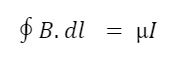Scientist Andre Marie Ampere discovered a law which set up a relationship between Net magnetic field generated by the current passing through a closed loop. The current must pass through a closed loop for the application of this law.
When a current passes through a straight wire, then we know that a magnetic field is generated around the wire at a distance, suppose ‘r’. Now Ampere’s Law gives us the formula to find the intensity of a magnetic field at a distance r from the wire when a current passes through the wire.
Definition:
When an electric current passes through a closed loop, a magnetic field is generated around the loop. The line integral of magnetic field intensity around a closed loop is equal to the total current passing through the closed path.
B= Magnetic field
dl= Small element of wire
μ= Magnetic constant
I= Current flowing through the wire
Properties of the magnetic field around a current carrying wire:
- The magnetic field lines are formed in a circular pattern around a wire.
- The magnetic lines are always generated in normal or perpendicular direction to the current carrying wire.
- The direction of the magnetic field depends upon the direction of current. If the direction of current is changed then the direction of the magnetic field is also changed.
- The strength of the magnetic field depends upon the magnitude of the current flowing through the wire.
Derivation of Magnetic field intensity:
Consider an infinitely long wire carrying a current I and now the magnetic field generated around the wire is B. The magnetic field is in a circular form. Here r is the radius of the circular loop.
Now the net magnetic field over a closed loop is given as:

The total length of the circular wire is its circumference that is 2πr.

Thus it is the mathematical expression of Ampere’s Law.
Application of Ampere’s Law:
Ampere’s Law is widely used for the calculation of the magnetic field due to the flow of the current through a symmetric wire.
Example:
- To measure the magnetic field intensity of an infinite line current.
- To measure the magnetic field of infinitely long transmission lines.
- To measure the magnetic field intensity of an infinite line current:
Now suppose P is a point at distance r from a current carrying straight wire. The magnetic field direction is the same as the direction of the length. So the angle is zero. Now the magnetic field as point P will be

The above formula will give the value of the magnetic field at point P.
Conclusion:
In this article we have learnt about Ampere’s Law and its application. We have learnt the derivation of the magnetic field. When an electric current is passing through a closed loop, then a magnetic field is generated around the loop so the line integral of magnetic field intensity around a closed loop will be equal to the total current passing through the closed path. We have also seen how to calculate the magnetic field at a particular distance from a current carrying wire.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out