Around 600 BC, Thales of Miletus in Greece is credited with discovering that amber rubbed with wool or silk cloth attracts light things. Electricity is derived from the Greek term Electron, which signifies amber. When light items like straw, pith balls, and shreds of paper are brushed together, they create an attractive force between them. Humans can achieve a similar effect at home by engaging in the activities listed below. Cut out long, thin strips of white paper and softly iron them. Bring them up near a TV or computer screen. It’s been noticed that the strips are drawn to the screen. In fact, it remains riveted to the television for an extended period of time.
Charging by induction
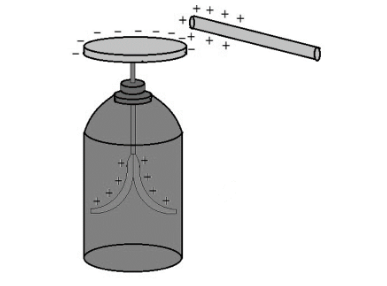
Induction charging is a means of charging a thing without it actually touching another charged object. During the charging by induction technique, the charged particle is held near an uncharged conductive substance that is grounded on a neutrally charged material. When a charge flows between two objects, the uncharged conductive substance develops a charge opposite the charged object’s polarity.
Electroscope
The Coulomb electrostatic force, which is measured with an electroscope, causes the test charge to move. Because the electrostatic charge of an object is proportional to its capacitance, electroscopes are widely employed as basic voltmeters. An electroscope requires a significant number of volts to detect a large enough concentration of charge.
Electroscopes are widely employed with high-voltage sources such as static electricity and electrostatic devices as a result of this. An electrometer is a device that measures electrostatic charge quantitatively.
Uses of electroscope
The electroscope can be used for a variety of things:
- The function of this device is to detect static charges.
- The nature of electric charges can be determined using an electroscope.
- The magnitudes of two separate charges can be compared using an electroscope.
Types of electroscopes
The two most popular types of electroscopes are as follows:
- Pith-ball electroscope: John Canton, a British physicist and schoolmaster, invented the pith-ball electroscope in 1754. It’s made up of one or two little non-conductive balls hanging from a silk or
Around 600 BC, Thales of Miletus in Greece is credited with discovering that amber rubbed with wool or silk cloth attracts light things. Electricity is derived from the Greek term Electron, which signifies amber. When light items like straw, pith balls, and shreds of paper are brushed together, they create an attractive force between them. Humans can achieve a similar effect at home by engaging in the activities listed below. Cut out long, thin strips of white paper and softly iron them. Bring them up near a TV or computer screen. It’s been noticed that the strips are drawn to the screen. In fact, it remains riveted to the television for an extended period of time.
Charging by induction
Induction charging is a means of charging a thing without it actually touching another charged object. During the charging by induction technique, the charged particle is held near an uncharged conductive substance that is grounded on a neutrally charged material. When a charge flows between two objects, the uncharged conductive substance develops a charge opposite the charged object’s polarity.
Electroscope
The Coulomb electrostatic force, which is measured with an electroscope, causes the test charge to move. Because the electrostatic charge of an object is proportional to its capacitance, electroscopes are widely employed as basic voltmeters. An electroscope requires a significant number of volts to detect a large enough concentration of charge.
Electroscopes are widely employed with high-voltage sources such as static electricity and electrostatic devices as a result of this. An electrometer is a device that measures electrostatic charge quantitatively.
Uses of electroscope
The electroscope can be used for a variety of things:
- The function of this device is to detect static charges.
- The nature of electric charges can be determined using an electroscope.
- The magnitudes of two separate charges can be compared using an electroscope.
Types of electroscopes
The two most popular types of electroscopes are as follows:
- Pith-ball electroscope: John Canton, a British physicist and schoolmaster, invented the pith-ball electroscope in 1754. It’s made up of one or two little non-conductive balls hanging from a silk or
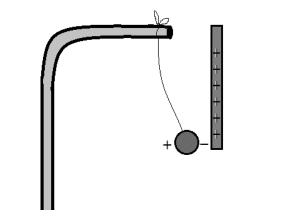
- linen thread from the hook of an enclosed stand. To test for the presence of a charge, bring the item closer to the uncharged pith-ball. If the test substance has a positive charge, electrons or negative charges in molecules will be drawn to it. They gravitate toward the material’s molecules that are nearest to it. On the other side, the positively charged molecule, the nucleus, repels and diverts away from the material. This method can be used to investigate the presence of electrostatic charge on a substance using a pith-ball electroscope.
- Gold-leaf electroscope: It was invented by British scientist Abraham Bennet in 1787 as a more sensitive electroscope than the Pith-ball electroscope. The gold-leaf electroscope detects and classifies electrical charges in the body. The electrostatic induction and repulsion theory underpins it. It consists of a single brass rod with two thin gold leaves on one end and a metal disc on the other. The two thin leaves are hung parallel to one another and in close proximity to one another, together with an electrically conductive material. The rod is put into the cylindrical glass jar, keeping the gold leaves inside and the disc outside. To keep the air within the jar dry, a little amount of CaCl2 is put within the gold-leaf electroscope, and the lower half is made of tin foil. Because they are fragile and sensitive, the leaves have no rigidity and hang timidly. They divide and form an angle when they charge, and the charge voltage is determined by the amount of impact on the leaves. On this electroscope, the potential, not the charge, is displayed. Looking at the angle of separation can also be used to determine the voltage.
Working of electroscope
Two thin gold leaves are attached to the bottom end of a vertical metal rod encased in a box to make an electroscope. The charge is transferred to the leaves when a charged gadget comes into contact with the metal knob at the top of the rod, causing them to diverge. The degree of divergence indicates the amount of charge.
- When the charge is positive, electrons in the metal of the electroscope have an attractive force and migrate upward out of the leaves. As a result of this, the leaves get a transient positive charge, and because like charges repel each other, the leaves separate. When the charge is released, the electrons return to their original positions, and the leaves relax.
- When the charge in the electroscope’s metal is negative, the electrons in the metal reject each other and move to the bottom leaves. As a result, the leaves acquire a brief negative charge, and
because like charges repel each other, the leaves split once more. When the charge is removed, the electrons return to their original place, and the leaves relax.
In both cases, the electrons return to their natural state as soon as the charged body is removed. In addition, the electroscope cannot tell whether a charge is positive or negative; it can only detect its presence in a body.
Conclusion:
The Coulomb electrostatic force, which causes the motion of the test charge, is used by the electroscope to detect the charge. Because the electric charge of an object is equal to its capacitance, an electroscope can be used as a primitive voltmeter. The term “electrometer” refers to a device that measures charge quantitatively.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out




