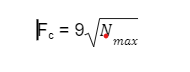Electromagnetic Waves travelling through transmitter and receiver after the reflection of the same from the ionosphere are known as Sky Waves. This way of EM waves Propagations is referred to as Sky wave Propagations.
What is Sky wave propagation?
Sky wave propagation is used in most radio transmissions at mid and high-level frequencies. Electromagnetic waves hereafter reflecting from the ionised zone in the upper side of the atmosphere are transmitted to larger areas. This layer of the atmosphere is known as the ionosphere. Frequency in the range 3 and 30 Megahertz is reflected by the ionosphere. This enables Sky wave propagation to be applied for communication purposes over a larger distance.
Need for Sky wave propagation:
To overcome the two major disadvantages of ground wave propagation, low-frequency signal transmission and short distance propagation. There was a need for a more efficient medium so that effective communication and transmission can happen.
Sky Wave Propagation enables more efficient communication over larger distances and higher frequencies.
Sky wave Propagation happens through utilisation of ionised layers of the Ionosphere due to the interaction of sun rays. It is imperative to understand the structure of the Ionosphere to properly understand the Sky wave Propagation.
Structure of Ionosphere and Sky wave propagation
- The ionosphere has four layers with a distinct count of atoms present in each.
- Outer layer – Minimum count of atoms
- The layer at the Centre(Innermost) – The Highest density of atoms
- Ionisation of a layer of the earth occurs after interaction with the cosmic rays from the sun.
- This ionisation enables the reflection of EM waves propagating towards the sky, thus creating an efficient transmission system.
- Accuracy of angle of sending and receptor antenna towards the Ionosphere facilitates the efficient transmission.
- Any transmission below 30 Megahertz will be reflected
- Above 30 Megahertz, the chances of waves penetrating the Ionosphere becomes high.
Skip Distance Concept in Sky Wave Propagation:
The skip distance is the stretch of space from the point at which an Em wave is transmitted and the point of reception after reaching the ionosphere and then reflected towards the surface.
The signals are emitted by the transmitter and move further away from it until they reach the ionosphere. Depending upon the angle of radiation, the emitted waves will reach the ionosphere at some point and time and then propagate towards the receptor. Angle of radiation is the angle at which the waves get emitted from the antenna.
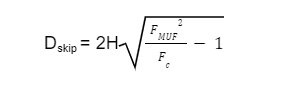
Skip Distances has numerous factor on which it is dependent, The formula for calculation of Skip Distance is:
Here:
Dskip = Skip Distance
H = Reflection point Height
FMUF = Maximum usable frequency
Fc = Critical Frequency
Understanding critical frequency
Critical frequency is the frequency breaching which EM waves can penetrate the ionosphere, and maintaining the same at lower level will keep the waves getting reflected.
Critical frequency is a concept derived from Total Internal reflection that happens in the atmosphere.
Critical Frequency of Sky Wave Propagation (between 3 -30 Megahertz) can be expressed as:
When we want to examine Critical Frequency as function of Maximum usable frequency it can be expressed as:
Fc =( FMUF cos𑁜)
Benefits of Sky wave propagation
- It is a useful tool for communicating over long distances.
- A wide range of applications are possible.
- Less loss of transmission efficiency due to the condition of the atmosphere.
Drawbacks of Sky wave propagation:
- The size of receptors can be a significant issue, as it is absolutely necessary when dealing with higher frequencies.
- There may be a difference in frequency at different times of the day (During daytime and nighttime)
Applications
- Used in Mobile Networks
- Satellite Networks
Key Points
- Higher frequency of electromagnetic wave propagations
- Range of frequency remains between 3-30megahertz
- Range of Frequency remains fixed in these propagations. Higher frequency can get absorbed through the ionosphere
- To overcome the limitation of ground wave propagation’s suitability for smaller ranges, sky wave propagation came into use.
- Using the reflected electromagnetic waves from the ionosphere, sky wave propagation can be used to transmit higher frequency of transmission for greater distance.
- Reduction of transmissions is usually lesser in these propagations
- Though greater distance and greater frequency nay require larger size of antennas
- There can be a difference in frequency during different hours of days (During daytime and nighttime)
Conclusion:
Sky wave Propagation uses the property of an ionised layer of ionosphere to reflect the EM waves back towards the surface of the earth. Using the same, it has gained the ability to transmit high frequency and through larger distances as well. Sky Wave Propagation has very well overcome the hassles of Ground Propagation with fewer attenuations, but it has a limitation of frequency. Transmission occurring over which, the EM waves can penetrate the ionosphere instead of reflecting, which creates a need for a signal transmission system for higher frequencies. Space Waves Propagation is the solution for the same.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out