Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction.
The term “decarboxylation reaction” refers to a chemical reaction in which a carboxyl group is removed and carbon dioxide is produced as a result (CO2). Decarboxylation is most commonly associated with a process between carboxylic acids that removes a carbon atom from a chain of carbons. Carboxylation is a totally reversible process that occurs as the first chemical step of photosynthesis, during which CO2 is added to the compound. It is the first chemical step in photosynthesis. Decarboxylases, on the other hand, are enzymes that catalyse the decarboxylation reaction.
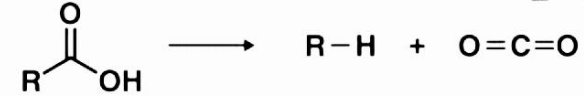
Carboxylation and decarboxylation occur in a metabolic environment
When it comes to biological chemistry, the most essential carbon-carbon bond forming and breaking occurs when an organic molecule, in the form of CO2, gains or loses a single carbon from another. A similar equation like this one is likely to have been in one of your introductory biology courses.
6CO2 + 6H2O + energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
It is the term used to describe the photosynthetic process, which is the mechanism by which plants harness energy from sunshine to make glucose from individual carbon dioxide molecules. It is known as the carboxylation reaction because it is the primary process in which carbon dioxide gets fixed (condensed with an organic molecule).
You should also be familiar with the reverse chemical equation, which is as follows:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
It is the oxidative breakdown of glucose that results in the formation of water, carbon dioxide, and energy that is described by the chemical process above. During the process of transformation, every carbon atom in glucose is transformed into a carbon dioxide molecule. The decarboxylation reaction is the primary step in which a carbon atom is separated from a bigger chemical compound. The citric acid cycle and the pentose phosphate pathway are responsible for the majority of the decarboxylation reactions that occur during the conversion of glucose to carbon dioxide.
Gallic acid is involved in the decarboxylation reaction.
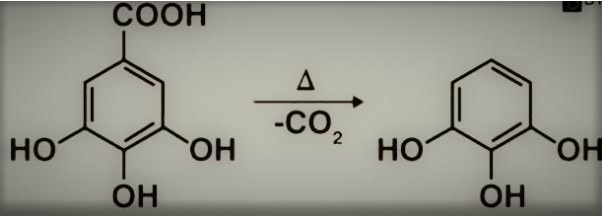
When heated over 150oC, carboxylic acids, which contain a carbonyl group and two carbon atoms, can quickly leak carbon dioxide.
Because it produces an unstable carbanion, many carboxylic acids do not lose CO2 in this manner. Nevertheless, when the presence of a carbonyl is present, an annulus may be created over two carbons whose resonance can be stabilised.
The following diagram illustrates the reaction:
Reaction of Decarboxylation

Conclusion
Despite the fact that the decarboxylation reaction appears to be a straightforward one-carbon removal reaction, it has been established that this reaction is a unique and valuable reaction in the creation of optically active carboxylic acids. Using a racemic carboxylic acid as a starting material, the optically active molecule can be synthesised through symmetrization by chemical carboxylation followed by asymmetrization by an enzyme reaction.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




