An isolated atom has electrons with distinct energies that differ from one another. If two isolated atoms are brought into very close contact, the electrons in the orbits of the two atoms will interact with one another, as seen in the diagram. Consequently, in the combined system, the energy levels of electrons will not remain constant, but will fluctuate, with the energies being somewhat lower and higher than the original values. As a result, at the location of each energy level, there are two energy levels that are closely spaced. In the case of a solid consisting of a ‘N’ number of atoms, and the electrons of these atoms interact and produce a ‘N’ number of closely spaced energy levels in place of discrete energy levels, this is referred to as a band of permissible energies. There are empty energy zones between the bands of permissible energies, which are referred to as the banned band of energies. It is supported by the Kronig-Penney model that there are these bands of energies present in the universe (allowed bands and forbidden bands). Even while finding the mathematical solution to Schrödinger’s wave equation is time-consuming, it does provide a hint as to the origin of energy bands in quantum mechanics.
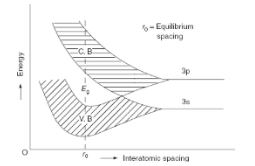
The development of energy bands has been discussed using the example of sodium (Na) metal as a case study. It is discovered that the energy levels of the valence electrons in solitary sodium atoms expand into bands when the atoms are brought together to create a solid. The electron energies of the 3S and 3P orbitals are depicted in the figure. At sodium’s interatomic gap, it is seen that these bands strongly overlap each other.
Sodium metal energy level sprinkling onto bands
Forbidden Band Gap :
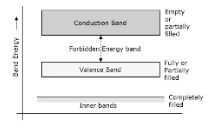
The prohibited energy gap is defined as the space between the valence band and the conduction band. As the name says, this is the band that is barred to play because they lack energy. As a result, no electron can be found in this band. Valence electrons pass through here on their way to the conduction band, and this is where they stay.
Having a larger forbidden energy gap indicates that the valence band electrons are tightly connected to the nucleus, which is a good thing. Now, in order to drive the electrons out of the valence band, some external energy is necessary, and this energy must be equivalent to the forbidden energy gap in order to be successful.
The valance band, the conduction band, and the forbidden gap are depicted in the following figure.
Insulators, Semiconductors, and Conductors are generated as a result of the formation of the forbidden gap, which is measured in microns.
Conductors :
Conductors are described as the materials or substances that allow electricity to pass through them without being affected by it. Additionally, conductors allow for the transmission of heat through them. Conductors include metals, the human body, the Earth, and animals, to name a few examples. As a conductor of electricity, the human body has exceptional properties. As a result, a current-carrying wire can travel freely through the body without encountering any resistance. Current can flow through conductors because they have free electrons on their surface. This feature of the material allows electricity to flow freely via conductors.
Conductors have a wide range of uses.
Conductors come in handy in a wide range of situations. In the real world, they’re useful for a variety of things. Thermometers, for example, are devices that measure a person’s body temperature and contain mercury. Aluminum is utilized in the creation of food preservation foils, which means that aluminum is employed in the production of these foils. As a result of its excellent conductivity of electricity and heat, it is used in cooking vessels as a nonstick coating. Iron is a frequent material utilized in the production of vehicle engines because of its ability to transmit heat. The iron plate is made of steel, which allows it to quickly absorb heat. Conductors are employed in automobile radiators to aid in the removal of heat away from the engine’s cooling system.
Semiconductors :
Semiconductors are defined as having conductivity that is intermediate between that of an insulator and that of a conductor. Because of this feature, semiconductors are extremely widespread in everyday electronic devices because they are less likely to short circuit than conductors are. The fact that they have a tiny band gap contributes to their distinctive conductivity. Short circuits are prevented by the presence of a band gap because electrons are not continually in the conduction band. In order for the solid to have some conductivity, it must have a strong enough flow of electrons from the valence to conduction bands. A small band gap allows for this to happen.
Electrons in the conduction band are no longer bound by the nuclear charge of the atom and are free to move freely around the band as a result of this. In this case, the electron is referred to as a negative charge carrier since its presence in this band results in electrical conductivity of the material when it is free to move. As soon as the electron exits the valence band, the state changes to that of a positive charge carrier, also known as a hole.
Intrinsic Semiconductors are pure semiconductors whose properties are wholly determined by the nature of the substance in which they are made. The number of electrons in the conduction band is the same as the number of holes in the valence band in this case. These semiconductors are also referred to as i-type semiconductors.
Extrinsic Semiconductors are impure semiconductors that have been “doped” in order to increase their conductivity and conductivity of electricity. Extrinsic semiconductors are classified into two categories: p-type and n-type. In order to extract electrons from the valence band, a “dopant” atom is introduced into the lattice structure. This atom is referred to as an acceptor in the scientific community. Eventually, as the number of acceptors in the lattice increases, the number of holes begins to outnumber the number of negative charge carriers, resulting in a p-type (positive-charge-carrier) semiconductor being formed. In N-type semiconductors, there are a huge number of donors, also known as “dopant” atoms, which are responsible for donating electrons to the conduction band.
Conclusion :
The development of energy bands has been discussed using the example of sodium (Na) metal as a case study. It is discovered that the energy levels of the valence electrons in solitary sodium atoms expand into bands when the atoms are brought together to create a solid.Semiconductors are defined as having conductivity that is intermediate between that of an insulator and that of a conductor. Because of this feature, semiconductors are extremely widespread in everyday electronic devices because they are less likely to short circuit than conductors are.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out