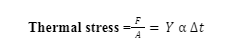Introduction
Thermal stress can be simply defined as the stress produced in a solid due to a change in temperature. All forms of matter have certain properties. Before we can move on to learn what thermal stress is, let us learn about the different terminologies related to the properties of mechanical solids.
Intermolecular Forces in a solid
All matter, be it solid, liquid, or gas, is made up of atoms. Atoms join to form molecules. In a solid, the atoms and molecules are packed closer together than in liquids or gases. Their arrangement is in such a way that each molecule exerts a particular force on its neighbouring molecule. This force is known as the intermolecular force in a solid.
The interatomic forces give structure to a molecule, while the intermolecular forces provide a structure to the material.
Elasticity
When an external force is applied to a solid body, it may get deformed or may become out of proportion. When a body is deformed, then internal forces develop inside that material to oppose the outside deforming force. The internal force tries to restore the body of the material to its original shape.
Thus, elasticity can be defined as the tendency of a body to get its original shape back after the deforming force is removed. The elasticity of every material differs. The more easily a body gains its original shape after the deforming force is removed, the more elastic that body is.
Perfectly Elastic Body
A perfectly elastic body is one that can regain its natural shape after the removal of the deforming forces. An example is quartz.
Partially Elastic
Partially Elastic bodies are those which only partially regain their original shape after the removal of the deforming forces. Neither are they fully elastic nor fully plastic.
Plasticity
A plastic body is one that stays in its deformed state even after the external force is removed. It does not regain its original shape even partially. This property of a solid is known as plasticity.
Stress
Stress can be defined as the ratio of the restorative internal force developed to oppose the deforming force to the area on which the force is applied.
In equilibrium, the magnitude of the stress produced is equal to the magnitude of the deforming force applied on a body.
Stress can be represented as:

Types of Stress
Stress can be of two types:
Normal stress
Normal stress can be defined as the ratio of the restoring force to the area perpendicular to the surface of the body. It is further classified into tensile stress and compressive stress.
Tangential Stress
Tangential stress is when the restorative force is parallel to the surface area of the body.
Strain
Strain can be simply defined as the ratio of the change in the shape or size of the body to the original shape or size of the body after the deforming force is applied. It does not have a unit.
Types of Strain
Strain is classified into three types:
Longitudinal strain
When the change in the shape of the body occurs along the length of the body, it is known as longitudinal strain. It is the ratio of the change in length of the body to the original length of the body.

Now that we are familiar with all the terminologies related to thermal stress, let us understand thermal stress.
Thermal Stress – What is Thermal Stress?
Thermal stress can be defined as the stress which develops in a body on applying force with a change in temperature. Due to the application of temperature, the body may expand or contract.
Thermal stress can also be expressed when the rod is clamped at both ends. The rod is kept in a fixed position, so it can’t move. Now, if we apply heat to this, then the temperature will increase. But since the rod is fixed at both ends, it will not have the space to expand. This will create stress. This stress is known as thermal stress.
Thermal stress in a rod can be expressed as:
Here, Y is the Young’s Modulus
coefficient of linear expansion
t is the change in temperature
Thermal Expansion
The increase in the size of a body due to an increase in temperature is known as the thermal expansion of a solid. It can be classified into three types:
Linear Expansion
When the length of a solid increases due to an increase in temperature, it is known as linear expansion.
Superficial or Area Expansion
When there is an increase in the surface area of a solid due to an increase in temperature, it is known as superficial expansion.
Volume Expansion
As the name suggests, when the volume of the solid increases because of an increase in temperature, it is known as volume expansion.
Conclusion
Through this article, we learned about stress and strain. Thermal stress is a type of stress that occurs when a change in temperature is applied. It can be expansive or contractive.
Thermal expansion is when a body increases in size due to a change in temperature. These are properties of solid matter.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out