Introduction
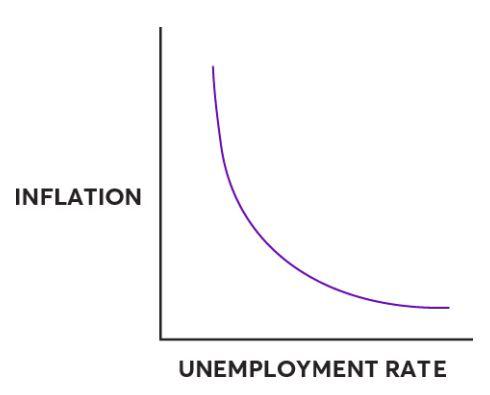
- It is a graphic curve which depicts the relationship between inflation and unemployment in an economy.
- Phillips Curve depicts that there is an inverse relation between inflation and unemployment.
Phillips Curve
- That is when inflation is high, unemployment is less in short terms and higher inflation lowers the unemployment.
- However, the implications of the Phillips curve have been found to be true only in the short term. Phillips curve fails to justify the situations of stagflation when both inflation and unemployment are alarmingly high. This concept was given by A.W. Philips.
- The policies to induce growth in an economy, increase in employment and sustained development are heavily dependent on the findings of the Phillips curve.
- However, the implications of the Phillips curve have been found to be true only in the short term.
- Phillips curve fails to justify the situations of stagflation, when both inflation and unemployment are alarmingly high.
Phillips Curve and Stagflation
- Stagflation occurs when an economy experiences stagnant economic growth, high unemployment and high price inflation. This scenario, of course, directly contradicts the theory behind the Phillips curve.
- When the central bank increases inflation in order to push unemployment lower, it may cause an initial shift along the short-run Phillips curve, but as worker and consumer expectations about inflation adapt to the new environment, in the long-run, the Phillips curve itself can shift outward.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out












