We read that the general form of the linear equation is represented as y = mx + b, where m and b are both constants. This is what we call the linear equation. The point or coordinate at which the line crosses the x-axis of the plane is referred to as the x-intercept, and it is also known as the x-intercept point. This indicates that the value of the y-coordinate in the appropriate linear equation will always be equal to 0 whenever it crosses the x-axis. Both the x-intercept and the y-intercept have a y-coordinate of zero, and the x-intercept has a y-coordinate of zero. The x-intercept, or horizontal intercept, is another name for this concept.
X Intercept Formula
There are a number of different equations and formulas that are linked with intercepts. The most common generic formulas are presented below for your convenience. The process of deriving each of these formulas involves entering the equation with the substitution y = 0 and then solving for x.
- The equation for a straight line can be written as follows: ax+by+c=0, where a, b, and c are all constants. You may calculate the x-intercept of the line by setting y equal to zero and the x-intercept =-c/a.
- The form of a straight line that represents slope and intercept is written as: y = mx+c, where m represents the slope of the line and c represents the y-intercept. The x-intercept of the line can be found by setting y equal to zero and writing the equation x-intercept = -c/m.
- The intercept form of a straight line is written as x/a + y/b = 1, where the x-intercept of the line is represented by the coordinates (a, 0), and the y-intercept is represented by the coordinates (0, b).
X Intercept on a Graph
You may determine the x-intercept of a line with the equation y = mx+b by replacing y = 0 with the equation.
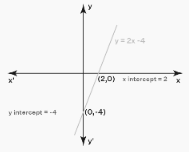
In order to get the x-intercept of any line, such as the line y = 2x-4, for instance, substitute the value 0 for y in the equation of the line.
Solution:
0 = 2x−4
4 = 2x 2 = x
Therefore, the value of 2 represents the x-intercept of the line y = 2x-4
In the same manner, if we set x equal to zero, we can calculate the y-intercept as follows: y = 2(0)4 = -4
Intercept of the Y
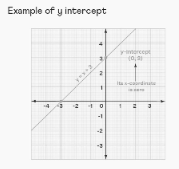
The point on a graph where it makes an intersection with the y-axis is referred to as the y-intercept. It is common knowledge that the x-coordinate of any point on the y-axis is equal to 0. Therefore, a y-intercept has an x-coordinate of 0 when plotted.
This is an illustration of what a y-intercept looks like. Consider the equation y = x+ 3 for a moment. This graph’s y-axis is intersected by it at the position (0,3). Therefore, the y-intercept of the line y = x+ 3 is at the point (0,3).
Y-Intercept Formula
The stages to get the y-intercept of a function with the equation y = f are as follows: (x),
- Simply put x = 0 in the equation there.
solve for y.
- Use the y-intercept as the point of representation (0, y).
An illustration of y-intercepts.
- (0, 2) is the value of the y-intercept for the equation y = 5x² + 2 because when we substitute x = 0, we obtain the value y = 5(0)² + 2 = 2.
Y-Intercept of a Straight Line
A horizontal, vertical, or slanted orientation is all possible for a straight line. The point (0, a) on the horizontal plane represents the y-intercept of a line with the equation y = a, but there is no such thing as a y-intercept for a vertical line. In the next exercises, we will learn how to find the y-intercept of a straight line when it is represented in a variety of ways.
The General Form of the Y-Intercept
In its most general form, the equation for a straight line is written as ax+by+c=0. To find the y-intercept, we first solve for y and then substitute x=0 into the equation.
a(0)+ by + c =0
by + c =0
y = – c/b
As a result, the y-intercept of the equation of a line expressed in general form is :(0, -c/b) or -c/b
Y-Intercept Represented Using the Slope-Intercept Form
In the form of an equation known as the slope-intercept form, the equation for the line is written as y = mx + b. According to the slope-intercept form’s own definition, the y-intercept of the line is denoted by the letter b. You can give it a shot by changing x=0 in the y=mx+b equation and seeing whether that gives you b as the y-intercept. Therefore, the value (0, b) or b is the y-intercept of the equation of a line when written in the slope-intercept form.
Y-Intercept Expressed Using the Point-Slope Form
In the form of an equation known as the point-slope form, the equation for the line is written as y-y1=m x-x1. To find the y-intercept, we first solve for y and then substitute x=0 into the equation.
y-y1 = m (0-x1)
y-y1= – mx1
y = y1 – mx1
Therefore, the y-intercept of the equation of a line expressed in point-slope form is either the value (0, y1 – mx1) or y1 – mx1.
Conclusion
The point or coordinate at which the line crosses the x-axis of the plane is referred to as the x-intercept, and it is also known as the x-intercept point. This indicates that the value of the y-coordinate in the appropriate linear equation will always be equal to 0 whenever it crosses the x-axis. Both the x-intercept and the y-intercept have a y-coordinate of zero, and the x-intercept has a y-coordinate of zero. The point on a graph where it makes an intersection with the y-axis is referred to as the y-intercept. It is common knowledge that the x-coordinate of any point on the y-axis is equal to 0. Therefore, a y-intercept has an x-coordinate of 0 when plotted.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




