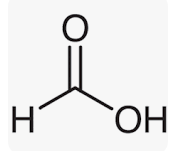
Formic Acid formula
Formic Acid is the most straightforward carboxylic acid. It has a Hydrogen atom that is covalently bound to a carboxylic acid group.
Methanoic Acid and Formic Acid are two more names for the chemical compound known as Formic Acid. It consists of covalent atoms. Covalent compounds are created when elements share electrons. Carbon has the greatest potential of all elements to form covalent compounds, and so all organic molecules are covalent compounds. If you examine the formula for formic acid, you will see that a Hydrogen atom is connected to a carboxylic acid functional group. Formic Acid’s molecular or chemical formula is HCOOH or HCO2H.
Formic acid is the most basic carboxylic acid. It has a hydrogen atom covalently linked to a carboxylic acid group. The modest size of the Hydrogen atom has little effect on the O-C-O bond angles in the carboxylic acid functional group. The angle of the O-C-O bond is 116.8 degrees. Hydrogen creates a connection with hydroxyl oxygen. 180 degrees is the dihedral angle of the H-C-O-O bond.
Properties of Formic acid
- It has a molecular mass of 46,025 grams per mole
- The melting temperature of Formic Acid is 8.4 degrees
- The boiling point of Formic Acid is 100.8 degrees
- The density of Formic Acid is 1.22 g/ml.
- Formic Acid is of the carboxylic group, it has a sour flavor.
- Miscible with methanol, acetone, ether, ethanol, ethyl acetate, and ether, respectively. Additionally, it is somewhat soluble in toluene, xylene, and benzene.
- Formic Acid may be synthesized from carbon dioxide, methyl formate, and formamide, among other substances.
- The importance of Formic Acid exceeds that of Acetic Acid.
Uses of Formic Acid
- Formic Acid is used in animal feed to reduce bacterial development during storage.
- As a preservative, Formic Acid may be employed.
- Formic Acid is used by beekeepers as a miticide against mites.
- Formic Acid is used in isobutanol from carbon monoxide.
- Formic Acid is an essential component of fuel cells.
Conclusion
Formic Acid is the most elementary kind of organic acid, consisting of a single Hydrogen atom coupled to the Carboxylic acid functional group. It naturally occurs in bee and ant stings. The physical and chemical characteristics of methanoic acid are determined by its structural formula. Formic Acid has several applications in the production of various compounds, preservatives, etc.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out