Friction is defined as the force that prevents the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other from being slowed or accelerated. Friction is a force that acts to slow the movement of two objects that are in contact with one another. The energy lost as a result of friction is converted into noise and heat. When the friction between two objects is strong enough to prevent movement between them, this is referred to as static friction. When the frictional force is not strong enough to completely stop the motion, kinetic friction is employed. The production of heat is one of the effects of kinetic friction.
As defined by the definition of friction, it is the force that opposes the motion of a solid object over another. Static friction is the most common type of friction. When two surfaces come into contact, friction and normal force are directly proportional to the contacting surfaces, and they are unaffected by how hard a surface is. Sliding friction decreases as the relative speed of the two objects increases, whereas fluid friction increases as the relative speed of the two objects increases; in addition, fluid friction is dependent on the viscosity of the fluid.
Each point on the body has only translational or linear motion when the body is in sliding motion. In the case of rolling motion, on the other hand, different points experience a combination of linear and rotational motion.
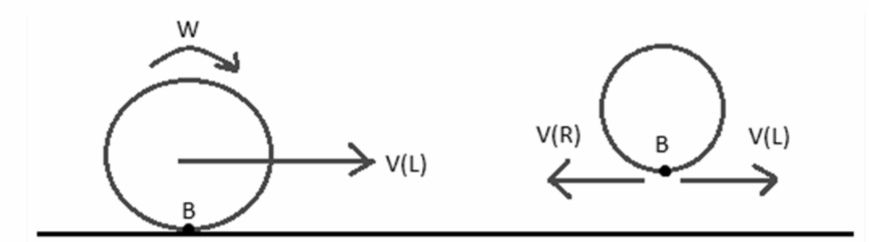
If we only consider rotational motion, then point B tends to move backwards, assuming that it has a velocity VR of rotation. Similarly, if we only consider linear motion, then point B moves with a velocity VL in the direction of the forward arrow. In this case, the resultant motion of the point B will be a superposition of the two velocities mentioned above. The rolling friction can act in one of the following directions depending on the values of VR and VL:
If VR > VL, then point B has a tendency to move backwards; however, as we know, friction opposes relative motion between the surfaces in contact, so it will act in the forward direction in this situation.
When VR exceeds VL, point B tends to move forward, and thus the friction acts in a counter-clockwise fashion to move it backward.
In addition, even though the ball is moving in the forward direction, the frictional force acting on the ball will be zero if VR = VL is achieved. This is in contrast to sliding friction, where the friction force will always act if the body is in motion and vice versa.
Different Types of Friction
The following are the different types of friction that are dependent on the types of motion:
Static Friction
Sliding Friction
Rolling Friction
Fluid Friction
Static Friction
In the case of a stationary object, static friction is the force of friction acting on the object. The fact that you push on a stationary block and it remains stationary indicates that it is being held in place by static friction, which is equal to and opposite to the force of your push.
Rolling Friction
When an object rolls on a surface, the force that resists motion is referred to as “rolling friction.” The term “friction” is technically incorrect; it should be “rolling resistance,” because when a body rolls perfectly on a surface, such as on a sheet of paper, there is no sliding friction between the object and the surface. Due to the elastic properties of the real world, both the bodies and the surface are subjected to deformations as a result of contact between the bodies in practice. Because the surface of contact is so small in real life, the net normal force is also small, and it is not sufficient to prevent a body from sliding and keep it stationary, as is the case with static friction. Because static friction increases with the increase in external force, rolling friction is typically less than static friction.
Sliding Friction
The frictional force that exists between two surfaces that are rubbing against each other is referred to as sliding friction.’ It’s a very simple and widely used concept. Because it is difficult to find a perfectly smooth surface in real life, when an object slides on any surface, it is subjected to a backward force as a result of the relative motion between the two adjacent surfaces when the object slides. It always acts in opposition to the motion. Whenever an object is in a static state, the applied force that attempts to slide the object is always equal to the force of friction acting on the object. At some point, the object begins to move in the direction of the external force. This is known as the transition point. When we gradually increase the applied force, this is what happens. There is no change in the amount of frictional force acting against the motion.
Fluid Friction
When fluid layers are moving in relation to one another, a type of friction known as ‘fluid friction’ occurs between them. Internal resistance to the flow of fluids is known as ‘viscosity,’ and it can be thought of as nothing more than the “thickness” of a fluid in a simplified sense.
Conclusion
Friction is a force that exists between two surfaces that are sliding, or attempting to slide, across one another. As an example, when you try to move a book across the floor, friction makes it more difficult. Whenever an object moves or attempts to move, friction always acts in the opposite direction of the object’s movement or attempt to move. Friction is always present and slows down a moving object.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out



