Prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA carry genetic information for prokaryotic and eukaryotic development, function, and reproduction, respectively. Eukaryotes have a membrane-bound nucleus, whereas prokaryotes do not have one. DNA in prokaryotes is double-stranded and circular. Eukaryotic DNA, on the other hand, is double-stranded and linear. The amount of DNA in prokaryotic cells is significantly less than that in eukaryotic cells. The enzyme DNA polymerase replicates both prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA. The primary distinction between prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA is that prokaryotic DNA is found in the cytoplasm, whereas eukaryotic DNA is found in the cell’s nucleus.
What is a Prokaryotic dna?
The Prokaryotic DNA refers to the DNA carried by the prokaryotes. Bacterial cytoplasm contains prokaryotic DNA. Circular plasmids, which carry additional information, are found in some prokaryotic DNA. This means that prokaryotic DNA lacks an enclosing nuclear membrane. A single circular chromosome contains all of the DNA found in prokaryotes. It is found in the cytoplasm’s nucleoid region. Nucleoid-associated proteins help to pack the prokaryotic chromosome into the nucleoid. They aid in the formation of a looped structure in prokaryotic DNA.
Prokaryotic DNA ranges in size from 160,000 to 12.2 million base pairs, depending on the species. There are only a few genes in prokaryotic DNA. prokaryotic DNA contains uracil, thymine, guanine, and cytosine bases, Operons are groups of functionally related genes. Because prokaryotic DNA is densely packed with genes, the amount of nonfunctional DNA is low. Prokaryotic DNA replication is straightforward. Each prokaryotic chromosome has a single replication origin where DNA replication begins. As a result, during replication, a single replication fork and bubble are formed. In prokaryotes, replication occurs at a relatively fast rate of 2000 nucleotides per second.
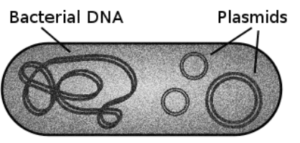
What is a Eukaryotic dna?
The Eukaryotic DNA refers to the DNA found in the eukaryotes. The nucleus of eukaryotic cells contains eukaryotic DNA. Some eukaryotic DNA can also be found in organelles such as chloroplasts and mitochondria. A nuclear membrane surrounds eukaryotic DNA. Eukaryotic DNA contains adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine bases,the DNA of eukaryotic organisms is organised into several linear chromosomes. Histones are proteins that play a role in the packaging of eukaryotic chromosomes within the nucleus. The packing of eukaryotic chromosomes is characterised by tight coiling and dense packing. The chromosomes of eukaryotes contain a large number of base pairs.
The majority of eukaryotic DNA is made up of multiple copies of the genome. The human genome is approximately 2.9 billion base pairs in length, organised into 23 homologous chromosome pairs. Eukaryotic genes encode only one protein. Alternative splicing of exons during post-transcriptional modifications can result in multiple proteins. Eukaryotic DNA has a low gene density. As a result, the amount of nonfunctional DNA in eukaryotic DNA is high. Eukaryotic DNA replication occurs via multiple replication origins. In eukaryotes, replication occurs at a slow rate of 100 nucleotides per second.
Differences Between Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells
- The structure of prokaryotic cells is quite simple. They lack a nucleus, organelles, and have only a small amount of DNA in the form of a single, circular chromosome. In contrast, eukaryotic cells have a nucleus, multiple organelles, and more DNA arranged in multiple, linear chromosomes
- Differences in DNA replication between prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms are largely due to differences in the size and complexity of their DNA and cells
- A typical eukaryotic cell contains 25 times more DNA than a prokaryotic cell
- There is only one point of origin in the prokaryotic cells, and replication occurs in two opposing directions at the same time in the cell cytoplasm. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, have multiple origins and use unidirectional replication within the cell’s nucleus
- Prokaryotic cells have one or two polymerases, whereas eukaryotic cells have four or more
- Prokaryotic cells replicate at a much faster rate than eukaryotic cells. Some bacteria require only 40 minutes, whereas animal cells, such as human cells, may require up to 400 hours. Furthermore, eukaryotes have their own process for replicating the telomeres at the ends of their chromosomes
- Prokaryotes have no ends to synthesise due to their circular chromosomes. Finally, while short replication occurs almost continuously in prokaryotes, eukaryotic cells only undergo DNA replication during the S-phase of the cell cycle
Conclusion
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA carry genetic information for prokaryotic and eukaryotic development, function, and reproduction, respectively. The amount of DNA in prokaryotic cells is significantly less than that in eukaryotic cells. The enzyme DNA polymerase replicates both prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA. The primary distinction between prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA is that prokaryotic DNA is found in the cytoplasm, whereas eukaryotic DNA is found in the cell’s nucleus. The Prokaryotic DNA refers to the DNA carried by the prokaryotes. They aid in the formation of a looped structure in prokaryotic DNA. The Eukaryotic DNA refers to the DNA found in the eukaryotes. The nucleus of eukaryotic cells contains eukaryotic DNA.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




