spring’.
The restoring force arising from within the object as a result of external force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the deformation of the material, mathematically this restoring force is:
F= -kx
Where,
F is restoring force
x represents the magnitude of the distortion or displacement from equilibrium as exhibited within the stretching of a spring
k is the proportionality constant, also referred to as spring constant.
This expression for this spring-mass system is understood as Hooke’s Law (mathematically).
Note: Here the negative sign indicates the direction of the restoring force from within is in the direction opposite to that of the displacement.
Experimental verification of Hooke’s Law
Procedure:
Step 1: Assemble the apparatus, as shown within the figure. 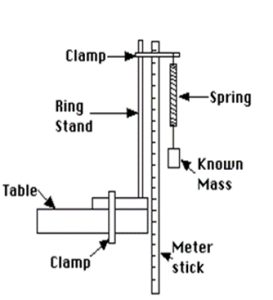
Step 2: Construct a knowledge table. Now take the reading of the load of a known mass that you simply hang from the spring and therefore the position of the top of the spring before and after the mass is loaded.
Step 3: Calculate the force applied to the spring and therefore the resulting stretch of the spring by using W = mg.
Step 4: Take approximately ten readings.
Step 5: For each reading, record the mass, the starting position of the spring (before hanging the mass) and therefore the ending position of the spring (while it’s being stretched).
Step 6:
Evaluate the value of the restoring force in the spring for all the trials.
Evaluate the increase in the length of the spring for all the trials.
Plot the graph between the restoring force and elongation produced in the spring.
Visibility of Hooke’s Law in real life setting
- Most commonly, in lifestyle, Hooke’s Law is applied in all the possible systems with springs due to their elasticity.
- Hooke’s law is visible not only within the engineering field but also utilized in the sector of life science.
- Hooke’s law is visible in breathing (expansion and contraction of lungs), skin (tightening and loosening), spring beds, diving boards and car’s suspension.
- Hooke’s law is a fundamental concept behind the working of scientific instruments such as the manometer, spring balance and balance of the clock.
- Various mechanical concepts such as seismology, acoustics and molecular mechanics derive inspiration from Hooke’s law.
Limitations of Hooke’s Law
The Hooke’s Law demonstrates limits in the following cases:
- As Hooke’s Law is applied only within the elastic region, it is ineffective as soon as the material loses its elasticity.
- Hooke’s Law gives accurate results just for solid bodies where the forces and deformations are small. It becomes invisible when forces of larger magnitude are applied.
- Hooke’s Law is not a universal law because of its limits.
Conclusion:
The graph of restoring force versus elongation for the spring is a straight line. This straight-line indicates that the elongation of a spring is directly proportional to the applied force. Hence, we will conclude that this spring-mass system follows Hooke’s Law.
Similarly, if we draw the stress-strain curve for low-carbon steel under tension test for static loading condition, then we will notice the extent of the proportional limit to which Hooke’s law is valid. When the plastic deformation in the material starts, Hooke’s Law loses its validity.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




