One of humanity’s greatest inventions is the electric motor. We would have been nothing more than shining bulbs with energy if it hadn’t been for the invention of the motor. Electrical energy is converted into mechanical energy by the electric motor.
Electric motors are typically designed to rotate continuously. The electric motor, to be precise, is utilised to generate rotational energy. Electric motors are a gadget that we all employ in our daily lives.
Electric motor
A machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy is known as an electric motor. When a current-carrying conductor is put in a magnetic field, it is subjected to forces that aid in shaft or axil rotation.
A motor is a mechanical device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Spinning blades in a mixer, for example, mash and incorporate contents. The mixer’s electric energy is turned into mechanical energy when the blade rotates, producing the desired action.
Parts of an electric motor
The following are the components of a basic motor:
- For a simple motor, a power supply – mainly DC
- A permanent magnet or an electromagnet
- Armature or rotor
- Axle
- Brushes
- Commutator
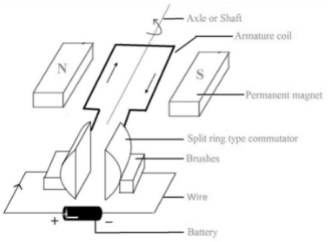
- Battery: A battery is a DC power source that is commonly used to power a basic motor. It feeds the armature coil with DC current.
- Brushes: The electric motor has two carbon brushes that act as a connection between the commutator and the battery terminals.
- Permanent magnets: Permanent magnets provide a powerful magnetic field.
- Commutator: The commutator is responsible for reversing current in the armature coil. It’s made up of two parts of a metallic ring. The two ends of the armature coil are attached to the metallic rings of these two parts.
- Armature core: The armature core holds the armature coil in place while also providing mechanical support.
- Armature coil: A single or more rectangle-shaped loops of insulated copper wire make up an armature coil.
- Axle or Shaft: This is the location where mechanical power is exchanged. On the shaft, the armature core and commutator are placed.
Types of electric motor
Motors are classified according to their power source:
- DC motor
- AC motor
Working of DC electric motor
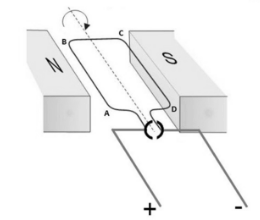
Towards the north pole, current flows from A to B, and near the south pole, current flows from C to D. As a result, the field lines and the current direction are perpendicular to each other. As a result, the sides AB and CD are subjected to a force whose direction is determined by Fleming’s left-hand rule.
Side AB is subjected to an upward force, whereas side CD is subjected to a downward force. As a result, the rectangular coil ABCD moves in a circular motion. Due to the split ring, current flows in the directions D to C near the north pole and B to A near the south pole after the half rotation. As a result, the force on both sides does not change direction, and the coil rotates constantly.
Types of DC motors
DC motors are classified as follows based on how the electromagnet poles and armature windings are connected:
- Separately excited DC motor: The poles and armature have two independent windings.
- Self-excited DC motor: The pole winding and armature winding are supplied with the same source.
There are two types of self-excited motor:
- Series DC motor: The pole and armature coils are connected in series, which means the same current passes through both of them.
- Shunt DC motor: The pole and armature windings are connected in parallel to the same source.
AC motor
Alternating current (AC) is used to power AC motors. The magnetic field can be rotated by utilising alternating current. Synchronous speed refers to the rotational speed of the field. The equation can be used to compute the synchronous speed:
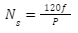
Here, Ns is the synchronous speed, f is the frequency of the AC supply and P is the number of Poles in the motor.
Types of AC motor
- Synchronous motor: The armature of a synchronous motor is magnetically bound to the field. As a result, it rotates along with the field at the same rate. As a result, it’s known as a synchronous motor.
Synchronous motors are classified as single-phase or three-phase synchronous motors, depending on the phase of the AC supply.
- Induction motor: The magnetic field rotates at the same rate as the armature, while the armature rotates at a slightly slower rate. There is a misalignment between the magnetic field speed and the rotor speed. As a result, asynchronous motors are sometimes known as induction motors.
Types of Induction motor based on the AC supply
- Single-phase induction motors use capacitors or split windings to create a spinning magnetic field in the stator winding, similar to single-phase synchronous motors. Single-phase induction motors are used in low-power devices such as domestic appliances.
- Three-phase induction motors are also known as self-starting motors since they don’t need any additional windings, capacitors, or other devices to start. As a result, these motors are the most basic of all motor types.
Conclusion
We’ve seen how the interaction between electricity and the magnetic field is used to create a moving force in this article. Motors are separated into two types based on the source of electricity: DC and AC motors. Depending on the source of electricity, the sorts of electricity, and the nature of the task to be done, we employ several types of motors.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out






