Introduction—Electron is one of the subatomic particles of an atom. Electrons usually move from one atom to another under specific conditions and they are characterized mainly by a negative electrostatic charge. This movement of electrons usually is random unless there is a force that gives it a specific direction.
So, electricity is basically when an electromotive force influences the directional movement of electrons.Different materials have diverse electrical resistance and conductance levels as electrical resistivity and conductivity are essential aspects of all materials.
What is Electrical Conductivity?
Electrical conductivity is a measurement that indicates the capacity of the material for carrying out the movement of electrical charges. The common signifier of electrical conductance is the Greek alphabet sigma(σ) and sometimes kappa or gamma. Any material’s unit of conductance is measured through Siemens per meter (S/m).
The electrical conductivity of any material is essential in understanding any heat damage, purity of water, etc. The value of electrical conductivity of materials is influenced by aspects like the state of stress of crystalline structures and the chemical composition of a substance.
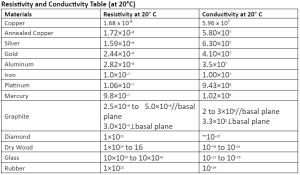
The conductivity value of any material will fall back upon the conduction of the annealed copper (5.80001 x 107 S/m). IACS or International Annealed Copper Standard helps to convert the value of any material’s electrical conductivity into a percentage.
What is Electrical Resistivity?
Electrical resistivity is the opposite condition of electrical conductivity. It refers to the resistance of any material to the force of the electric current.This resistivity can be plotted between a scale of low to high. In Physics, electrical resistivity is represented through the Greek symbol ρ for rho.
Electric resistive materials resist the flow of electric current through themselves, but they can also change the electric energy into other forms of energy like light or heat.An ohmmeter is the SI unit for electrical resistivity.
Electrical Resistivity versus Electrical Conductivity
The relationship between electrical resistivity and conductivity is reciprocal. The resistivity value is measured in the SI unit of an ohmmeter and the conductance unit is derived from the SI unit of Siemens/ meter (Centimeter).
A certain number and its reciprocal unit are always 1. For instance, if the number is 2, its reciprocal will be ½. So this reflects the fact that an increase in resistivity indicates a decrease in conductivity and vice versa, which means that a material cannot have high electrical conductivity and high electrical resistivity at the same time. The equation of this relationship is ρ= 1/σ.
The conversion between electrical conductivity and resistivity is simple as electrical resistivity is the opposite conductivity condition. For instance, two micro-ohm centimeters of resistivity of any material translates into ½ microSiemens/ Centimeter of conductivity.
Follow this formula to convert the value of resistivity from micro ohm centimeters to % IACS conductivity-
172.41/ Resistivity= % IACS.
List of electric conductors
Generally, the ability of a material to adapt to the electric flow makes it an ideal conductor. Materials that support an easy flow of electric charge are called conductors. On the other hand, materials with a lower ability to support electric energy flow or resist the flow of electrical movement are called an electrical resistor.
So, every material that helps the quick or easy flow of an electric charge is the electrical conductor. Many materials can be counted as electrical conductors, but do remember every conductor has different electrical conductivity measurements.
Here is a list of some well-known Electric Conductors: –
- Copper
- Silver
- Gold
- Aluminum
- Mercury
- Iron
- Steel
- Seawater
- Concrete
Some other strong conductors are
- Graphite
- Lime juice
- Brass
- Platinum
- Polluted water
List of electric resistors/ insulators
As we know, the ability of a material to resist the flow of electric energy is called the electrical resistivity of the material. There are also plenty of electrical resistors available across the world. But just like the conductors, every electrical resistor also does have different measurements of electrical resistivity.
Here is a list of some electric resistors/ insulators
- Rubber
- Dry wood
- Diamond
- Dry cotton
- Pure water
- Plastic
- Oil
- Asphalt
Some other solid resistors/ insulators are
- Fiberglass
- Dry paper
- Ceramic
- Quartz
- Porcelain
Conclusion–
Electrical resistivity and conductivity are an essential part of physics and electrical engineering. Generally, the SI unit measures the unit of conductance and the unit of resistance among different materials. The concepts of electrical resistivity and conductivity are more profound and you can check the reference links to get more in-depth knowledge about them.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




