The partial derivative is extracting specific components from a living organism to create something new.
In biotechnology, the partial derivative is used to create genetically modified organisms. It is used to produce medicine and food.
The partial derivative is a process by which a biotechnologist or genetic engineer can isolate and grow individual cells from a complex organism.
The partial derivative is used in the biotechnology industry to generate genetically modified organisms (GMOs) for research, industrial, and therapeutic purposes. Biotech companies use it to create new strains of plants or animals that are more efficient at producing certain products. This process is also essential because it helps us understand how genes work and affect our health.
A partial derivative is a process used to produce the desired product of a chemical compound. It is the process of breaking down and separating the desired compound into its components.
This process is used in biotechnology to produce specific compounds, such as antibiotics, hormones, and vaccines.
Partial derivative calculator:
A partial derivative calculator is a device used when a scientist wants to calculate the partial derivative of a molecule.
Chemists, biochemists, and biologists can use the partial derivative calculator. It is also helpful for those who need to calculate the molecular composition of an unknown compound.
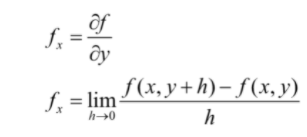
A partial derivative calculator contains a list of known compounds that have been divided into their respective molecular formulas. This way, scientists can easily find the molecular formula for any compound they are trying to find.
The partial derivative is extracting a portion of the DNA sequence from a DNA molecule.
In biotechnology, the partial derivative is used to find out the sequence of an individual gene. The partial derivative is done by using PCR (polymerase chain reaction) or by using restriction enzymes to cut out short pieces of DNA from the genome and determine which sequence they contain.
The partial derivative is a calculation in biotechnology that divides the target molecule into its constituent parts.
The partial derivative calculator in biotechnology is a tool used to calculate the amount of each component of a given molecule. It determines how much of each part is present in a given sample.
The partial derivative calculator is used for many different purposes, and it has proven useful for various industries such as pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.
Partial derivative example :
The partial derivative is a technique used in biotechnology to generate new proteins from existing ones. In this technique, a protein is broken down into smaller pieces and reconstituted using recombinant DNA technology.
The partial derivative has been used to create new proteins for various purposes such as drug discovery, industrial production, and research. However, more recently, it has been used in the development of vaccines that can induce an immune response against multiple diseases.
The partial derivative has also been used to create RNAi molecules that can be delivered through injection or orally so they can silence specific genes or avoid certain diseases by interfering with their expression.
The partial derivative is extracting the desired molecule from a larger molecule. In biotechnology, partial derivatives can be used to produce specific molecules in large quantities.
The partial derivative is a method of extracting molecules from a larger molecule to produce the desired molecule in high quantities. The process involves breaking down the larger molecule into smaller molecules and then using chemical reactions to combine all these smaller molecules into one single compound.
For decades, this approach has been employed in biotechnology in various applications, including medicines, cosmetics, and food production.
The partial derivative is a method in biotechnology used to isolate and identify genes responsible for specific traits in organisms.
Partial derivative uses a portion of one molecular chain and combines it with another chain to produce a new molecular chain.
Partial derivative chain rule :
The partial derivative chain rule is the most commonly used technique in biotechnology. The partial derivative of the concentration of a reactant concerning time is equal to zero if the reaction proceeds at a constant rate. A first-order reaction is calculated from the knowledge of the rate constant.
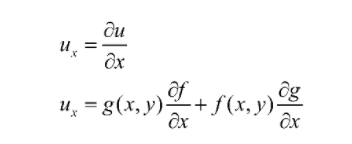
The partial derivative is calculated using a chain rule for derivatives and involves some algebraic manipulation. The partial derivative is a biotechnology technique used in the production of proteins. This process involves using an enzyme to metabolize one or more precursor molecules, resulting in a product with different molecular weights and charges.
The partial derivative chain rule is a biotechnology tool that helps understand the relationships between genes and proteins. The partial derivative is one of the essential tools used in biotechnology. It is used to understand how different genes are related to each other and how they affect protein production.
The partial derivative chain rule helps understand how different genes are related to each other and how they affect protein production.
Conclusion:
The partial derivative is when a molecule is broken down into its parts. In biotechnology, it is used to extract compounds from biological samples. The partial derivative can be achieved by adding a reagent to a mixture. The partial derivative chain rule states that if you want to know the concentration of one compound, you can determine it by multiplying the attention of all the other compounds in the mixture.
There are three types of partial derivative:
1) nucleophilic substitution (the parent group becomes an oxygen atom)
2) elimination (the parent group becomes hydrogen atoms)
3) In addition (atoms from one or more other groups combine with atoms.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




