We know a dipole is a pair of opposite charges that are separated by a distance. This article will give you the details on the force acting on a dipole in a uniform magnetic field known as torque. Torque is the force that makes the object rotate about an axis. It is a vector quantity, and its direction depends on the direction of the force on the axis. You may know that magnetic dipoles are used in magnetic compass needles and bar magnets in real life. We will also learn what happens to a dipole in a uniform magnetic field? Or, What is an oscillating electric dipole?
Torque Acting on a Dipole in a Uniform Magnetic Field
Let quantity yz be the area of loop A from which the electric current passes. The loop will act as the electric dipole when the current passes through it. Current is fed into the loop by a single wire, which is wound around the perimeter several times.
The force will be exerted on each side of the loop by the magnetic field. This force is called torque and it is given by multiplying by the number of turns in the wire N, current I, and area A. The product of all these three values is written as a single quantity μ, giving the magnitude of the torque of the dipole in a uniform magnetic field as
τ=μB, in a simple form.
The moment of the arm will shrink if the loop turns upon its axis.
For example, when the top segment of the loop rotates back and the bottom rotates front by 900, then the forces on those segments will be directed away from each other. The forces will be acting straight on the axis and therefore the torque will be zero.
Torque and magnetic fields are the quantities that have direction and therefore they are vector quantities. The torque created by them is related to the position of the loop in the magnetic field. We can account for the loop position by defining a magnetic dipole moment:
μ≡NIA
Here, A is the vector that has an equal magnitude to the area of the loop and is in the direction which is perpendicular to the plane of the loop.
The right hand’s direction can be given by the right-hand rule: Curl the fingers of your right hand in a direction that gives the direction of the current around the loop, and the thumb of that hand points the direction of the vector.
What is Dipole Radiation?
Dipole radiation can be defined as an extension, or an advance next step physically in spherical wave radiation. In specific terms, it is taken as a harmonically oscillating electric dipole, having an angular frequency ω and a dipole moment p0 along the ẑ direction of the form. Thus, now you may have got the answer: What is an oscillating electric dipole?
Radiation power of an oscillating electric dipole (Dipole Radiation)
The radiation given out by electric dipole (short) doing oscillation is written as,
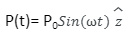
where p0=q0l =I0l/w. We have found from the previous experiments that the mean electromagnetic energy flux in far-field is written in the form as,
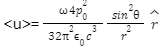
Let’s assume the origin of the spherical polar coordinate system has a dipole at its. Therefore, the element of solid angle, d = sin Ɵ d Ɵ d position in the center of the coordinates, radiates the power, which is given by,

The above formula is for the dipole of a shorter length than the wavelength of the radiation. It completely states the pattern of radiation of an electric dipole that is in oscillatory motion. You must have understood from the above equation that the power emitted by the elemental solid angle is power not at all dependent on r. If this wasn’t the case, then the energy would never have been conserved.
Conclusion
Thus, it can be concluded that when we place the dipole in the uniform magnetic field, it will start to oscillate due to the force, which is called torque. Torque is the force that makes the object rotate about an axis. Dipole radiation is an extension or an advanced next step physically in spherical wave radiation. In specific terms, it is taken as a harmonically oscillating electric dipole, having an angular frequency ω and a dipole moment p0 along the ẑ direction of the form. Power radiated into a given element of solid angle is independent of r. The total energy of the oscillating electric dipole is conserved.
 Profile
Profile Settings
Settings Refer your friends
Refer your friends Sign out
Sign out





