In real life, we are surrounded by waves almost everywhere. WiFi, mobile networks, and several other wireless methods of communication consist of waves with different wavelengths. It was discovered that light has a wave nature by Sir Thomas Young’s experiments. Since so many physical events around us are mostly made up of waves, it has become extremely important to study the principle of superposition waves.
What is a wave?
A wave is defined as a disturbance that travels and transports energy from the source to the receiver, but which cannot transport matter.
In physics, a wave is defined as a disruption or oscillation that flows across time and space, and its main function is to transfer energy. Wave motion transports energy from one location to another with negligible displacement that is not permanent.
Some Important Properties Related to a Waves
Wavelength
The distance between two successive occurring crests of a wave in a sound or electromagnetic wave is called the wave’s wavelength.
- The symbol used for denoting wavelength is ‘λ’
- The Formula is λ = v / f
- ‘v’ in the formula is the speed of the wave, and ‘f’ is the wave’s frequency.
Frequency
The frequency of a wave is defined as the number of occurrences that happen per unit of time. To make the definition simple, the wave’s frequency is defined as the number of times the wave passes through one point in a unit of time.
- It is measured in Hertz and represented by ‘f’.
- The formula for the frequency of a wave is: f = v / λ
Velocity
The velocity of a wave is defined as the multiplication of the frequency and wavelength of the given wave. It is represented by ‘v’.
- The formula for the velocity of a wave is: v = displacement / time
Amplitude
The height of a propagated wave is called the wave’s amplitude and is represented by ‘A’.
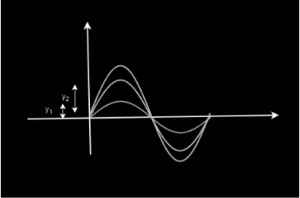
Principle of Superposition of Waves
The principle of superposition of waves tells us that when two or more waves overlap in space, the net resulting disturbance is equal to the algebraic addition of the individual disturbances of the respective waves.
- When two or more waves move through a similar medium, they are likely to interact.
- They maintain their waveform after combining, although the resulting wave is generally distinct from both of the constituent waves.
- The superposition concept aids in describing the resulting wave when two or more waves mix.
The diagram below depicts two waves that cause displacement in the particles of the specified medium. The principle of superposition asserts that in this circumstance.
What is the Interference of Light in Waves?
When two or more waves, having an equal frequency and sharing a constant phase arrive simultaneously at a specific point, it is called interference of Light in Waves.
The Three Effects of the Principle of Superposition of Waves
- Two waves that share the same frequency travel with a similar pace in the same direction in a certain medium, they are then superposed. Thus, they depict an effect that is called the Interference of Waves.
- Two waves that have the same frequency with a similar pace in opposite directions in a certain medium are superposed. They produce stationary waves.
- Two waves that have a slightly different frequency and that travel with a similar speed in the same direction in a certain medium, are considered superposed. They produce a beat or various beats.
Two common types of Superpositions in Waves
Interference of light in waves is separated into two categories, namely: constructive interference of waves and destructive interference of waves.
Constructive Interference of Waves
Suppose two waves overlay with one another in the same phase.
- The amplitude of the result is equal to the addition of the two amplitudes of individual waves, respectively.
- This result gives us the maximum intensity of light.
- This is called constructive interference of waves.
Destructive Interference of Waves
Suppose two waves overlay with one another in two different or separate phases.
- The amplitude of the result is the same as the subtraction of the amplitude of individual waves.
- This results in the intensity of light value being minimum
- This is called destructive interference of waves.
Conclusion
Waves are an extremely important part of physics. The concept of waves helps us explain a wide range of physical phenomena such as light and matter, including atoms and electrons.
This topic is extremely important to help build the foundations of a student wanting to pursue a higher degree in Physics.
The main aim of this article is to impart knowledge related to the concept of the principle of superposition of waves and other various definitions related to different types of waves.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out