Inductance is a property of an electrical conductor or a circuit that generates an electromagnetic force when the flow of current changes. Inductance is the ability of a conductor to oppose the change in the current passing through the circuit. Energy is used to build the magnetic field, and the energy is released when the field disintegrates or falls.
- The symbol for inductance is L.
- The S.I. unit of inductance is Henry. It is named after American scientist Joseph Henry, who discovered electromagnetic induction.
- Another unit for inductance is Webers per Ampere.
- 1H = 1Wb/A
Types Of Inductance
- Mutual induction is the basic operating principle behind relays and motors.
- Self-induction is the type of inductance due to the EMF (electromagnetic field) that is self-induced in the coil.
Understanding Inductance
- The inductance of one coil is 1H
- The current flowing through the coil in the circuit changes at one ampere per second
- The induced voltage is represented in VL
As the current in the circuit flows in a conductor, a magnetic field is built around the coil, which affects how current is built up when the circuit is completed. Inductance helps to explain how a circuit operates for direct as well as alternating current.
Straight wires and coils are used as inductors because the turning of wires in a coil increases the magnetic field between turns, and hence the inductance is increased. The turning of coils enables wires to be accumulated in a smaller volume, so it saves space.
Faraday’s Law
Faraday’s law says that the magnitude of EMF that is induced in an electrical circuit is directly proportional to the rate of change in the magnetic flux.
The formula that governs this law is,
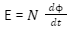
Here, the number of turns in the coil is N
E = Induced electromagnetic field across the coils
= Magnetic flux and t represent the time
Magnetic flux changes in an amount of a certain time which is calculated by:
Converting the equation above into Lenz’s law will give:
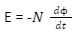
Factors affecting Inductance
- Inductance depends on the shape as well as the size of the conductor. For instance, if it is a coil, then the number of coils affects the inductance.
- The type of material besides the conductor also affects the inductance.
- The type of iron—for instance, if the material is coiled on soft iron, then the current will be higher. The use of iron core increases inductance as self-inductance is higher.
- Permeability of the coil
- Length of the coils
- Area of the coil
Inductance Formula and Derivation
The formula for inductance is-
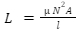
Where,
L stands for inductance (H)
stands for permeability (Wb/Am)
N is the number of turns of the coil
A is the coil area (m2), and l is the coil length (m)
When the DC source has its switch turned on, the current in the circuit flows to a specific value from its resting position, which is 0.
There is a flux shift caused by the flow of current in the circuit. The flux shift, also known as a
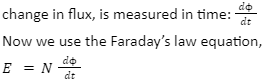
But according to Lenz’s law,

Conclusion
Inductance is produced when a magnetic field, which is created when current is passed through the circuit, obstructs or opposes any changes in the circuit when current is passed through it. Its unit of measurement is Henry (H). The two major types of inductances are self-inductance and mutual inductance. The formula for inductance is derived with the help of Faraday’s and Lenz’s laws.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




