Equipotential Surface
For a given charge distribution, the locus of all the points having the same potential is called Equipotential Surface.
Equipotential surface, as the name defines, is a surface on which potential is equal everywhere. It means that if we draw a surface in such a way that the electric potential is the same at all the points of the surface, then it is said to be an equipotential surface.
Here are some examples of equipotential surfaces:
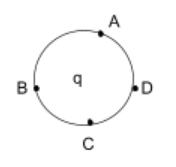
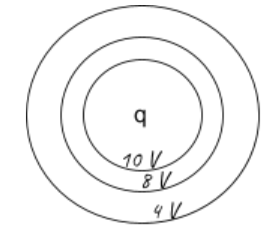
- For a point charge: Consider a point charge (q), then the equipotential surface will be a sphere, as shown below.
Where, the potential at points A, B, C, D will be equal.
“Concentric spheres with a charge at the centre of spheres are equipotential surfaces.”
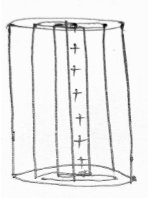
- For linear charge: Consider a line charge density, then the equipotential surface will be cylindrical, as shown below.
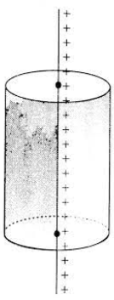
“Concentric cylinders with a linear charge at the axis of cylinders are equipotential surfaces.
Let us explore how to visualise equipotentials. One way of doing that is by drawing something called Equipotential surfaces.
Properties of Equipotential Surfaces
- The potential difference between any two points on an equipotential surface is always zero. In the given equipotential surface below, the potential at point A will be equal to the potential at point B. Hence,
(VA-VB) = 0
Or
VA = VB
- The component of an electric field parallel to the equipotential surface is zero, as the potential does not change in this direction. Thus, the electric field is always perpendicular to the equipotential surface.
- Potential decreases as we move farther from the centre.
- An equipotential surface due to line charge is cylindrical.
- An equipotential surface due to point charge is spherical.
- Equipotential Surfaces never intersect each other because if they do so then there will be two values at a single point which is not possible.
- If a charge is moved from one point to another point on the equipotential surface, then work done will be zero.
- All the metallic surfaces are always equipotential (Conductors).
Now, it is time to go through some problems on equipotential surfaces.
Problem 1: So what exactly are these surfaces?
As the name suggests, these are 3D surfaces over which potential (V) at every point is equal.
- Note:
The surfaces are closer to the centre and are going farther and farther away. Why is that?
Well, it has got something to do with the strength of electric fields. Electric force close to the charge is very strong, so equipotential surfaces are closer. As we go farther away from the charge, the field weakens, and so, the surfaces go farther away from each other.
Problem 2: Why do electric fields become weaker, when they move away on equipotential surfaces?
The relation between electric field and potential is given as
E = V/d
Where E is the electric field,
V is the potential, and
d is distance.
So as the distance increases on the equipotential surface then the potential will be constant so the value of the electric field will decrease.
Problem 3: How to draw an equipotential surface?
If you want to draw an equipotential surface, then just draw the electric field
lines first and then make a surface perpendicular to it. This will be your
equipotential surface.
Here are some examples:
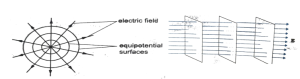
Problem 4: How to draw an equipotential surface for a uniformly increasing electric field in z-direction?
The equipotential surfaces are in the XY plane. As the magnitude of the field increases along the positive Z direction, the distance between successive equipotential surfaces decreases.
If electric fields were constant, the distance between successive equipotential surfaces would stay constant.
Problem 5: A particle having a charge of 10 C is moving on an equipotential surface of 5 V. Find the work done if the particle moves 2m on the surface.
Work done can be calculated by the following formula
W = -qΔV
Given q = 10 C
Since the particle is moving on an equipotential surface ΔV= 0.
So work done W = 0.
Key Points
- The best example of an electric potential surface is a conductor.
- Electric Field is directed from an equipotential surface at the higher potential to an equipotential surface at the lower potential.
- Potential is a scalar quantity.
- Equipotential surfaces are always perpendicular to the electric field.
- Potential varies inversely proportional to distance ‘r’.
- Equipotential surfaces give us a picture of the electric field and charge configuration.
Conclusion
An equipotential surface is that surface where the value of potential is the same at any point on the surface. This shows that potential V is constant if distance ‘r’ is constant. If you are given any charge distribution, then first draw electric field lines through the given distribution and then make a surface perpendicular to lines. This will be an equipotential surface to that of the given charge distribution.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out