The Green Revolution contributed to extended meals-grain manufacturing and White Revolution ensured availability of milk. But those revolutions intensively exploited our herbal resources. So, there may be a want to grow meal manufacturing without degrading our surroundings and stressing the balance by keeping it.
Need for improvement in Food Resources
- To grow our manufacturing performance for each plant and cattle to fulfill the meals necessities of the developing populace of the country
- To make sure Food safety relies upon each availability of meals and get entry to it
- To adapt sustainable practices in agriculture and animal husbandry
Scientific control practices need to be undertaken to gain excessive yields from farms. For sustained livelihood, practices which include combined farming, intercropping, and included farming should be adopted.
Improvement in Crop Yields
The main organizations of sports for enhancing crop yields may be labelled as:
- Crop range development
- Crop manufacturing development
- Crop safety control.
Crop variety Improvement
Varieties or traces of plants may be decided on through breeding for numerous beneficial traits which includes ailment resistance, product best, excessive yields, etc. It may be executed through following strategies:
-
Hybridization: It refers to crossing among genetically distinctive flowers
- Crossing can be inter-varietal (among special varieties), interspecific (among special species of the identical genus) or inter-generic (among special genera)
- Genetic Engineering: By introducing a gene that could offer the favored characteristic. This affects genetically changed plants
Desired characteristics for variety improvement
- Higher yield: To grow the productiveness of the crop in step with acre
- Improved best: Quality concerns of crop merchandise range from crop to crop
- Baking best is vital in wheat, protein best in pulses, oil best in oilseeds and retaining best in culmination and vegetables
- Biotic and abiotic resistance: Crop manufacturing can move down because of biotic (illnesses, insects, and nematodes) and abiotic (drought, salinity, water logging, heat, bloodless and frost) stresses
- Change in adulthood length: The shorter the length of the crop from sowing to harvesting, the greater reasonably priced is the range. It lets them develop more than one round or plant in 12 months
- Wider adaptability: Help in stabilising the crop manufacturing below special environmental conditions
- Desirable agronomic traits: Developing sorts of favored agronomic characters assist provide better productivity
- Tallness and profuse branching are applicable characters for fodder plants
- Dwarfness is favored in cereals, in order that much less vitamins are eaten up through those plants
Crop Production Management
Tallness and profuse branching are applicable characters for fodder plants
Dwarfness is favoured in cereals, in order that much fewer vitamins are eaten up through those plants
Nutrient Management
Nutrients are provided to flowers through air, water, and soil. There are sixteen vitamins that are important for flowers and may be labeled as:
- Macronutrients: These are required through flowers in huge quantities
- Micro-vitamins: These are required through flowers in small quantities
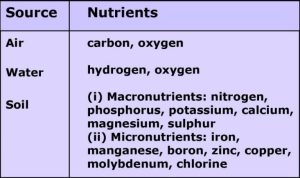
Deficiency of those vitamins impacts physiological strategies in flowers which includes reproduction, boom, and susceptibility to illnesses. To grow the yield, the soil may be enriched through offering those vitamins inside the shape of manure and fertilizers.
- Manure: It is ready through the decomposition of animal excreta and plant waste
- It facilitates enriching soil with vitamins and natural memory and growing soil fertility
- In sandy soils, it facilitates in growing the water keeping capacity
- In clayey soils, it facilitates in drainage and in fending off water logging
Classification of Manure: Based at the sort of organic fabric used, it could be labeled as:
- Compost and Vermicompost:
- The manner in which farm waste fabric is decomposed in pits is called composting
- Common farm waste substances are cattle excreta (cow dung), vegetable waste, home waste, sewage waste, straw, eliminated weeds, etc
- The compost is wealthy in natural memory and vitamins
- Compost is likewise organised through the use of earthworms to hasten the manner of decomposition of plant and animal refuse. This is known as vermicompost
- Green manure: enriching the soil in nitrogen and phosphorus
- Fertilisers: Fertilisers are commercially produced plant vitamins and deliver nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium
- Fertilisers are a component within the better yields of excessive-fee farming
- It needs to be implemented cautiously in phrases of right dose, time, and watching pre and post-utility precautions for his or her whole utilisation
- Excess fertiliser can result in water pollution. It additionally destroys soil fertility
Organic Farming
It is a farming machine with minimum or no need of chemical compounds as fertilisers, herbicides, insecticides etc. and with a large number of natural manures, recycled farm wastes, and bio-agents, with wholesome cropping systems.
