Osmosis is the transfer of hydrogen atoms from a solution with a high concentration of water molecules to a solution with a lower concentration of water molecules through a cell’s semipermeable membrane.Only some molecules or ions can flow through a selectively permeable membrane.
How does osmosis work:
Osmosis works by bringing the concentrations on both sides of a membrane to the same level. Because the solute particles are unable to get through the membrane, the water (or other solvent) must flow. Osmosis is thermodynamically advantageous because the closer the system approaches equilibrium, the more stable it becomes.
Example:
When red blood cells are placed in freshwater, an example of osmosis can be seen. A semipermeable membrane covers the cell membrane of red blood cells. Because the concentration of ions and other solute molecules inside the cell is higher than outside, water enters the cell via osmosis. The cells swell as a result of this. Because the concentration cannot approach equilibrium, the amount of water that can enter the cell is limited by the pressure exerted on the contents of the cell by the cell membrane. The cell often takes in more water than the membrane can handle, leading it to explode.
Osmolarity:
The overall concentration of solutes in a solution is referred to as osmolarity. A low osmolarity solution has fewer solute particles per litre of solution, whereas a high osmolarity solution contains more solute particles per litre of solution. When solutions with different osmolarities are split by a membrane permeable to water but not to solute, water will migrate from the side with lower osmolarity to the side with greater osmolarity.
Three elements comprise relative osmolarities between solutions: hyperosmotic, hypoosmotic, and isosmotic. When two solutions with distinct osmolarities are compared, the higher osmolarity solution is said to be hyperosmotic, whereas the lower osmolarity solution is said to be hypoosmotic.When two solutions have the same osmolarity, they are said to be isosmotic.
Tonicity:
In healthcare settings and biology labs, it’s common to think about how solutions affect water transport into and out of cells. The capacity of an extracellular solution to enable water to move into or out of a cell via osmosis is referred to as tonicity. Tonicity is different from osmolarity in that it takes into account both relative solute concentrations and the cell membrane’s permeability to those solutes.
To explain whether a solution will cause water to move into or out of a cell, three terminologies are used: hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic.
When a cell is soaked in a hypertonic solution, it loses volume due to a net discharge of water. The solution is hypertonic to the cell if the concentration of solutes in it is higher than that within the cell and the solutes cannot penetrate the membrane.
When a cell is soaked in a hypotonic solution, it expands in volume due to a net inflow of water. If the solute concentration outside the cell is lower than within the cell and the solutes cannot pass the membrane, the solution is hypotonic to the cell.
There is no net flow of water into or out of a cell when it is immersed in an isotonic solution, and the volume of the cell remains static. If the solute concentration outside of the cell is the same as within the cell and the solutes cannot penetrate the membrane, the solution is isotonic to the cell.
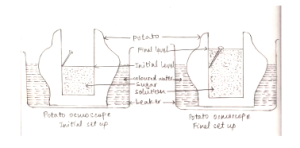
Osmosis as seen through a potato Osmoscope diagram:
Procedure:
Remove the peel from a medium or big potato. With the use of a knife, carve a cavity in it.
Clean and fill a big petri dish with water. Add 2 or 3 drops of red food colouring to the dish’s water to colour it.
Place the tuber in a dish with coloured water and fill the cavity with a 20 percent sugar solution.
Place an alpin on the potato cavity’s wall to indicate the original level of sugar solution.
Set aside one hour for the setup.
Observation:
After an hour, the level of sugar solution inside the cavity of the potato osmoscope rises and stabilises after a length of time.
Explanation:
Living cells encircle the hollow of the potato.
Each cell’s plasma membrane works as a semipermeable membrane within the cell wall.
Water diffuses into the potato osmoscope through the cell walls of potato tuber cells when it is placed in a dish filled with water. Endosmosis is the process by which water from a petri dish diffuses from a higher concentration to a lower concentration.
As a result, the initial concentration of sugar solution rises. This endosmosis process continues until hydrostatic pressure is achieved.
Example of osmosis:Red blood cells enlarge up when exposed to freshwater, and plant root hairs take up water are examples of osmosis. Soak gummy sweets in water to observe an easy demonstration of osmosis. The sweets’ gel functions as a semipermeable membrane.
Example of Diffusion:Diffusion can take many forms, such as the aroma of perfume permeating an entire room or the movement of tiny molecules across a cell membrane. Adding a drop of food colouring to water is one of the simplest ways to demonstrate diffusion. Diffusion is the most important transport process, notwithstanding the presence of other transport mechanisms.
Conclusion:
One of the most important ways that plants and animals establish equilibrium is through osmosis. It is possible for living creatures to live if the body’s circumstances are kept steady. In the human body, osmosis is critical, especially in the gastrointestinal and renal systems. Osmosis is a process that assists in the extraction of nutrients from food. It also helps to eliminate waste from your bloodstream.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




