Any gating system should strive to provide a defect-free casting. This can be accomplished by taking into account the following requirements.
- A gating system should avoid abrupt or right-angle direction changes.
- Before freezing, a gating mechanism should be used to fill the mold cavity.
- The metal should flow smoothly and without turbulence into the mold. In the mold, a turbulent metal flow tends to generate dross.
- Slag, dross, and other mold materials should not be permitted into the mold cavity.
- The metal entrance into the mold cavity should be properly managed to prevent atmospheric aspiration.
So that the casting cools without shrinkage voids or distortions, a sufficient thermal gradient must be maintained.
Metal flow should be kept constant to avoid gating or mold erosion.
The gating mechanism should ensure that there is adequate molten metal in the mold cavity.
The following factors must be kept under control in order for the gating system to work properly.
- Pouring equipment, such as ladles, pouring basins, and so on.
- The molten metal’s temperature and fluidity.
- The rate at which liquid metal is poured.
- The sprue’s type and size.
- The runner’s type and size.
- Gate size, quantity, and location between runner and casting.
Riser design:
Most alloys have significant volume reduction as they solidify. The magnitude of this shrinkage, which yields values for a variety of metals used in commercial alloys.
As a result, the objective of a feeder head is to supply a reservoir of liquid metal under a suitable pressure head to continue flow into the casting.
Shrinkage faults such as significant internal cavities, centre line, or filamentary voids will occur if the final casting is not supplied.
Liquid shrinkage: As the liquid metal loses superheat and cools to its solidification temperature, it loses volume.
Solidification shrinkage: It occurs when a liquid metal solidifies into a higher-density solid. This contraction will happen at a single temperature for pure metals, but it will happen over a temperature range or freezing interval for alloys.
Feed metal volume:
The riser must be sufficient to meet the casting’s liquid and solidification shrinkage requirements. Furthermore, because the riser will harden, the overall shrinkage requirement will be for the riser/casting combination. The entire amount of feed will be determined by the alloy, the amount of superheat, the casting geometry, and the molding medium.
Mold dialation:
After a mold cavity has been filled with liquid metal, mold wall movement might enlarge the casting, requiring more feed metal. The molding media, the mold filling temperature, and the alloy all influence mold dilatation.
Casting geometry:
The size of the riser required to meet a casting’s feed requirements is influenced by the shape of the casting, for the obvious reason that the longer the casting takes to solidify, the longer the riser must retain a reservoir of liquid metal.
Optimum riser design:
The techniques engineer’s in riser design can be summarised as ensuring that risers will produce the feed metal:In the appropriate quantity, in the right location, and at the right time.To maximise mold yield and lower production costs, the riser/casting junction should be constructed to minimise riser removal costs.
Riser location:
The techniques engineer must use the notion of directional solidification to identify the proper riser location.
The alloy and its mode of solidification, the mold medium, and the casting design will all influence the capacity to achieve such directional solidification.
Castings with uniform wall thickness and castings with wall sections of varied thickness must be evaluated separately.
Progressive and Directional Solidification:
In a casting, the interaction of progressive and directional solidification. After the mold cavity has been filled, solidification will usually begin at the mold wall, where a solid metal skin will form. The skin of the mold will expand inward as heat is lost to it.
Solidification mode:
The ability of an alloy to promote and sustain directional solidification is highly dependent on how it solidifies. Based on their freezing ranges, alloys can be divided into three categories:
- Short – <50°
- Intermediate -50 to 110°
- Long ; >110°
Castings of Uniform Wall Thickness:
The alloy and section configuration will work together to provide a maximum feeding distance for a casting to solidify without centerline shrinkage.
Castings With Sections of Varying Thicknesses;
The majority of commercially produced castings are made up of various thickness and configuration pieces. Thinner, faster forming regions are sandwiched between thicker, slower solidifying sections. The heavier parts will then operate as risers, supplying the lesser sections’ feed metal requirements.
Duration of Liquid Feed Metal Availability;
To calculate the riser size required to ensure that liquid feed metal is available for as long as the solidifying casting requires, a variety of methods have been created. A few of the most often utilised methods will be briefly described.
Shape factor method:
The National Research Laboratory (NRL) developed a method for determining riser size by multiplying the length and width of a casting section by the thickness of the section and dividing the result by the form factor.
Geometric method:
The geometric method, which was first developed to determine side risers for malleable iron castings, uses the typical conical shape of the shrinkage cavity generated in a riser as it concurrently feeds metal into the casting and hardens inward from its walls.
The modulus method :
It is based on the idea that utilising Chvorinov’s rule, one may approximate the freezing time of a casting or a casting section.
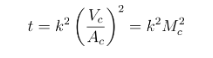
Conclusion:
A gating system should avoid right-angle or sudden direction shifts. A gating device should be utilised to fill the mold cavity before freezing.As an alloy solidifies, it loses a large amount of volume. This shrinkage’s magnitude, which produces values for a variety of metals used in commercial alloys. As a result, the goal of a feeder head is to provide a reservoir of liquid metal at a proper pressure head so that the casting can continue to flow.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




