Mitosis is a stage of the cell cycle during which replicated chromosomes are split into two new nuclei. Mitosis is a type of cell division that produces genetically identical cells with the same number of chromosomes. Hence, equational division is also a name for the mitosis. Mitosis is preceded by the S phase of interphase (during which DNA replication occurs) and is frequently followed by telophase and cytokinesis, which separates one cell’s cytoplasm, organelles, and cell membrane into two new cells with nearly equal shares of these biological components. The mitotic (M) phase of an animal cell cycle is defined by the division of the mother cell into two genetically identical daughter cells at each step of mitosis.
Mitosis definition:
Mitosis is a type of cell division that produces two daughter cells with the same number and type of chromosomes as the parent nucleus. It is common in normal tissue growth.
Stages of mitosis:
Prophase:
Prophase is the first stage of mitosis, when chromosomes recruit condensin and begin a condensation process that will last until metaphase. In most species, cohesin is entirely removed from the arms of sister chromatids during prophase, allowing individual sister chromatids to be resolved. Cohesin, on the other hand, is retained near the centromere, the chromosome’s most restricted region. As the two pairs of centrioles and microtubules migrate to opposing polesDuring prophase, the spindle begins to form as the duplicated centrosomes begin to polymerize.
Prometaphase:
Prometaphase begins with the nuclear envelope abruptly fragmenting into many tiny vesicles that will later be divided between the future daughter cells. Before the spindle can be formed, the nuclear membrane must be broken down. Because the centrosomes in animal cells are located outside the nucleus, the microtubules , Until the nuclear membrane breaks apart, the microtubules growing spindle does not have access to the chromosomes.
Metaphase:
The centromeres of all the cell’s chromosomes line up at the equator of the spindle during metaphase, when chromosomes are at their most compressed.Because chromosomes are most visible at this stage, metaphase is very important in cytogenetics. Mitotic poisons, such as colchicine, can also be employed to prevent cells from entering metaphase in the lab. During metaphase, Video microscopy shows that chromosomes stop moving for a short time during metaphase. The right way to put together the spindle is determined by a complicated checkpoint mechanism, and only cells with spindles that are in the right place go into anaphase.
Anaphase:
The sudden separation of sister chromatids marks the transition of cells from metaphase to anaphase. The protease separase quickly breaks down the cohesin molecules that connect the two sister chromatids, causing them to separate.
Telophase and cytokinesis:
Telophase, or the point at which the chromosomes reach their poles, signifies the end of mitosis. The nuclear membrane repairs and the chromosomes decondense to their interphase states after that. During telophase, two new cells are formed by splitting the cytoplasm into two parts. The genetic makeup of the daughter cells that are made by this method is the same.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip:
In the root tips, the meristematic cells that make up mitosis are the best to study. Because monocotyledonous plants’ chromosomes are larger and more apparent, onion root tips are utilised to research mitosis. The time it takes for mitosis to occur varies depending on the type of cells and organism. Temperature and time both have an impact on mitosis.
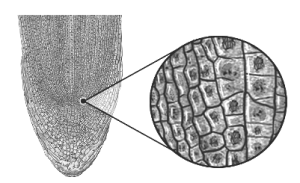
Diagram: Mitosis in an Onion Root Tip
Effects of Mitosis:
1) Mitosis produces new cells that are genetically similar to each other. Mitosis aids in the growth of organisms and the repair of damaged tissue.
2) Mitosis is a type of cell division in which one cell (the mother) splits to produce two genetically identical new cells (the daughters). In the process of cell division, cells go through a process, which is called mitosis. In this stage, the DNA in the cell’s nucleus is split into two equal parts.
Functions of Mitosis:
- It aids in tissue repair or replacement
- It promotes organism growth.
- It aids in the reproduction of asexual organisms.
- It aids embryonic development.
Similarities between Mitosis and Meiosis:
- They both participate in cells.
- Both entail cell division (cell multiplication)
Conclusion:
Mitosis is a large-scale physical restructuring of cell contents that causes two new cells to form that are identical to their mother. It entails the formation of particular motility complexes that split the cytoplasm and separate the chromosomes. Protein modification and regulated proteolysis drive mitosis regulation, which is connected to the execution of important mitotic processes through a series of quality control points. Approaches that combine biochemistry, genetics, and cell biology have given researchers a new perspective on the complexity of mitosis that will keep them busy for a long time. Mitosis is a complicated process, but unravelling these knots should help us better understand it in the setting of architecturally different tissues, as well as new therapeutic avenues for proliferative disorders.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