Irrigation
It is the exercise of offering water to the land for the boom of plants
- Irrigation on the proper levels all through their developing season can grow the yields of any crop
- Sources of irrigation: Wells, canals, Rivers, Tanks, River Lift Systems, etc
- Recent initiatives: These consist of rainwater harvesting and watershed control
- This entails constructing small check-dams which result in a growth in floor water levels
- The check-dams forestall the rainwater from flowing away and decrease soil erosion
Cropping patterns
Different ways of growing crops can be used to give maximum benefit such as:
- Mixed cropping: Mixed cropping is developing or greater plants concurrently at the identical piece of land
- Mixed cropping: Mixed cropping is developing or greater plants concurrently at the identical piece of land
- Inter-cropping: Inter-cropping is developing or greater plants concurrently at the identical discipline in an exact pattern
- Principle:
- A few rows of 1 crop change with some rows of a 2nd crop
- The plants are decided on such that their nutrient necessities are special
- Example: soybean + maize, finger millet (bajra) + cowpea (lobia)
- Benefits:
- It guarantees most utilisation of the vitamins provided
- It additionally prevents pests and illnesses from spreading to all of the flowers belonging to 1 crop in a discipline
- Crop rotation: Crop rotation: It is the development of various plants on a chunk of land in a pre-deliberate succession. Depending upon the length, crop rotation is achieved for special crop combinations
- The availability of moisture and irrigation centres determine the selection of the crop to be cultivated after one harvest
- If crop rotation is achieved well then 3 or 3 plants may be grown in a 12 months with proper harvests
Crop protection management
Field plants may be infected through many weeds, insect pests and illnesses. If this isn’t always managed at the right time, then the entire crop will be lost.
Weeds: These are undesirable flowers within the cultivated discipline. For example, Xanthium (gokhroo), Parthenium (gajar ghas), Cyperinus rotundus (motha), etc.
- They compete for meals, space, and light
- Weeds take in vitamins and decrease the boom of the crop
- Removal of weeds all through the early levels of crop boom is important for an awesome harvest
Insects: Generally, insect pests attack the plants in three ways:
- They reduce the root, stem, and leaf
- They suck the mobileular sap from numerous elements of the plant
- They bore into stem and culmination
Disease: Diseases in flowers are resulting from pathogens which include bacteria, fungi, and viruses. These pathogens may be found in and transmitted through the soil, water, and air.
Methods of crop protection:
- Chemical’s strategies: Pesticides are chemical compounds and consist of herbicides, insecticides, and fungicides. These chemical compounds are sprayed on crop flowers or used for treating seeds and soil
- Mechanical Methods: These consist of strategies like hoeing, internet traps, etc
- Cultural Methods: Seed mattress preparation, summer time season ploughing, intercropping and crop rotation
- Technological strategies: Use of resistant varieties
Storage of grains:
Storage losses in agricultural produce may be very excessive. Factors chargeable for such losses are:
- Biotic: insects, rodents, fungi, mites, and bacteria
- Abiotic: irrelevant moisture and temperatures within the vicinity of the garage
Losses in the garage of grains: The above elements cause degradation at best, loss in weight, negative germinability, discoloration of produce, all main to negative marketability.
- Measures: The above elements may be managed through right remedy and through systematic control of warehouses
- Preventive and manage measures are used earlier than grains are saved for destiny use
- This consists of strict cleansing of the produce earlier than the garage, right drying of the produce first in daylight after which in shade, and fumigation the use of chemical compounds which could kill pests
Conclusion
Agriculture is the process of growing plants and rearing domesticated animals to provide food, fodder, fibre, and a variety of other desirable items. It is an applied science that includes all areas of crop production such as horticulture, livestock raising, fisheries, forestry, and so on. Lastly, agriculture is described as the art, science, and business of growing crops and raising animals for economic gain.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out













