An electric dipole is a separation of electrical charges that are opposite. Its quantification can be done by its dipole moment (μ). The occurrence of an electric dipole takes place when positive and negative charges are separate from each other. A good example here can be a proton and an electron. This can be very clearly understood with the help of the electric dipole diagram. A small distance separates the charges in the electric dipole. In nature, the dipoles can either be permanent or temporary. Let us learn more about them with the help of the electric dipole diagram. For better understanding, the electric dipole example has also been provided here.
Electric Dipole Diagram Explanation
The electric dipole consists of two charges of opposite signs. Moreover, their separation is by a small distance. Many molecules in nature act like dipoles. The reason for this is that the charges separate within the molecule, thereby leaving the following:
- Net positive side
- Net negative side
Now let us imagine that there are two charges with the help of an electric dipole diagram. Consider each of the two charges has the following properties:
- Same magnitude
- Opposite sign
Now let us focus on the interactions between the following two:
- Charge pair
- Other charges
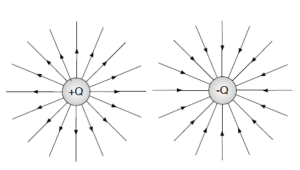
Now, let us consider the electric field. The beginning of the field lines must be on a positive charge. Their ending should either be on a negative charge or infinity into space.
The density of field lines represents the strength of the field. Here, the charges shall be characterised with equal magnitude. Therefore, there shall be a similar density near each charge. The electric dipole diagram below shows the field lines from each charge in isolation.
In the electric dipole diagram below, a connection of the lines has been shown.
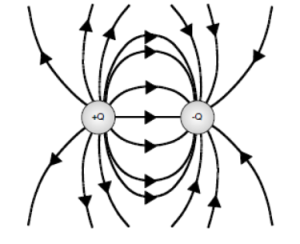
This work can be checked by carrying out a calculation of a few sample electric field vectors.
Electric Dipole Example
Some example of dipoles are below:
Polar molecule: A good example here can be a water molecule. A net negative charge is the molecule’s oxygen side. Also, a net positive charge is on the side of the two hydrogen atoms. So, the charges of the water molecule are partial in nature. Consequently, polar molecules like water are dipoles.
Electric Dipole Moment Direction
Experts call a precise measurement of the electric dipole strength as electric dipole moment. The derivation of the dipole moment magnitude is possible by multiplying the following:
- Product of either of the charges
- Separation distance ‘d’ between them
This is in agreement with the mathematical and scientific results. One must understand that the dipole moment here is a vector measure. Also, its direction is negative to positive charge.
The formula for electric dipole moment is provided below:
p = q d
Here,
- The electric dipole moment is represented by p
- The charges magnitude is q
- The magnitude of the distance between them is d
A relation also exists between the dipole moment and the difference in electro-negativity. As the difference in electro-negativity rises, so does the dipole moment and vice-versa.
The distance that separates opposite electrical charges will also impact the dipole moment magnitude.
Conclusion
An electric dipole is a separation of electrical charges that are opposite. This can be understood efficiently with the help of an electric dipole diagram. For this purpose, we need to consider the two charges with two properties – the same magnitude and opposite sign.. Physicists call a precise measurement of the electric dipole strength as electric dipole moment. This direction points towards the positive charge from the negative charge.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




