Poisson’s ratio is an important specification in mechanical engineering and material science. During force application towards a bar, the Poisson’s ratio deforms either elongate or reduces in the longitudinal (axial) direction. Simultaneously a distortion is seen in the horizontal direction also.
Tensile distortion is positive besides compressive distortion is observed as negative. The Poisson’s ratio refers to the negative sign of the transverse tension ratio towards axial strain. Hence materials contain a positive proportion. Furthermore, other names of Poisson’s ratio are Poisson ratio and Poisson coefficient, which is usually denoted by the small letter ‘nu’ of the Greek series.
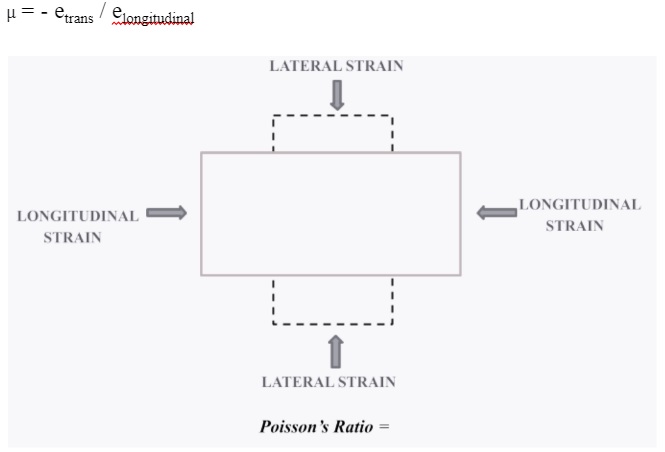
Define Poisson’s ratio
It is considered the transverse and lateral strain (relative construction) from normal value to implemented pressure to the axial strain into the applied load direction.
Poisson’s Ratio can be represented as
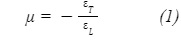
Here
μ = Poisson’s ratio
εT = transverse strain
εL= longitudinal strain
‘Strain’ is considered as “deformation of a substance as a result of stress”.
Longitudinal (or axial) strain can be expressed as
L = dl / L1 (2)
Where
L = longitudinal or axial strain
dl = change in length (m, ft)
L1 = initial length (m, ft)
Contraction or diminution strain can be represented as
T = dr / r (3)
Where
T= transverse, lateral or radial strain (dimensionless – or m/m, ft/ft)
dr = change in radius (m, ft)
r = initial radius (m, ft)
The effective formations to fracture hydraulically have the minimum Poisson’s ratios. However, Poisson’s ratio could be calculated from a fundamental sample. A basic sample is considered for the experimental purpose and extensive force is used.
(Strain in x- and y-directions) and Eq.4 is used to calculate Poisson’s ratio.
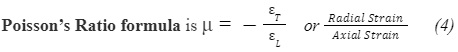
Poisson’s ratio –why generally positive
Practically all general materials, for example, the rubber band become smaller into the division when the band is stretched. Thereby, in the spectrum aspect is that major materials resist any change in the capacity as calculated by the K (bulk modulus) greater than the materials resist any variety in shape as estimated by the G (shear modulus).
As per the structural view, as interatomic bonds restructure with deformation, thereby Poisson’s ratio commonly remains positive. In auxetic materials, the Poisson’s ratio is usually negative.
Poisson’s Ratio Units
Poisson Ratio is considered as the ratio of transverse stress and longitudinal stress. The change happens at the material’s linear dimension. Hence, a unit of change of linear dimension is the same as the initial unreformed dimension. So the Poisson’s Ratio holds no units in the CGS system or SI.
Poisson’s ratio: anisotropy systems
Anisotropy refers to the effectiveness of exhibiting valuables with multiple values when determined along axes (longitudes or latitudes) in separate directions. In anisotropic materials comprising crystals, fibrous mixture, honeycomb, physical attributes involving Poisson’s ratio and coefficient of elasticity depend upon direction. Poisson’s ratio comprises positive and negative signs of inconsistent massive magnitude within anisotropic solids
The mutual relationship between Poisson’s ratio (μ), Bulk modulus (K), and Young’s modulus (E) is,
E = 3K ( 1-2μ)
Define, Poisson’s Ratio is Null for a material
Poisson’s ratio reaching zero means the object does not deform laterally nor axially. This resulted in a value of zero and cork is such an object, which holds almost zero value and presents no deformation under tension. Because of that cork has been used for sealing the bottle as it will not change under any stress and will protect the material inside the bottle.
List of some material and their Poisson’s Ratio
Materials | Poisson’s Ratio |
Stainless Steel | 0.30-0.31 |
Cast Iron | 0.21-0.26 |
Sand | 0.20-0.455 |
Rubber | 0.4999 |
Steel | 0.27-0.30 |
Gold | 0.42-0.44 |
Saturated clay | 0.40-0.49 |
Conclusion
This concluded that Poisson’s ratio is defined as the ratio between two strains that are lateral and longitudinal within the elastic limit. It is also demonstrated that when a solid is weighted within an elastic limit the ratio provides a constant value. The Poisson’s ratio of a stable and linear substance should be within -1.0 and +0.5. Most of the substances possess values starting within 0.0 and 0.5. The Poisson’s ratio is convenient to measure the rate of deformation under certain stress. However, when Poisson’s ratio is positive that is for tactile deformation and the negative value of Poisson’s ratio represents the compressive deformation.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




